The content should be formatted for readability on a webpage. ```html
Understanding ProCom Fireplace Parts: A Comprehensive Guide
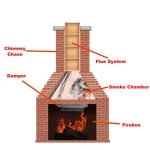
ProCom Heating, Inc. is a well-established manufacturer specializing in vent-free heating solutions, including gas fireplaces, stoves, and associated accessories. Consequently, understanding the different components and replacement parts associated with ProCom fireplaces is crucial for homeowners, technicians, and retailers alike. This article provides a detailed overview of commonly encountered ProCom fireplace parts, their functions, and key considerations for maintenance and repair.
Pilot Assemblies: The Heart of Ignition
The pilot assembly is critical for igniting and maintaining the flame in a gas fireplace. It comprises several interconnected parts, each playing a specific role. The primary components include the pilot burner, thermocouple or thermopile, and the pilot gas tubing. The pilot burner delivers a small, continuous flame that ignites the main burner when needed. The thermocouple, a heat-sensing device, generates a small electrical current when heated by the pilot flame. This current is used to keep the main gas valve open. A thermopile, similar to a thermocouple, generates a larger electrical current, often used in millivolt systems, which power the gas valve without needing an external power source. The pilot gas tubing transports gas from the gas valve to the pilot burner. Understanding the functionality of each component within the pilot assembly is essential for diagnosing ignition issues. If the pilot light fails to stay lit, it could indicate a faulty thermocouple, a clogged pilot burner, or a problem with the gas supply.
Troubleshooting pilot assembly issues often involves cleaning the pilot burner orifice with a specialized tool to remove any debris that may be obstructing the gas flow. Additionally, the thermocouple should be tested with a multimeter to ensure it is producing the required electrical current. Replacing a faulty thermocouple or pilot assembly is a relatively straightforward process but requires careful attention to detail and adherence to safety precautions, including turning off the gas supply before commencing any work.
Gas Valves: Regulating Gas Flow and Safety
The gas valve is the primary control mechanism for regulating the flow of gas to the main burner. It is responsible for controlling the amount of gas delivered to the fireplace, thereby controlling the flame height and heat output. Gas valves also incorporate safety features, such as a flame failure response system, which shuts off the gas supply if the pilot light is extinguished. ProCom fireplaces utilize various types of gas valves, including millivolt valves, electronic ignition valves, and manual control valves. Millivolt valves rely on the electrical current generated by the thermopile to operate. Electronic ignition valves use an electronic igniter, such as a spark igniter, to light the pilot flame. Manual control valves require the user to manually turn the gas on and off.
A malfunctioning gas valve can manifest in several ways, including the inability to ignite the fireplace, erratic flame behavior, or a complete shut-off of the gas supply. Diagnosing gas valve problems often involves using a multimeter to check for proper voltage and continuity. A common issue is a sticking gas valve, which can be caused by debris or corrosion. In some cases, cleaning the gas valve may resolve the issue. However, if the gas valve is severely damaged or malfunctioning, it should be replaced by a qualified technician due to the potential safety risks associated with natural gas leaks.
When replacing a gas valve, it is crucial to select a replacement part that is compatible with the specific model of ProCom fireplace. The gas valve should have the same gas type (natural gas or propane) and the same inlet and outlet size. Furthermore, it is essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully when installing a new gas valve.
Burners and Logs: Achieving Optimal Heat and Aesthetics
The burner is the component that distributes the gas and mixes it with air to create a controlled flame. ProCom fireplaces often use ceramic or metal burners. The design of the burner influences the flame pattern and the efficiency of combustion. Over time, burners can become clogged with dust, debris, or soot, which can affect the flame quality and reduce the heat output. Cleaning the burner regularly can help maintain optimal performance.
The ceramic logs are designed to mimic the appearance of real wood logs and enhance the aesthetic appeal of the fireplace. They are typically made from heat-resistant ceramic materials. While durable, ceramic logs can crack or break over time due to exposure to high temperatures. Replacement logs are available in various shapes and sizes to match different ProCom fireplace models. When replacing logs, it is crucial to position them correctly according to the manufacturer's instructions. Proper log placement is essential for ensuring proper airflow and preventing the logs from interfering with the flame or gas flow.
The burners on ProCom fireplaces vary in design depending on the model. Ensuring that the burner is properly cleaned and free of debris is important in maintaining optimal performance. A dirty burner can cause incomplete combustion, leading to the buildup of carbon monoxide. Therefore, regular cleaning and inspection of the burner are essential safety measures.
Thermocouples and Thermopiles: Ensuring Continuous Pilot Flame
Thermocouples and thermopiles are thermoelectric devices responsible for ensuring the pilot light remains lit. As mentioned previously, the thermocouple generates a small electrical current when heated by the pilot flame, which keeps the gas valve open. Similarly, the thermopile generates a larger current, often used in millivolt systems. The thermocouple is a safety device that shuts off the gas supply if the pilot light is extinguished, preventing a buildup of unburned gas.
A faulty thermocouple is one of the most common causes of pilot light problems in gas fireplaces. Testing the thermocouple with a multimeter is a straightforward process. The multimeter should be set to measure millivolts (mV). The thermocouple should produce a minimum voltage specified by the manufacturer, typically around 20-30 mV. A reading below this range indicates that the thermocouple is failing and needs to be replaced. Replacing a thermocouple is a relatively inexpensive and straightforward repair that can often be performed by a homeowner with basic technical skills.
Thermopiles are robust devices designed to provide long-lasting performance. However, they can still fail over time due to corrosion or physical damage. Testing a thermopile involves a similar process to testing a thermocouple. The multimeter should be set to measure millivolts (mV), and the thermopile should produce a voltage within the manufacturer's specified range, typically between 500-750 mV. A reading outside this range indicates that the thermopile is faulty and needs to be replaced.
Igniters: Starting the Flame with Precision
Igniters are responsible for initiating the pilot flame in ProCom fireplaces with electronic ignition systems. There are two main types of igniters: spark igniters and hot surface igniters. Spark igniters generate a high-voltage spark that ignites the gas. Hot surface igniters use a heating element to heat up to a high temperature, which then ignites the gas.
A malfunctioning igniter will prevent the fireplace from lighting. Troubleshooting igniter problems involves checking the igniter for spark or heat. For spark igniters, visually inspect the igniter for a spark when the ignition button is pressed. If there is no spark, the igniter may be faulty. For hot surface igniters, check the heating element to see if it is glowing red when the ignition is activated. If the element is not heating up, the igniter may be faulty.
Replacing an igniter is a relatively simple process. It involves disconnecting the old igniter and connecting the new igniter. When replacing an igniter, ensure that the replacement igniter is compatible with the specific model of ProCom fireplace.
Safety Controls and Sensors: Ensuring Safe Operation
ProCom fireplaces incorporate several safety controls and sensors to ensure safe operation. These include flame sensors, oxygen depletion sensors (ODS), and high-temperature limit switches. Flame sensors monitor the presence of the pilot flame and shut off the gas supply if the flame is extinguished. ODS sensors monitor the oxygen levels in the room and shut off the gas supply if the oxygen levels drop below a safe threshold. High-temperature limit switches shut off the gas supply if the fireplace overheats.
These safety devices are essential for preventing gas leaks, carbon monoxide poisoning, and other safety hazards. If any of these sensors malfunction, they can shut down the fireplace or prevent it from starting. Testing these sensors requires specialized equipment and expertise. Therefore, it is recommended to have a qualified technician inspect and repair these safety devices.
Regular maintenance and inspection of these safety controls are crucial for ensuring the safe operation of the fireplace. Homeowners should familiarize themselves with the location and function of these safety devices and follow the manufacturer's recommendations for maintenance and testing.
Fans and Blowers: Enhancing Heat Distribution
Many ProCom fireplaces are equipped with fans or blowers that circulate warm air throughout the room. The fan or blower helps to distribute the heat more evenly and increase the overall heating efficiency of the fireplace. Over time, fans and blowers can accumulate dust and debris, which can reduce their performance and increase noise levels. Cleaning the fan or blower regularly can help maintain optimal performance and extend its lifespan.
A malfunctioning fan or blower may not operate at all, operate intermittently, or produce excessive noise. Troubleshooting fan or blower problems involves checking the power supply, cleaning the fan blades, and lubricating the motor. If the fan or blower motor is faulty, it will need to be replaced.
Replacing a fan or blower is a relatively straightforward process. Be sure to disconnect the power supply before commencing any work. Remove the old fan or blower and install the new fan or blower, ensuring that it is properly aligned and secured. Connect the power supply and test the fan or blower to ensure it is operating correctly.
```
Procom Heating

Procom Heating

Procom Heating

Procom 32in Zero Clearance Fireplace Insert With Remote Control Mod Buyersdepot Com

Procom Ventless Dual Fuel Stove 25 000 Btu 170097 The Home Depot

Procom 29in Ventless Gas Dual Fuel Fireplace Insert 26 000 Btu T Stat Control Model Fbnsd28t At Com

Procom 32in Zero Clearance Fireplace Insert With Remote Control Mod Buyersdepot Com

Procom Vent Free 25k Btu Standing Gas Stove Fireplace Qnsd250t Hvacdirect Com

Procom Fbnsd400t Zc 32 000 Btu Vent Free Dual Fuel Build Com

Procom 28 In Dual Fuel Ventless Gas Fireplace System Corner Combo Mantel 10 000 Btu Antique White At Tractor Supply Co