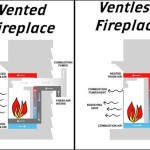
Wood Burning Stove and Fireplace Regulations: A Comprehensive Overview
The allure of a wood-burning stove or fireplace is undeniable. They offer a source of heat, a focal point for a room, and a connection to a simpler time. However, the operation of these appliances is heavily regulated due to concerns regarding air quality, safety, and energy efficiency. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial for homeowners, installers, and manufacturers alike. This article provides a detailed overview of the regulations surrounding wood-burning stoves and fireplaces, focusing on the key areas of emissions, safety standards, and installation guidelines.
The regulatory landscape for wood-burning appliances is complex, involving federal, state, and local jurisdictions. Each level of government has implemented rules aimed at minimizing the negative impacts of wood smoke and ensuring the safe operation of these devices. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, mandatory removal of appliances, and even legal action.
Emission Standards and the EPA
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a central role in regulating wood-burning stoves and fireplaces in the United States. The EPA's primary focus is on reducing particulate matter (PM) emissions from these appliances. Particulate matter, particularly PM2.5, is a significant air pollutant that can penetrate deep into the lungs and cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and other health issues. Wood smoke is a major source of PM2.5, especially in areas where wood heating is common.
The EPA has established emission standards for wood-burning stoves since 1988. These standards have been progressively tightened over the years. The original emission limit was set at 8.5 grams of particulate matter per hour for non-catalytic stoves and 4.1 grams per hour for catalytic stoves. Catalytic stoves utilize a catalyst to burn off pollutants more efficiently.
In 2015, the EPA finalized more stringent emission standards, often referred to as the "Step 2" standards. These regulations required all new wood stoves manufactured after May 15, 2020, to meet an emission limit of 2.0 grams per hour. This standard significantly reduced the allowable emissions from wood-burning stoves, prompting manufacturers to develop and implement cleaner-burning technologies.
The EPA certification process is rigorous. Manufacturers must submit their stove designs for testing at EPA-approved laboratories. These laboratories measure the stove's emissions under controlled conditions using standardized test methods. If the stove meets the EPA's emission standards, it receives an EPA certification, and the manufacturer can legally sell the stove in the United States.
The EPA's regulations primarily target manufacturers and retailers of wood-burning stoves. However, homeowners also have a responsibility to ensure that their stoves are operating correctly and that they are using the appropriate fuel. Burning unseasoned wood, for instance, can significantly increase emissions and reduce the efficiency of the stove. The EPA encourages homeowners to use seasoned wood (wood that has been air-dried for at least six months) and to follow the manufacturer's instructions for operating the stove.
While the EPA standards apply at the federal level, states and local jurisdictions may have additional regulations regarding wood burning. Some areas, particularly those with air quality issues, may implement burn bans during periods of high pollution. These bans restrict or prohibit the use of wood-burning stoves and fireplaces to help improve air quality.
Safety Standards and Building Codes
In addition to emission standards, wood-burning stoves and fireplaces are subject to various safety standards and building codes. These regulations aim to prevent fires, carbon monoxide poisoning, and other hazards associated with the operation of these appliances.
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is a non-profit organization that develops safety standards for a wide range of products, including wood-burning stoves and fireplaces. UL standards are widely recognized and respected, and many building codes require that wood-burning appliances be UL-listed. UL listing signifies that the appliance has been tested and meets certain safety requirements.
UL 1482 is the standard for wood-burning room heaters, and UL 127 is the standard for factory-built fireplaces. These standards cover aspects such as the structural integrity of the appliance, the performance of safety features, and the labeling requirements. Appliances that meet these standards are considered to be safer and more reliable.
Building codes, such as the International Residential Code (IRC) and the International Building Code (IBC), also address the installation and use of wood-burning stoves and fireplaces. These codes specify requirements for clearances to combustible materials, chimney construction, and ventilation. Adhering to these codes is essential to prevent fires and ensure the safe operation of the appliance.
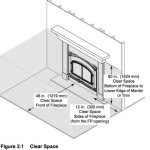
Clearance to combustible materials is a critical safety consideration. Wood-burning stoves and fireplaces generate significant heat, and if they are placed too close to combustible materials such as walls, furniture, or curtains, a fire can result. Building codes specify minimum clearances that must be maintained between the appliance and combustible materials. These clearances vary depending on the type of appliance and the wall protection that is used. Failure to maintain adequate clearances can lead to a fire hazard.
Chimney construction is another important aspect of safety. A properly constructed chimney is essential for venting combustion gases safely and efficiently. Building codes specify requirements for chimney height, diameter, and materials. The chimney must be able to withstand high temperatures and corrosive gases. Regular chimney inspections and cleaning are also vital to prevent chimney fires and carbon monoxide poisoning.
Ventilation is also a crucial safety consideration. Wood-burning stoves and fireplaces consume oxygen during combustion, and if a home is not adequately ventilated, carbon monoxide can build up to dangerous levels. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that can be fatal. Building codes may require the installation of carbon monoxide detectors in homes with wood-burning appliances.
Installation Guidelines and Best Practices
Proper installation is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of wood-burning stoves and fireplaces. Incorrect installation can lead to fires, carbon monoxide poisoning, and other hazards. It is highly recommended that wood-burning appliances be installed by qualified professionals who are familiar with the applicable building codes and safety standards.
Before installing a wood-burning stove or fireplace, it is essential to obtain the necessary permits from the local building department. Obtaining permits ensures that the installation will be inspected and approved by building officials. These inspections help to verify that the installation meets the required safety standards and building codes.
The installation of a wood-burning stove or fireplace typically involves several steps, including preparing the installation site, installing the chimney, connecting the appliance to the chimney, and testing the operation of the appliance. Each of these steps must be performed carefully and according to the manufacturer's instructions and the applicable building codes.
Preparing the installation site involves ensuring that the floor is level and that the area around the appliance is protected from heat. A non-combustible hearth is typically required to protect the floor from sparks and embers. The hearth must be of adequate size and thickness to provide sufficient protection.
Installing the chimney is a critical aspect of the installation process. The chimney must be properly sized and constructed to ensure adequate draft. The chimney should extend at least three above the highest point where it passes through the roof and at least two feet higher than any structure within 10 feet. The chimney should also be properly sealed to prevent leaks.
Connecting the appliance to the chimney involves using the appropriate connectors and ensuring that the connection is airtight. The connector pipe should be of the correct size and material and should be properly secured to both the appliance and the chimney. Any gaps or leaks in the connection can allow combustion gases to escape into the home.
After the installation is complete, it is essential to test the operation of the appliance to ensure that it is functioning correctly. This test should include checking the draft, verifying that the appliance is burning cleanly, and ensuring that there are no leaks in the chimney or connector pipe. A qualified professional can perform this test and make any necessary adjustments.
In addition to proper installation, regular maintenance is also essential for the safe and efficient operation of wood-burning stoves and fireplaces. This maintenance should include regular chimney inspections and cleaning, as well as inspection and maintenance of the appliance itself. Chimney inspections should be performed at least once a year, and chimney cleaning should be performed as needed to remove creosote buildup. Creosote is a flammable substance that can accumulate in the chimney and cause chimney fires.
By understanding and adhering to the regulations and best practices surrounding wood-burning stoves and fireplaces, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of these appliances while minimizing the risks associated with their operation. This includes selecting EPA-certified stoves, ensuring proper installation and clearances, maintaining chimneys, and using seasoned wood as fuel. Local jurisdictions may also have specific regulation that homeowner need to be aware of.

Fireplace Recess Size Diagram

Hearth Regulations Size Thickness Requirements Me And My Glass

Stove Hearth Size And Thickness Stoves

Hearth Regulations Size Thickness Requirements Me And My Glass

Stoves Suitable For A 12mm Hearth Installation

Building Regulations And Wood Burning Stoves

Fnr 100

Installing Multi Fuel Stoves Or Wood Burner

Building Regulations And Wood Burning Stoves

Enlarging Your Fireplace Guide Wood Burning Stoves Living Room
Related Posts