Modular Fireplace Kits: A Comprehensive Guide
Modular fireplace kits offer a versatile and efficient solution for homeowners and contractors seeking to install a fireplace without the complexities and labor costs associated with traditional masonry construction. These kits, comprised of pre-engineered and pre-fabricated components, streamline the installation process, making fireplaces more accessible and affordable for a wider range of individuals and projects.
A modular fireplace kit typically includes the firebox, which is the core component where the fire is contained; the surround, which provides the exterior aesthetics; the chimney system, responsible for safely venting combustion gases; and all necessary hardware and instructions for assembly. The modular design philosophy allows for a simplified and standardized installation, significantly reducing the time and skill required compared to building a fireplace from scratch with bricks and mortar.
The appeal of modular fireplace kits extends beyond convenience. They often offer enhanced performance characteristics, such as superior heat retention and cleaner burning capabilities, due to advanced design and material selection. Furthermore, the controlled manufacturing environment ensures consistent quality and adherence to stringent safety standards. This article will delve into the various aspects of modular fireplace kits, exploring their benefits, design considerations, installation processes, and factors to consider when selecting the right kit for a specific application.
Understanding the Benefits of Modular Fireplace Kits
Modular fireplace kits present several compelling advantages over traditional masonry fireplaces. These benefits are primarily related to cost, time, performance, and design flexibility.
Reduced Installation Costs: One of the most significant advantages is the reduction in installation costs. Traditional masonry fireplaces require skilled masons and significant labor hours, which can be a substantial expense. Modular kits minimize the need for specialized labor. The pre-engineered components are designed for relatively straightforward assembly, often allowing homeowners with basic construction skills to complete the installation themselves or significantly reduce the labor costs by hiring a general contractor instead of a specialized mason. The predictable nature of the installation also reduces the risk of cost overruns associated with unforeseen challenges that can arise during traditional construction.
Faster Installation Time: The prefabricated nature of modular kits drastically reduces installation time. A traditional masonry fireplace can take days or even weeks to construct, depending on its complexity. A modular kit, on the other hand, can often be installed in a matter of hours or a few days, depending on the specific design and the installer's experience. This accelerated timeline minimizes disruption to the homeowner and allows for quicker project completion.
Consistent Quality Control: Modular kits are manufactured in controlled factory environments, ensuring consistent quality and adherence to stringent safety standards. This contrasts with traditional masonry construction, where the quality can vary depending on the skill and experience of the mason. The standardized manufacturing process also allows for precise tolerances and tight fits, which can improve the performance and longevity of the fireplace.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options: While often perceived as less customizable than traditional fireplaces, modular kits offer a wide range of design options to suit various architectural styles and personal preferences. Manufacturers offer different surround materials, including stone veneers, brick, tile, and metal, allowing homeowners to create a fireplace that complements their existing décor. Moreover, the modular design facilitates integration with other design elements, such as built-in shelving or media centers.
Improved Performance and Efficiency: Modern modular fireplace kits often incorporate advanced combustion technologies that improve performance and efficiency compared to older masonry designs. These features can include insulated fireboxes, air wash systems, and catalytic combustors, which promote cleaner burning and reduce emissions. The improved heat retention properties of some modular kits can also lead to lower heating costs over time.
Key Design Considerations for Modular Fireplace Kits
Selecting the right modular fireplace kit involves careful consideration of several design factors, including size, style, fuel type, and venting requirements. A thorough understanding of these factors is essential to ensure that the chosen kit meets the specific needs and preferences of the homeowner.
Size and Placement: The size of the fireplace should be proportional to the room in which it will be installed. A fireplace that is too large can overwhelm a small space, while one that is too small may not provide adequate heat or visual impact. The placement of the fireplace is also crucial. Consider factors such as traffic flow, furniture arrangement, and the location of existing structural elements. It is also important to ensure that the chosen location meets the clearance requirements specified by the manufacturer and local building codes.
Style and Aesthetics: The style of the fireplace should complement the overall aesthetic of the home. Modular kits are available in a wide range of styles, from traditional to contemporary. Consider the existing architectural details and décor when selecting a style. The choice of surround material, such as stone, brick, or tile, can significantly impact the appearance of the fireplace. Also consider the firebox opening shape and size, and whether you prefer a more traditional arched opening or a modern, linear one.
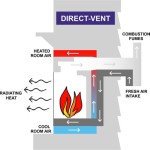
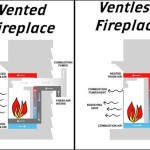
Fuel Type: The choice of fuel type will influence the type of modular kit required. Common fuel options include wood, gas, and electric. Wood-burning fireplaces offer the traditional ambiance of a real fire, but they require a chimney and proper ventilation. Gas fireplaces are more convenient and offer cleaner burning, but they require a gas line connection. Electric fireplaces are the easiest to install and operate, but they do not provide the same level of heat as wood or gas fireplaces. Each fuel type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice will depend on individual preferences and practical considerations.
Venting Requirements: Proper venting is essential for the safe and efficient operation of a fireplace. Wood-burning and gas fireplaces require a chimney or vent system to exhaust combustion gases. The type of venting required will depend on the fuel type and the design of the fireplace. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions and local building codes when installing the venting system. Electric fireplaces do not require venting, making them a simpler option for certain applications.
Efficiency and Heat Output: Consider the efficiency and heat output of the fireplace when making your selection. The efficiency of a fireplace is a measure of how much of the fuel's energy is converted into usable heat. Higher efficiency fireplaces will burn less fuel and produce more heat. The heat output of a fireplace is measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs). Choose a fireplace with a heat output that is appropriate for the size of the room you intend to heat. Also consider the thermal mass of the chosen kit; some materials will retain heat longer than others, providing radiant heat even after the fire is extinguished.
Installation Process and Important Considerations
The installation of a modular fireplace kit is generally simpler than building a traditional masonry fireplace, but it still requires careful planning and execution. Adherence to the manufacturer's instructions and local building codes is essential for ensuring a safe and functional installation.
Pre-Installation Planning: Before beginning the installation, carefully review the manufacturer's instructions and local building codes. Ensure that you have all the necessary tools, materials, and permits. Verify the structural integrity of the floor and walls where the fireplace will be installed. Check for any obstructions, such as electrical wiring or plumbing, that may need to be relocated. Proper planning will help to avoid potential problems and delays during the installation process.
Foundation and Framing: Depending on the weight of the fireplace, you may need to reinforce the floor with a concrete pad or additional framing. The manufacturer's instructions will specify the required foundation. Build a frame around the fireplace opening to provide support for the surround. Ensure that the framing is level and plumb. This step is crucial for ensuring that the fireplace is stable and aesthetically pleasing.
Assembly of the Firebox: The firebox is the core component of the fireplace. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully when assembling the firebox. Ensure that all connections are secure and properly sealed. Pay particular attention to the seams and joints, as these are potential areas for leaks. Use the appropriate sealant to prevent the escape of smoke and gases.
Installation of the Venting System: The venting system is responsible for safely exhausting combustion gases. The type of venting required will depend on the fuel type and the design of the fireplace. Follow the manufacturer's instructions and local building codes when installing the venting system. Ensure that all connections are secure and properly sealed. Use the appropriate chimney cap to prevent rain and debris from entering the chimney.
Installation of the Surround: The surround provides the exterior aesthetics of the fireplace. The surround can be made of various materials, such as stone, brick, or tile. Follow the manufacturer's instructions when installing the surround. Use the appropriate adhesive or fasteners to secure the surround to the framing. Ensure that the surround is level and plumb. Pay attention to the details, such as the grout lines and the alignment of the tiles.
Final Inspection and Testing: After the installation is complete, conduct a thorough inspection to ensure that everything is installed correctly. Check for any leaks or gaps. Test the fireplace to ensure that it is functioning properly. Consult with a qualified professional to perform a final inspection and ensure that the fireplace meets all safety requirements. This is especially important for gas fireplaces, where a gas leak could pose a serious hazard.
Ongoing Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a fireplace. Clean the chimney regularly to remove creosote buildup. Inspect the firebox and venting system for any signs of damage or deterioration. Replace any worn or damaged parts promptly. Following a regular maintenance schedule will help to extend the life of your fireplace and prevent costly repairs.
In conclusion, modular fireplace kits offer a cost-effective, time-saving, and aesthetically versatile alternative to traditional masonry fireplaces. Careful consideration of design, fuel type, and venting requirements, coupled with adherence to manufacturer instructions and local building codes, are crucial for a successful installation. By understanding the benefits and complexities associated with modular fireplace kits, homeowners and contractors can make informed decisions and create a warm and inviting focal point in any living space.

Outdoor Fireplace Kits Masonry Stone

Diy Outdoor Fireplace Kit Fremont Makes Hardscaping And Easy

Outdoor Fireplace Kits Stonewood S Cape Cod Ma Nh Ct

Diy Outdoor Fireplace Kit Fremont Makes Hardscaping And Easy

Outdoor Fireplace Kits Southwest Stone Supply

Outdoor Fireplace Kits Cornerstone Rocks

Outdoor Fireplace Kits Masonry Stone

Stone Age Manufacturing 18 Inch Veranda Diy Outdoor Fireplace Kit

Masonry Fireplace Kits Prefabricated Mason Lite

Diy Outdoor Fireplace Kit Fremont Makes Hardscaping And Easy
Related Posts