Propane Stove Fireplace: A Comprehensive Guide
Propane stove fireplaces offer a blend of aesthetic appeal and practical heating solutions for residential and commercial spaces. They provide a controlled and efficient way to generate heat, mimicking the visual charm of a traditional wood-burning fireplace without the associated complexities and environmental concerns. These appliances rely on propane gas as their fuel source, burning it within a contained unit to produce radiant and convective heat. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of propane stove fireplaces, covering their functionality, advantages, installation considerations, maintenance requirements, and safety protocols.
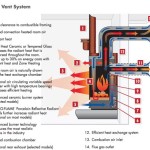
The fundamental principle behind a propane stove fireplace is the controlled combustion of propane. The appliance typically consists of several key components: a propane burner, a firebox or combustion chamber, a ventilation system, and a control mechanism. Propane gas is supplied to the burner via a regulated connection, which ensures a consistent and safe flow of fuel. The burner is designed to mix propane with air in precise proportions, leading to efficient and clean combustion. The firebox houses the burner and provides a visually appealing enclosure for the flames. It is usually constructed from materials that can withstand high temperatures, such as cast iron or steel. The ventilation system is crucial for safely removing exhaust gases from the house, and the control mechanism allows the user to adjust the flame height and heat output.
Propane stove fireplaces come in a variety of designs and styles to suit different aesthetic preferences and heating needs. They can range from freestanding models that resemble traditional wood-burning stoves to insert models that are designed to fit into existing fireplace openings. Some models also include features like realistic-looking artificial logs, glowing embers, and variable flame settings to enhance the visual appeal. The choice of model will depend on factors such as the size of the room to be heated, the available space, the desired aesthetic, and the budget.
Key Benefits of Propane Stove Fireplaces
Propane stove fireplaces present several advantages over traditional wood-burning fireplaces and other heating alternatives. These benefits encompass efficiency, convenience, environmental considerations, and safety factors.
Efficiency: Propane stove fireplaces are generally more efficient than wood-burning fireplaces. Wood-burning fireplaces often suffer from significant heat loss through the chimney, with a large portion of the generated heat escaping into the atmosphere. Propane stoves, on the other hand, are designed to maximize heat transfer to the room, utilizing advanced burner technology and insulated fireboxes to minimize heat loss. This improved efficiency translates to lower fuel consumption and reduced heating costs.
Convenience: Compared to wood-burning fireplaces, propane stoves offer a significant increase in convenience. There is no need to chop, stack, and store wood, eliminating the physical labor and storage space requirements associated with traditional fireplaces. Starting a propane stove is as simple as turning a knob or pressing a button, providing instant heat without the need for kindling and careful tending of the fire. Furthermore, propane stoves produce minimal ash and soot, reducing the cleaning burden and maintenance requirements.
Environmental Considerations: Propane is a relatively clean-burning fuel compared to wood. Wood-burning fireplaces release particulate matter and other pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and potentially impacting respiratory health. Propane stoves produce significantly fewer emissions, making them a more environmentally friendly heating option. Additionally, propane is a domestically produced fuel source, reducing reliance on foreign energy sources.
Safety: Modern propane stove fireplaces are equipped with safety features designed to prevent accidents and ensure safe operation. These features may include automatic shut-off valves that stop the flow of gas in the event of a malfunction, oxygen depletion sensors that monitor the air quality and shut off the stove if oxygen levels become dangerously low, and childproof controls that prevent accidental ignition. When installed and maintained properly, propane stoves offer a safe and reliable heating solution.
Installation and Venting Requirements
Proper installation is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of a propane stove fireplace. The installation process typically involves connecting the stove to a propane supply line, venting the exhaust gases to the outside, and ensuring compliance with local building codes and regulations. It is highly recommended to have a qualified and licensed technician perform the installation to ensure that all safety requirements are met.
Propane Supply Connection: The propane stove must be connected to a propane supply line that is properly sized and rated for the appliance. The connection should be made by a qualified technician using approved fittings and materials. The propane supply line may be connected to a dedicated propane tank or to a central propane system that serves multiple appliances. It is essential to follow all relevant codes and regulations regarding propane storage and handling.
Venting: Proper venting is essential for safely removing exhaust gases from the house. Propane stoves typically require a direct-vent system, which draws combustion air from outside and vents exhaust gases directly to the outside through a sealed pipe. The venting system must be installed according to the manufacturer's instructions and local building codes. Improper venting can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning, a serious health hazard.
Clearances and Spacing: Propane stoves require specific clearances from combustible materials to prevent fire hazards. The manufacturer's instructions will specify the minimum clearances required for the stove's sides, back, and top. It is important to adhere to these clearances to ensure the safe operation of the appliance. The stove should also be placed on a non-combustible surface, such as tile or stone.
Permits and Inspections: In many jurisdictions, a permit is required to install a propane stove fireplace. It is important to check with the local building department to determine the permit requirements and to ensure that the installation is inspected by a qualified inspector. This will help to ensure that the installation complies with all applicable codes and regulations.
Maintenance and Safety Protocols
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a propane stove fireplace. Proper maintenance can help to prevent malfunctions, extend the lifespan of the appliance, and maintain its aesthetic appeal. Additionally, adherence to safety protocols is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring the well-being of occupants.
Regular Cleaning: The exterior of the propane stove should be cleaned regularly to remove dust and debris. A soft cloth and mild detergent can be used to clean the appliance's surfaces. The burner and firebox should also be inspected periodically for any signs of soot or carbon buildup. If necessary, the burner can be cleaned with a brush and vacuum cleaner. The glass door of the stove should be cleaned with a glass cleaner designed for fireplaces.
Vent Inspection: The venting system should be inspected annually by a qualified technician to ensure that it is free from obstructions and in good working condition. Birds' nests, leaves, and other debris can block the vent, leading to a buildup of carbon monoxide. The vent should also be inspected for any signs of corrosion or damage.
Pilot Light and Burner Inspection: The pilot light and burner should be inspected periodically to ensure that they are functioning properly. The pilot light should be a steady blue flame, and the burner should produce a clean, even flame. If the pilot light is yellow or flickering, or if the burner produces a smoky flame, it may indicate a problem with the gas supply or the burner itself. A qualified technician should be consulted to diagnose and repair any issues.
Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Carbon monoxide detectors are essential for safety. These detectors should be installed in areas near the propane stove and in sleeping areas. The detectors should be tested regularly to ensure that they are functioning properly. It is important to replace the batteries in the detectors at least once a year.
Professional Inspection: It is recommended to have a professional inspection of the propane stove fireplace at least once a year. A qualified technician can perform a thorough inspection of the appliance, identifying any potential problems and making necessary repairs or adjustments. This will help to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the stove and to prolong its lifespan.

Propane Fireplaces Gas Stoves Id Mt Wy Fall River

Freestanding Gas Burning Stoves Sierra Hearth And Home

Freestanding Gas Stoves Friendly Fires

Fplc Freestanding Stoves Natural Gas And Propane

Propane Freestanding Stoves From Stewart S Hearth In Miramichi

Freestanding Gas Stoves Stove Fireplaces Napoleon

Comparing Wood And Propane Heat Tiny Stove

Kingsman Propane Fireplace Fdv200s Canadian Off Grid Depot

Fplc Freestanding Stoves Natural Gas And Propane

Freestanding Gas Stoves Friendly Fires
Related Posts