Zero Clearance Fireplace Installation: A Comprehensive Guide
Zero clearance fireplaces, also known as prefabricated fireplaces, offer a versatile and efficient heating solution for homes. Unlike traditional masonry fireplaces that require extensive construction and a substantial foundation, zero clearance models are designed to be installed directly against combustible materials. This characteristic significantly simplifies the installation process and reduces overall costs, making them an attractive option for homeowners seeking the ambiance and warmth of a fireplace without the complexities of conventional builds.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding zero clearance fireplace installation, covering essential considerations, preparation steps, installation procedures, and safety protocols. The information presented is intended for a general audience and should not substitute professional advice. It is highly recommended to consult with qualified professionals for the actual installation process.
Understanding Zero Clearance Design and Safety Features
The "zero clearance" designation refers to the fireplace's ability to be installed adjacent to combustible materials like wood framing, drywall, and insulation without posing a fire hazard. This is achieved through a combination of design features, including a fully insulated firebox, a double-walled construction, and strategically placed air vents. The insulated firebox contains the intense heat of the fire, while the double-walled construction allows air to circulate between the inner and outer layers, dissipating heat and keeping the external surfaces cool. The air vents further facilitate airflow and prevent heat buildup.
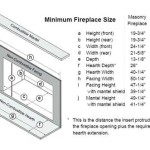
Despite the "zero clearance" designation, it is crucial to adhere to the manufacturer's specifications regarding clearances to combustible materials. These specifications are detailed in the installation manual and must be strictly followed to ensure safe operation. Ignoring these guidelines can lead to overheating, potential fire hazards, and voiding of the warranty. Typical clearance requirements may vary depending on the model and manufacturer, but they often involve specific distances to framing, mantels, and hearth extensions.
Another critical safety feature is the chimney system. Zero clearance fireplaces typically utilize a prefabricated chimney system specifically designed for the unit. These systems are rigorously tested and listed by independent safety organizations like UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or Intertek. Using the correct chimney system is essential for proper venting and preventing dangerous flue gas leaks. Substituting alternative chimney components can compromise safety and lead to serious consequences, including carbon monoxide poisoning and house fires.
Pre-Installation Planning and Preparation
Before commencing the installation process, meticulous planning and preparation are essential. This involves selecting the appropriate fireplace model, assessing the installation location, gathering necessary tools and materials, and obtaining any required permits.
Choosing the right fireplace depends on several factors, including the desired heating capacity, aesthetic preferences, and budget. Fireplace models are available in various sizes, styles, and fuel types, including wood-burning, gas-burning, and electric. Wood-burning fireplaces offer a traditional ambiance and powerful heat output, but they require a readily available wood supply and regular maintenance. Gas-burning fireplaces provide convenient operation and consistent heat, while electric fireplaces offer ease of installation and versatile placement options.
The installation location should be carefully assessed to ensure it meets the fireplace's clearance requirements and structural support needs. The floor must be level and capable of supporting the weight of the fireplace and any surrounding materials. Consider the proximity to combustible materials and the availability of venting options. Gas fireplaces require a gas line connection, while electric fireplaces need access to a dedicated electrical circuit.
Gather all necessary tools and materials before starting the installation. Essential tools include a level, measuring tape, drill, screwdriver, saw, and safety glasses. Materials include the fireplace unit, chimney system, flashing, fasteners, and any required framing materials. Consult the installation manual for a complete list of required tools and materials.
Check local building codes and regulations to determine if any permits are required for fireplace installation. Obtaining the necessary permits ensures that the installation complies with safety standards and avoids potential fines or penalties. The permit application process may involve submitting architectural plans and undergoing inspections by local building officials.
Step-by-Step Installation Procedures
The installation process for a zero clearance fireplace generally involves the following steps. However, it's crucial to always refer to the manufacturer's specific installation manual for detailed instructions tailored to the specific model being installed.
1. Framing and Opening Preparation: Construct the framing to create the opening for the fireplace, ensuring that the dimensions match the manufacturer's specifications. Use level and plumb lines to ensure the framing is square and aligned. Install any required headers or supports to adequately support the weight of the fireplace.
2. Fireplace Placement: Carefully position the fireplace within the framed opening, ensuring that it rests evenly on the floor. Check for level and plumbness and make any necessary adjustments. Secure the fireplace to the framing using appropriate fasteners, following the manufacturer's recommendations.
3. Chimney Installation: Assemble the chimney sections according to the manufacturer's instructions. Ensure that each section is securely connected and properly sealed. Extend the chimney through the roof, maintaining the required clearance to combustible materials. Install flashing around the chimney penetration to prevent water leaks.
4. Venting and Gas Line Connections (if applicable): For gas fireplaces, connect the gas line to the fireplace unit, ensuring a tight and leak-free connection. Test the gas line for leaks using a soap and water solution. Install any required venting components, such as vent pipes or termination caps, according to the manufacturer's instructions. Ensure proper venting to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
5. Electrical Connections (if applicable): For electric fireplaces, connect the fireplace to a dedicated electrical circuit, following all applicable electrical codes. Ensure that the wiring is properly grounded and protected. Test the electrical connections to verify proper operation.
6. Finishing and Trim: Install any finishing materials, such as drywall, stone, or brick, around the fireplace opening. Attach trim pieces to conceal any gaps or imperfections. Ensure that all finishing materials comply with the fireplace's clearance requirements.
7. Hearth Extension Installation: Install the hearth extension in front of the fireplace opening, providing a non-combustible surface to protect the floor from sparks and embers. The hearth extension should extend at least 16 inches beyond the front of the fireplace opening and 8 inches beyond each side, unless specified otherwise by the manufacturer.
8. Final Inspection and Testing: Conduct a thorough inspection of the entire installation to ensure that all components are properly installed and functioning correctly. Test the fireplace to verify that it operates safely and efficiently. Check for any leaks, unusual noises, or other indications of problems.
It's important to note that this is a generalized overview. Specific procedures may vary significantly based on the fireplace model and fuel type. Always refer to the manufacturer's detailed installation manual and consult with qualified professionals for any questions or concerns.
Following the installation, a thorough inspection is critical to ensure compliance with safety standards and proper functionality. A qualified professional should inspect the installation to verify that all components are correctly installed and that the fireplace operates safely. This inspection may include checking clearances to combustible materials, verifying proper venting, and testing gas line connections.

Zero Clearance Fireplaces Gas Wood
.aspx?strip=all)
Zero Clearance Fireplaces Explained Regency Fireplace S

Fireplace Install In Winchester Tn Huntsville Al Zero Clearance
Zero Clearance Factory Built Fireplace Installation And Operation Manual Do Not Discard

Zero Clearance Wood Gas Fireplaces Richmond Va Prefab
Zero Clearance Fireplace Questions My Firefighter Nation
Zero Clearance Factory Built Fireplace Installation And Operation Manual Do Not Discard

What Is A Zero Clearance Fireplace Install One Almost Anywhere 2024

Is A New Zero Clearance Fireplace Right For You Design Styles Sizes

Top 9 Benefits Of Installing A Zero Clearance Fireplace We Love Fire
Related Posts