Understanding Wood Burning Fireplace Gas Ignition: Essential Aspects for a Safe and Efficient Fire
Wood burning fireplaces are a classic element of cozy and inviting living spaces. While traditional methods involve manual ignition, gas ignition systems offer a convenient and reliable alternative. This article delves into the essential aspects of wood burning fireplace gas ignition, ensuring a safe and efficient fireside experience.
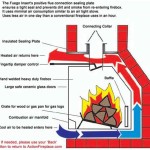
1. Pilot Light and Thermocouple
The pilot light is a small flame that continuously burns in a pilot assembly, providing a steady source of ignition when required. Its flame heats a thermocouple, generating a voltage that activates a gas valve. When the valve opens, gas flows through the assembly and ignites automatically when combined with the pilot flame.
2. Igniter
An igniter, often an electric spark or glow plug, is used to initiate the pilot light. It is typically activated by a remote control or a wall-mounted switch. The igniter creates a spark that jumps a gap between two electrodes, igniting the gas at the pilot assembly.
3. Gas Valve
The gas valve is responsible for controlling the flow of gas to the pilot assembly. It is activated by the voltage generated by the thermocouple. When the thermocouple senses the presence of a pilot flame, it sends a signal to the valve, opening it to allow gas to flow.
4. Flame Sensor
A flame sensor is an essential safety feature that monitors the presence of a flame in the fireplace. It is located near the pilot assembly and generates a signal that keeps the gas valve open as long as the flame is detected. If the flame is interrupted, the sensor signals the valve to close, preventing gas from flowing.
5. Manual Controls
Manual controls, such as a remote control or wall-mounted switch, allow the user to turn the gas ignition system on and off. They also provide the option to adjust the flame height and heat output, ensuring a comfortable and controllable fireside experience.
Benefits of Gas Ignition
- Convenience: Gas ignition eliminates the need for messy fire starters or matches, offering instant ignition with the touch of a button.
- Safety: Automatic ignition systems reduce the risk of gas leaks or accidents compared to manual ignition methods.
- Efficiency: The pilot light continuously provides a source of ignition, ensuring a quick and reliable start-up when the main flame is needed.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of a wood burning fireplace gas ignition system. It is recommended to have the system inspected annually by a qualified technician. Troubleshooting can be performed by checking the pilot light, igniter, flame sensor, and gas valve for proper operation.
Conclusion
Wood burning fireplace gas ignition systems provide a convenient, safe, and efficient way to enjoy the warmth and ambiance of a wood fire. Understanding the essential aspects of these systems ensures a reliable and trouble-free experience. By following proper maintenance practices and addressing any issues promptly, homeowners can prolong the lifespan of their gas ignition system and create a cozy and inviting fireside retreat for years to come.

Log Lighters Gas Starter Pipes Steel Cast Iron

How To Install A Log Lighter Fireplace Gas Starter Pipe

Greenstart Igniter Made In America Fireplace Xtrordinair

Can A Wood Burning Fireplace Be Converted To Gas The Flame Company

Elevation 36 Direct Vent Fireplace Natural Gas Electronic Ignition

Superior 36 Inch Electronic Ignition Vent Free Outdoor Gas Fireplace With Remote Vre3236

Gas Fireplace Starters In Chicago Capital Chimney Corp

How Gas Fireplaces Work With An Ipi Vs Milivolt Ignition System Kozy Heat

Superior Drc6340 40 Direct Vent Electronic Ignition Natural Gas Fireplaces Usa

Woodbridge Dvi1000 Direct Vent Gas Insert Fireplace 29 With Electronic Ignition System Natural Wb Dvi1000n E
Related Posts