Natural Gas Fireplace Insert Efficiency: Understanding the Factors and Maximizing Performance
Natural gas fireplace inserts represent a popular heating solution for homeowners seeking to upgrade existing masonry fireplaces or construct new supplemental heating sources. The efficiency of these inserts, measured by their ability to convert natural gas fuel into usable heat, is a critical factor in determining their cost-effectiveness and environmental impact. Understanding the various elements that influence natural gas fireplace insert efficiency enables homeowners to make informed decisions and optimize their heating systems.
Efficiency in this context refers to the percentage of potential energy contained within the natural gas that is actually converted into heat delivered to the living space. A higher efficiency rating translates to decreased fuel consumption, reduced heating costs, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Conversely, a less efficient insert will require more fuel to achieve the same level of warmth, leading to increased expenses and a greater environmental footprint.
Several factors contribute to the overall efficiency of a natural gas fireplace insert. These include the insert's design, construction materials, venting system, maintenance practices, and the homeowner's settings and operational habits. Optimizing each of these aspects can significantly improve the insert's performance and deliver substantial savings over its lifespan. Furthermore, understanding these efficiency drivers is critical when comparing different models during the purchase process.
Factors Affecting Natural Gas Fireplace Insert Efficiency
The efficiency of a natural gas fireplace insert is not a static value; it is influenced by a complex interplay of design features, installation quality, and operational parameters. These factors can be broadly categorized into the following areas:
Insert Design and Technology: The inherent design and technological features of a natural gas fireplace insert form the foundation of its efficiency. Manufacturers continually innovate to improve combustion efficiency and heat transfer.
Modern inserts often incorporate features such as sealed combustion chambers, which draw combustion air from outside the house, eliminating the need to use heated indoor air and preventing drafts. This design also minimizes the risk of backdrafting and carbon monoxide leakage. The sealed combustion process is more controlled and complete, resulting in better fuel utilization and reduced emissions.
Another critical aspect is the heat exchanger design. Efficient heat exchangers maximize the surface area for heat transfer from the combustion gases to the air circulating around the insert. Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as cast iron or steel, are commonly used to facilitate this process. The design of the heat exchanger, including the shape, size, and configuration of the fins or tubes, significantly impacts the rate at which heat is transferred into the room.
Some advanced inserts incorporate modulating gas valves, which automatically adjust the gas flow rate based on the desired temperature setting. This allows the insert to operate at lower heat outputs when the room is already warm, reducing fuel consumption and preventing overheating. In contrast, fixed-output inserts always burn at a constant rate, even if the room is nearing the desired temperature, leading to wasted energy.
The type of burner used in the insert also affects efficiency. Advanced burner designs, such as ribbon burners or ceramic burners, promote more complete and uniform combustion. These burners distribute the gas and air mixture more evenly, resulting in a hotter and cleaner flame. This improves the efficiency of heat generation and reduces the production of pollutants.
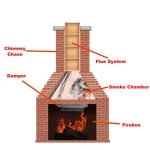
Venting System Configuration: The venting system plays a crucial role in removing combustion gases safely and efficiently from the fireplace insert. Proper venting ensures that the insert operates correctly and prevents the buildup of harmful byproducts, such as carbon monoxide, inside the home. It also influences the overall efficiency of the system.
The venting system must be properly sized and installed according to the manufacturer's specifications and local building codes. Using the wrong type of vent pipe or improperly connecting the sections can lead to leaks, blockages, and reduced efficiency. A blocked or restricted vent will impede the flow of combustion gases, causing the insert to operate inefficiently and potentially creating a dangerous situation.
Direct vent systems are generally more efficient than natural vent systems. Direct vent systems draw combustion air from outside the house and exhaust combustion gases directly outside through a sealed vent pipe. This prevents the loss of heated indoor air and eliminates the risk of backdrafting. Natural vent systems, on the other hand, rely on natural convection to draw combustion air from inside the house and exhaust gases through the chimney. This can create drafts and reduce the overall heating efficiency of the home.
The length and configuration of the vent pipe also affect efficiency. Longer vent runs can increase the resistance to airflow, reducing the efficiency of the system. Sharp bends or turns in the vent pipe can also impede airflow and reduce efficiency. It is important to minimize the length of the vent run and use smooth, gradual bends whenever possible.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the venting system are essential to ensure optimal performance and safety. The vent pipe should be inspected annually for signs of damage, corrosion, or blockage. Any debris or obstructions should be removed promptly. The vent cap should also be inspected to ensure that it is properly installed and functioning correctly.
Maintenance and Operational Practices: Even the most efficient natural gas fireplace insert will not perform optimally if it is not properly maintained and operated. Regular maintenance and adherence to best practices are essential to maximizing efficiency and extending the lifespan of the appliance.
Regular cleaning of the burner and firebox is crucial to maintaining efficient combustion. Dust, soot, and other debris can accumulate on the burner and inside the firebox, impeding airflow and reducing the efficiency of heat transfer. The burner should be cleaned periodically with a soft brush or vacuum cleaner. The firebox can be cleaned with a damp cloth.
The glass door of the fireplace insert should be kept clean to maximize radiant heat output. A dirty or sooty glass door will block the transmission of radiant heat into the room, reducing the efficiency of the system. The glass door can be cleaned with a glass cleaner specifically designed for fireplace inserts.
The pilot light should be properly adjusted to ensure efficient ignition and combustion. An improperly adjusted pilot light can waste gas and reduce the efficiency of the system. The pilot light should be inspected periodically and adjusted if necessary. Consult the manufacturer's instructions for the proper procedure.
Homeowners should avoid overusing the fireplace insert. While it can provide supplemental heat, it is not intended to be the primary heating source for the entire home. Overusing the insert can lead to increased fuel consumption and higher heating costs. It is important to use the insert only when needed and to adjust the temperature setting to maintain a comfortable level of warmth.
Understanding Efficiency Ratings
When evaluating natural gas fireplace inserts, it is crucial to understand the meaning and significance of efficiency ratings. Several different metrics are used to measure efficiency, and it is important to compare models based on the same criteria.
AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency): AFUE is a measure of the overall efficiency of a heating appliance over an entire heating season. It represents the percentage of fuel that is converted into usable heat, taking into account both steady-state efficiency and losses during startup and shutdown cycles. A higher AFUE rating indicates a more efficient appliance.
However, AFUE ratings for fireplace inserts can be misleading, as they are often based on laboratory testing conditions that do not accurately reflect real-world usage. Factors such as venting system configuration, installation quality, and homeowner behavior can significantly impact the actual efficiency achieved in the home.
Steady-State Efficiency: Steady-state efficiency is a measure of the efficiency of a heating appliance when it is operating at a constant heat output. It represents the percentage of fuel that is converted into usable heat under stable operating conditions. It provides a snapshot of the insert’s efficiency when it is running continuously.
While steady-state efficiency can be useful for comparing different models, it does not take into account losses during startup and shutdown cycles, which can be significant in fireplace inserts that are used intermittently.
EnerGuide Rating: In some regions, such as Canada, the EnerGuide rating is used to indicate the energy efficiency of appliances, including natural gas fireplace inserts. The EnerGuide rating provides an estimate of the annual energy consumption of the appliance, based on standardized testing procedures. A lower EnerGuide rating indicates a more energy-efficient appliance.
When comparing efficiency ratings, it is important to consider the specific testing conditions and the limitations of each metric. It is also important to look beyond the ratings and consider other factors, such as the insert's design features, venting system configuration, and the homeowner's operational practices.
Strategies for Maximizing Efficiency
Beyond selecting an efficient model, homeowners can implement several strategies to further optimize the efficiency of their natural gas fireplace inserts and reduce their heating costs. These strategies encompass installation, operation, and maintenance practices.
Professional Installation: Proper installation by a qualified technician is crucial for ensuring optimal efficiency and safety. The installer should be experienced in working with natural gas fireplace inserts and knowledgeable about local building codes and safety regulations. A properly installed insert will operate more efficiently and reliably, and it will be less likely to experience problems that could lead to reduced efficiency or safety hazards.
The installer should ensure that the venting system is properly sized and installed according to the manufacturer's specifications. The vent pipe should be securely connected and sealed to prevent leaks. The installer should also check the gas pressure and adjust the burner settings to ensure optimal combustion. Proper installation also involves sealing any air leaks around the fireplace opening to prevent drafts and heat loss.
Smart Thermostat Integration: Integrating the fireplace insert with a smart thermostat can help to regulate the temperature and optimize fuel consumption. Smart thermostats allow homeowners to program the insert to operate at different temperature settings throughout the day, based on their needs. They can also be remotely controlled, allowing homeowners to adjust the temperature from anywhere using a smartphone or tablet.
By setting the thermostat to a lower temperature when the home is unoccupied or during sleeping hours, homeowners can reduce fuel consumption and save money. Smart thermostats can also learn the homeowner's preferences and automatically adjust the temperature settings to optimize comfort and efficiency.
Zone Heating: Using the fireplace insert for zone heating can help to reduce energy waste and lower heating costs. Zone heating involves heating only the rooms that are being used, rather than heating the entire home. The fireplace insert can be used to provide supplemental heat to a specific room or area, while the central heating system is turned down or off.
This approach is particularly effective for homes with open floor plans or large rooms. By focusing the heat on the occupied areas, homeowners can avoid wasting energy heating unoccupied spaces. Zone heating can also improve comfort by allowing homeowners to customize the temperature in different areas of the home.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Regular maintenance and inspections are essential for ensuring that the fireplace insert continues to operate efficiently and safely. Homeowners should follow the manufacturer's recommendations for cleaning and maintenance. The burner, firebox, and vent pipe should be inspected regularly for signs of damage, corrosion, or blockage.
Professional inspections should be conducted at least once a year by a qualified technician. The technician can identify any potential problems and perform necessary repairs or adjustments. Regular maintenance and inspections will help to extend the lifespan of the fireplace insert and ensure that it continues to operate at peak efficiency.

Gas Fireplace Inserts Pros And Cons Of Ventless Fireplaces

How To Buy A Gas Fireplace Insert Buyer S Guide From Regency
.aspx?strip=all)
Top 11 Gas Fireplace Insert Trends Of 2024

Gas Fireplace Faq Fireplaces Direct Learning Center

Convert To Gas Installing Fireplace Inserts Doctor Flue

A Step By Guide To Understanding Fireplace Inserts

Freestanding High Efficiency Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces Inserts Stoves Godby Hearth And Home

Liberty Lri6e High Efficient Large Gas Insert Fireplace S Hearth Home

If You Ve Been Considering Gas Fuel A Fireplace Insert Is Great Option

The Top 3 Reasons To Choose A Gas Insert Over Log Set Hearthside Hearth Blog
Related Posts