Radiant Flame Gas Fireplaces: A Deep Dive into Design, Functionality, and Considerations
Radiant flame gas fireplaces offer a compelling alternative to traditional wood-burning fireplaces, providing warmth, ambiance, and convenience without the associated mess and maintenance. These appliances utilize natural gas or propane to generate visually appealing flames and distribute heat, making them a popular choice for residential and commercial spaces. This article explores the key aspects of radiant flame gas fireplaces, encompassing their design variations, operational principles, installation considerations, and safety features.
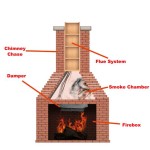
The core principle behind a radiant flame gas fireplace is the combustion of natural gas or propane within a controlled environment. A burner system, typically constructed from stainless steel or cast iron, distributes the gas evenly, allowing for consistent flame patterns. The flames, in turn, heat a set of ceramic logs or glass media, which then radiate heat into the surrounding room. The efficiency of a gas fireplace is determined by its ability to convert fuel into usable heat, often expressed as an Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating. Higher AFUE ratings indicate greater efficiency, resulting in lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact.
Beyond the basic functionality, radiant flame gas fireplaces offer a diverse range of aesthetic options. From traditional log sets that mimic the appearance of real wood to contemporary glass media and abstract designs, there are models to suit various architectural styles and personal preferences. The flame height and intensity are typically adjustable, allowing users to customize the ambiance and heat output. Furthermore, many models incorporate features such as remote controls, thermostats, and electronic ignition systems for enhanced convenience and control.
Understanding Radiant Heat Output
The term "radiant flame" refers to the primary method of heat transfer in these fireplaces: radiant heat. Radiant heat warms objects and people directly, rather than heating the air first, as with forced-air heating systems. This results in a more even and comfortable distribution of warmth within the room. The effectiveness of radiant heat depends on several factors, including the size of the fireplace, the type of media used (logs or glass), and the insulation of the surrounding walls. Fireplaces with larger surface areas and higher BTU (British Thermal Unit) ratings will generally produce more radiant heat.
The materials used in the construction of the fireplace also play a significant role in its radiant heat output. Ceramic logs, for instance, are designed to absorb and radiate heat efficiently, providing a realistic and comfortable warmth. Glass media, on the other hand, tends to produce a more modern aesthetic and can offer a different radiant heat profile. The placement of the fireplace within the room is also crucial. A fireplace located on an exterior wall may lose some of its heat to the outside, while a fireplace placed in a central location will distribute heat more evenly throughout the space.
In addition to radiant heat, some gas fireplaces also incorporate a convective heat component. This involves the circulation of air around the firebox, which is then heated and released into the room. Convection heating can help to distribute heat more quickly and evenly, particularly in larger spaces. However, it is important to note that radiant heat remains the primary source of warmth in most radiant flame gas fireplaces.
Exploring Design Variations and Installation Requirements
Radiant flame gas fireplaces are available in a wide array of designs, catering to diverse tastes and architectural styles. These designs can be broadly categorized into freestanding units, insert models, and built-in fireplaces. Freestanding gas fireplaces resemble traditional wood stoves and can be placed virtually anywhere with proper venting. Insert models are designed to fit into existing masonry fireplaces, providing a convenient and efficient upgrade. Built-in fireplaces are integrated into the wall during construction or renovation, offering a seamless and customized look.
The installation of a radiant flame gas fireplace requires careful planning and adherence to local building codes and regulations. A qualified professional should be consulted to ensure proper venting, gas line connections, and electrical wiring. Venting options include direct vent, B-vent, and vent-free systems. Direct vent fireplaces draw combustion air from outside and exhaust directly to the outside, offering optimal safety and efficiency. B-vent fireplaces utilize existing chimneys or vents, while vent-free fireplaces do not require any venting. Vent-free fireplaces, however, may be subject to stricter regulations due to concerns about indoor air quality.
Gas line connections must be performed by a licensed gas fitter to ensure safe and leak-free operation. The fireplace should be properly grounded to prevent electrical hazards. Furthermore, adequate clearance must be maintained around the fireplace to prevent combustible materials from overheating. Regular maintenance, including cleaning the burner and venting system, is essential for optimal performance and safety. The cost of installation can vary significantly depending on the type of fireplace, the complexity of the venting system, and the labor costs in the area.
Addressing Safety Features and Operational Considerations
Safety is a paramount concern when operating any gas appliance, and radiant flame gas fireplaces are equipped with several features to mitigate potential risks. Carbon monoxide detectors are essential for alerting occupants to the presence of this odorless and potentially lethal gas. Oxygen depletion sensors (ODS) automatically shut off the gas supply if oxygen levels in the room become too low, preventing incomplete combustion and carbon monoxide buildup. Some models also incorporate features such as safety screens or glass barriers to prevent accidental contact with the hot surface of the fireplace.
Proper ventilation is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation. Direct vent fireplaces offer the safest option, as they completely isolate the combustion process from the indoor environment. B-vent fireplaces require a properly functioning chimney to exhaust combustion gases safely. Vent-free fireplaces rely on room ventilation to disperse combustion byproducts, which may not be adequate in all situations. It is essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions regarding ventilation and to ensure that the fireplace is properly maintained.
Operational considerations include adjusting the flame height and intensity to achieve the desired level of warmth and ambiance. Many gas fireplaces come with remote controls that allow users to adjust the settings from the comfort of their seats. Thermostats can be used to maintain a consistent room temperature. It is important to avoid placing combustible materials too close to the fireplace, as they could pose a fire hazard. Children and pets should be supervised around the fireplace to prevent accidental burns. Regular inspections and maintenance by a qualified technician can help to ensure that the fireplace is operating safely and efficiently.
The long-term operational costs of a radiant flame gas fireplace depend on several factors, including the price of natural gas or propane, the efficiency of the fireplace, and the frequency of use. Gas prices can fluctuate significantly, so it is important to factor this into the overall cost of ownership. Energy-efficient models with high AFUE ratings will generally have lower operating costs. Regular maintenance can also help to improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption. While initial installation costs can be higher than traditional wood-burning fireplaces, the convenience, safety, and energy efficiency of radiant flame gas fireplaces make them a compelling choice for many homeowners.

Comfort Glow Radiant Flame Gas Log Rf30t Heater Fmc

Which Gas Fires Are The Most Efficient Direct Fireplaces

Fireplace Heater Propane Radiant Flame Ventless Nex Tech Classifieds

Flare Design Fascia Deepline Radiant Gas Fire Direct Fireplaces

Napoleon Mirro Flame Porcelain Reflective Radiant Panels For 36 Elevation X Fireplaces

Superior 36 Inch B Vent Radiant Gas Fireplace Brt4536 North Country Fire

Radiant Plus Fireplace Inserts Made In Usa Lopi Stoves

Radiant Heat Cross Timbers Vent Gas Log Set With Ember Burner Hargrove Logs

Flare Classic Collection Slimline Radiant Inset Gas Fire Direct Fireplaces

Napoleon Ascent 42 Gas Fireplace Gallery Of Western Michigan
Related Posts