Vented Gas Fireplace Installation: A Comprehensive Guide
Vented gas fireplaces offer a significant upgrade in both aesthetics and functionality to many homes. They provide the ambiance of a traditional wood-burning fireplace without the associated hassle and mess, while also offering an efficient and controlled source of supplemental heat. However, proper installation is paramount to ensure safe and reliable operation. This article provides a comprehensive overview of vented gas fireplace installation, covering essential aspects from pre-installation considerations to post-installation checks.
A vented gas fireplace is designed to mimic the appearance and functionality of a traditional wood-burning fireplace. The "vented" aspect refers to the requirement of a chimney or flue system to exhaust combustion byproducts, such as carbon monoxide, outside the home. This venting system is a critical safety feature, preventing the buildup of harmful gases within the living space. Unlike vent-free models, vented fireplaces prioritize complete combustion and removal of exhaust, contributing to improved indoor air quality and reduced risk of health hazards. Choosing the right model and ensuring a compliant installation are the first steps toward enjoying the benefits of a vented gas fireplace.
Before embarking on the installation process, thorough planning and preparation are crucial. This involves assessing the existing structure, selecting the appropriate fireplace model, understanding local building codes, and gathering necessary materials and tools. Failure to adequately prepare can lead to costly delays, safety hazards, and potential code violations. The early stages of planning set the foundation for a successful and safe fireplace installation.
Key Point 1: Pre-Installation Assessment and Planning
The first step in installing a vented gas fireplace is a comprehensive assessment of the site and existing infrastructure. This includes evaluating the existing chimney, determining the gas line availability, and assessing the structural integrity of the surrounding area. These factors will significantly influence the choice of fireplace model and the complexity of the installation process.
Chimney Inspection: A professional chimney inspection conducted by a qualified chimney sweep is essential. The inspector will assess the chimney's condition, including the presence of cracks, blockages, or deterioration. This inspection will determine whether the existing chimney is suitable for use with a gas fireplace or if repairs or relining are required. In some cases, a new chimney may need to be constructed. The chimney must be sized appropriately for the fireplace's BTU (British Thermal Unit) output to ensure proper venting.
Gas Line Availability: Determine the availability of a gas line near the intended fireplace location. If a gas line is not readily available, a licensed plumber will need to run a new line from the gas meter to the fireplace. The gas line must be properly sized to provide adequate gas pressure to the fireplace. Insufficient gas pressure can lead to poor flame quality and reduced heating efficiency. Verify the gas type (natural gas or propane) and ensure the fireplace is compatible.
Structural Considerations: Evaluate the structural integrity of the wall or area where the fireplace will be installed. Ensure the wall is capable of supporting the weight of the fireplace and any associated framing or finishing materials. Check for any existing electrical wiring or plumbing that may need to be relocated. Consider the proximity of combustible materials, such as wood framing, and ensure proper clearances are maintained according to the manufacturer's specifications and local building codes.
Local Building Codes and Permits: Before starting any work, obtain the necessary building permits from the local authorities. Building codes vary by jurisdiction and may specify requirements for chimney construction, gas line installation, and fireplace clearances. Failure to obtain the required permits can result in fines and delays. Familiarize oneself with all applicable codes and regulations before proceeding with the installation.
Fireplace Selection: Choose a vented gas fireplace that is appropriately sized for the room and meets the aesthetic preferences. Consider the BTU output, venting requirements, and safety features of different models. Consult with a qualified fireplace dealer to determine the best option for specific needs and circumstances. Ensure the selected fireplace is certified by a recognized testing agency, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CSA (Canadian Standards Association).
Materials and Tools: Gather all necessary materials and tools before beginning the installation. This may include gas piping, fittings, venting components, framing lumber, drywall, insulation, and various hand and power tools. Having all the necessary materials on hand will help to streamline the installation process and minimize delays.
Key Point 2: Installation Procedure
Once the pre-installation assessment and planning are complete, the actual installation process can begin. This involves framing the fireplace enclosure, installing the venting system, connecting the gas line, and installing the fireplace insert or logs. Strict adherence to the manufacturer's instructions and local building codes is crucial for a safe and proper installation.
Framing the Fireplace Enclosure: Construct a frame around the fireplace opening using lumber that meets local building code requirements. Ensure the frame is square, level, and plumb. Maintain proper clearances between the fireplace and combustible materials, as specified by the manufacturer's instructions. The frame should be securely attached to the surrounding wall studs or floor joists.
Venting System Installation: Install the venting system according to the manufacturer's instructions and local building codes. This may involve connecting to an existing chimney or installing a new chimney. Ensure all venting components are properly sealed and connected to prevent leaks. Use the correct type of venting material for the specific fireplace model. Consider using a listed and labeled chimney liner when connecting to an existing masonry chimney. Maintain proper clearances between the venting system and combustible materials.
Gas Line Connection: A licensed plumber should connect the gas line to the fireplace. The plumber will ensure the gas line is properly sized and tested for leaks. A shut-off valve should be installed in the gas line near the fireplace for safety. The gas line connection must comply with all applicable plumbing codes.
Fireplace Insert/Log Installation: Install the fireplace insert or log set according to the manufacturer's instructions. Ensure the logs are positioned correctly within the firebox to maintain proper flame characteristics and prevent damage to the fireplace components. The fireplace insert should be securely fastened to the frame. Before proceeding, verify all connections and components are properly installed, following the manufacturer's instructions.
Electrical Connections: Most vented gas fireplaces require an electrical connection for the ignition system and blower (if equipped). A licensed electrician should make the electrical connections, ensuring they comply with all applicable electrical codes. Use the correct gauge wire and ensure all connections are properly grounded.
Key Point 3: Post-Installation Inspection and Testing
After the installation is complete, a thorough inspection and testing process is essential to ensure the fireplace is operating safely and efficiently. This involves checking for gas leaks, verifying proper venting, and testing the ignition system and controls. Addressing any issues identified during the inspection process is critical before using the fireplace.
Gas Leak Testing: Check all gas line connections for leaks using a gas leak detector or a soapy water solution. Apply the soapy water solution to the connections and look for bubbles. If any leaks are detected, immediately shut off the gas supply and repair the leaks before proceeding. A professional plumber may be required to repair complex gas line leaks.
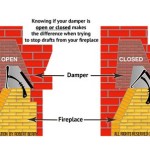
Venting System Verification: Confirm the venting system is functioning properly by observing the draft. Light a small piece of paper and hold it near the fireplace opening. The smoke should be drawn up the chimney, indicating a proper draft. If the smoke is not drawn up the chimney, there may be a blockage or other issue with the venting system. Contact a qualified chimney sweep to inspect and repair the venting system.
Ignition System and Controls Testing: Test the ignition system and controls to ensure they are functioning properly. Verify the pilot light ignites easily and the main burner operates smoothly. Test all control features, such as the flame height adjustment and blower speed. Ensure all safety features, such as the flame sensor and automatic shut-off valve, are working correctly.
Carbon Monoxide Detection: Install a carbon monoxide detector near the fireplace to provide an early warning of any carbon monoxide leaks. Test the carbon monoxide detector regularly to ensure it is functioning properly. Replace the batteries in the carbon monoxide detector annually. Carbon monoxide detectors are essential for the safe operation of any gas-burning appliance.
Final Inspection and Documentation: Schedule a final inspection with the local building inspector to ensure the installation complies with all applicable codes and regulations. Provide the inspector with all necessary documentation, including the fireplace manufacturer's instructions, gas line inspection reports, and electrical inspection reports. Obtain a certificate of occupancy or other documentation indicating that the fireplace installation has been approved.
Homeowner Education: Educate the homeowner on the proper operation and maintenance of the fireplace. Provide instructions on how to light the pilot light, adjust the flame height, and clean the fireplace. Emphasize the importance of regular chimney inspections and carbon monoxide detector maintenance. Encourage the homeowner to contact a qualified service technician for any repairs or maintenance beyond their capabilities.
Installing a vented gas fireplace can significantly enhance the comfort and ambiance of a home. Careful planning, proper installation techniques, and thorough post-installation inspection are crucial to ensure safe and reliable operation. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of a vented gas fireplace for years to come.
Gas Fireplace Venting Explained Heatilator

How To Select And Install A Gas Fireplace Log Set Fireplaces Direct Learning Center

Benefits Of Direct Vent Fireplaces
Gas Fireplace Venting Explained Heat Glo

If You Have A Gas Fireplace It May Or Not Chimney Flue

Gas Fireplace Installation Ina Beach Wilmington Hampstead Nc Log Services

What Are The Best Ways To Vent A Gas Fireplace Zoroast

Vented Vs B Vent Direct Free Dixie S

What Is A Direct Vent Fireplace Fireplaces Learning Center
Gas Fireplace Venting Explained Heat Glo
Related Posts