Understanding Underwriters Laboratories (UL) Fireplace Standards
Underwriters Laboratories (UL), a globally recognized safety science organization, plays a crucial role in establishing safety standards for a wide range of products, including fireplaces. These standards are designed to mitigate risks associated with fireplace operation, encompassing aspects from fire containment and heat management to material safety and exhaust venting. Adherence to UL standards is essential for manufacturers to ensure their fireplaces are safe for consumers and comply with regional and national building codes.
The UL certification mark on a fireplace indicates that the product has undergone rigorous testing and evaluation by UL engineers. This process involves assessing the fireplace's design, construction, and performance under normal and foreseeable abnormal operating conditions. The goal is to identify potential hazards and ensure that the fireplace meets the minimum safety requirements established by UL. This rigorous testing process contributes significantly to consumer confidence and overall fire safety.
Key Areas Covered by UL Fireplace Standards
UL's fireplace standards address several critical aspects of fireplace safety including construction, material selection, performance testing, and marking requirements.
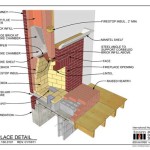
Construction and Design: The structural integrity of the fireplace is a primary concern. UL standards specify requirements for the materials used in fireplace construction, including their resistance to high temperatures and structural stresses. The design must ensure that the fire is contained within the designated firebox and that there are no pathways for sparks or embers to escape. Specific dimensions and clearances are also stipulated to prevent overheating of adjacent combustible materials.
The design of the firebox, including the shape, size, and material composition, directly impacts the efficiency and safety of the fireplace. UL standards require that the firebox be constructed from non-combustible materials capable of withstanding continuous exposure to high temperatures without degradation. Seams and joints must be robust and airtight to prevent smoke leakage. Specific designs are tested to ensure even heat distribution and efficient combustion.
Material Selection: The materials used in the construction of a fireplace must meet certain safety criteria outlined by UL. These criteria address flammability, heat resistance, and the potential for off-gassing of harmful substances. Materials used for insulation, seals, and gaskets must also be evaluated to ensure their suitability for high-temperature environments. The selection of appropriate materials is crucial for ensuring the long-term safety and reliability of the fireplace.
Metals used in fireplace construction, such as steel and cast iron, must be of specific grades and thicknesses to ensure they can withstand the stresses and temperatures generated during operation. Non-metallic materials, such as firebrick and ceramic fiber insulation, must also meet strict performance requirements related to their ability to resist heat and prevent the spread of fire. The use of substandard or untested materials can significantly compromise the safety of the fireplace and increase the risk of fire.
Performance Testing: UL standards mandate a battery of performance tests designed to simulate real-world operating conditions and identify potential safety hazards. These tests include fire endurance tests, thermal cycling tests, and stability tests. Fire endurance tests assess the ability of the fireplace to contain a fire for a specified period of time without structural failure or the spread of fire to adjacent materials. Thermal cycling tests evaluate the impact of repeated heating and cooling cycles on the structural integrity of the fireplace. Stability tests ensure that the fireplace remains stable and does not tip over during normal operation.
The specific tests conducted depend on the type of fireplace and its intended use. For example, freestanding fireplaces may be subjected to more rigorous stability tests than built-in fireplaces. Gas fireplaces undergo additional tests to ensure the safe and efficient combustion of gas and the proper operation of safety controls. These performance tests provide valuable data that helps UL engineers assess the safety of the fireplace and identify any areas that require improvement.
The Role of UL Listing and Labeling
A fireplace that has been tested and certified by UL is typically marked with a UL listing mark. This mark serves as a visual indicator to consumers and building inspectors that the fireplace meets the applicable UL safety standards. The listing mark is usually accompanied by additional information, such as the model number, the type of fuel the fireplace is designed to burn (e.g., wood, gas, or electric), and any specific installation requirements.
The UL listing mark is not a guarantee of absolute safety, but it provides a reasonable assurance that the fireplace has been designed, manufactured, and tested to meet accepted safety standards. Consumers should always look for the UL listing mark when purchasing a fireplace to ensure that it has been independently evaluated for safety. It is also important to follow the manufacturer's installation instructions and operating guidelines to ensure the safe and proper operation of the fireplace.
Furthermore, the UL listing mark provides a benchmark for building inspectors and code officials. Many building codes require that fireplaces be UL listed to ensure compliance with safety regulations. The UL listing mark simplifies the inspection process by providing a readily identifiable indicator of safety compliance. Building inspectors can rely on the UL listing mark as evidence that the fireplace meets the minimum safety requirements established by the code.
Ongoing Monitoring and Surveillance
UL's commitment to safety extends beyond the initial certification process. UL maintains an ongoing surveillance program to ensure that manufacturers continue to produce fireplaces that comply with the applicable safety standards. This program involves periodic inspections of manufacturing facilities and random testing of products purchased from the market. If UL identifies any non-compliance issues, it can take corrective actions, such as requiring the manufacturer to modify the product or even withdrawing the UL listing.
The ongoing surveillance program helps to maintain the integrity of the UL listing mark and ensures that consumers can continue to rely on UL-certified products for safety. It also provides an incentive for manufacturers to maintain high standards of quality and safety in their manufacturing processes. This continuous monitoring is crucial for adapting to changes in technology and materials used in fireplace manufacturing.
The UL surveillance program also plays a vital role in identifying and addressing emerging safety hazards. As new products and technologies are introduced into the marketplace, UL engineers conduct research and testing to assess their potential impact on safety. This proactive approach helps to prevent accidents and injuries by identifying and addressing potential safety hazards before they become widespread. The ongoing monitoring and surveillance activities reinforce UL's commitment to promoting safety and protecting consumers.
In The Market For A Fireplace Heatilator

Ventis Hes170 Wood Burning Stove

Setting Safety Standards

Superior Custom Series Wood Fireplace Brf 4375 The Cozy Cabin Lennox Hearth Parts

The Ez Door For Superior Fireplaces Steel Fireplace Home Renovation
Preway Be48 Question Hearth Com Forums Home

Zero Clearance Wood Fireplace Ventis He350 Best Fireplaces

Wood Burning Fireplaces Hearth And Home Pe Va

An Indoor Gas Fireplace For The Home Lawn Leisure

Majestic 42 Inch Biltmore Woodburning Fireplace
Related Posts