```html
Indoor Gas Fireplaces: A Comprehensive Guide
Indoor gas fireplaces offer a convenient and aesthetically pleasing alternative to traditional wood-burning fireplaces. They provide instant warmth, eliminate the need for wood storage and handling, and offer various design options to complement any interior décor. This article provides a comprehensive overview of indoor gas fireplaces, covering their types, advantages, installation considerations, maintenance requirements, and safety features.
Types of Indoor Gas Fireplaces
Gas fireplaces are broadly classified into several types based on their venting system, installation method, and design. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the appropriate model for a specific space and application.
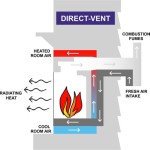
Direct Vent Fireplaces: These fireplaces are sealed units that draw combustion air from outside and vent exhaust gases directly outdoors through a dedicated venting system. The vent typically runs horizontally through an exterior wall or vertically through the roof. Direct vent fireplaces are known for their high efficiency and safe operation due to the sealed combustion chamber, which prevents indoor air contamination. They offer flexible installation options as they do not rely on existing chimneys.
Vent-Free Fireplaces: Also known as ventless fireplaces, these units do not require a flue or chimney. They burn gas so cleanly that the combustion byproducts are considered safe enough to be released directly into the living space. Vent-free fireplaces are typically equipped with oxygen depletion sensors (ODS) that automatically shut off the gas supply if oxygen levels in the room drop too low. Although convenient due to their easy installation, vent-free fireplaces are subject to certain regulations and restrictions in some jurisdictions. It's crucial to consult local building codes and ensure adequate room ventilation before installing a vent-free model.
B-Vent Fireplaces: These fireplaces utilize existing chimneys or vent systems. They draw combustion air from the room and vent exhaust gases up the chimney. B-vent fireplaces are less efficient than direct vent models as they rely on natural draft for venting, which can be affected by weather conditions. They are a suitable option for homeowners who want to replace an existing wood-burning fireplace with a gas unit without major structural modifications.
Insert Fireplaces: Gas fireplace inserts are designed to fit into existing masonry fireplaces. They offer a convenient way to convert an inefficient wood-burning fireplace into a more efficient and convenient gas-fueled unit. Inserts are available in various sizes and styles to suit different fireplace openings. They typically require a flexible vent liner to be installed inside the existing chimney to ensure proper venting.
Linear Fireplaces: Characterized by their long, horizontal design, linear fireplaces offer a modern and contemporary aesthetic. They are often used as a focal point in living rooms or entertainment areas. Linear fireplaces are available in various venting options, including direct vent and vent-free models.
Advantages of Indoor Gas Fireplaces
Compared to traditional wood-burning fireplaces, gas fireplaces offer several significant advantages, contributing to their increasing popularity among homeowners.
Convenience: Gas fireplaces provide instant warmth at the flick of a switch or the push of a button. There is no need to gather, stack, and season firewood, or deal with ashes and soot. The ease of use and immediate gratification are major selling points for many users.
Efficiency: Modern gas fireplaces, particularly direct vent models, are highly efficient, converting a significant portion of the fuel into usable heat. This results in lower energy bills compared to wood-burning fireplaces, which can lose a considerable amount of heat up the chimney.
Cleanliness: Gas fireplaces eliminate the mess associated with wood-burning fireplaces. There are no ashes to clean up, no creosote buildup in the chimney, and no smoky odors. This contributes to a cleaner and healthier indoor environment.
Control: Gas fireplaces offer precise temperature control. Users can easily adjust the flame height and heat output to maintain a comfortable room temperature. Some models are equipped with thermostats and remote controls for added convenience.
Aesthetics: Gas fireplaces are available in a wide range of styles and designs to complement any interior décor. From traditional log sets to contemporary glass media, there are options to suit every taste. The realistic flame appearance of modern gas fireplaces mimics the ambiance of a wood-burning fire without the associated hassles.
Safety: Gas fireplaces are generally safer than wood-burning fireplaces. They eliminate the risk of stray embers, sparks, and uncontrolled fires. Many models are equipped with safety features such as oxygen depletion sensors and safety shut-off valves.
Installation Considerations and Safety
Proper installation is paramount to the safe and efficient operation of a gas fireplace. It is highly recommended to hire a qualified and licensed HVAC professional or gas fireplace installer to ensure compliance with local building codes and manufacturer's instructions.
Gas Line Connection: Connecting a gas fireplace to the existing gas line requires expertise and precision. A licensed plumber or gas fitter should perform this task to ensure a leak-free and safe connection. The gas line must be properly sized to meet the fireplace's gas consumption requirements.
Venting: Proper venting is crucial for removing combustion byproducts safely from the home. The type of venting required depends on the type of gas fireplace being installed. Direct vent fireplaces require a specific venting system approved by the manufacturer. B-vent fireplaces require a properly sized chimney or vent system.
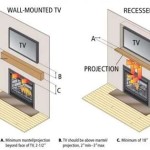
Clearances: Maintaining proper clearances between the fireplace and combustible materials is essential for preventing fires. The minimum clearance requirements are specified by the manufacturer and should be strictly adhered to. This includes clearances to walls, ceilings, mantels, and furniture.
Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Installing carbon monoxide detectors near the fireplace is a vital safety precaution. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that can be produced by incomplete combustion. Detectors will alert occupants to the presence of carbon monoxide, allowing them to evacuate the premises and seek medical attention.
Local Building Codes: Before installing a gas fireplace, it is crucial to consult local building codes and obtain any necessary permits. Building codes regulate various aspects of fireplace installation, including venting requirements, clearances, and gas line connections.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a gas fireplace. Simple maintenance tasks can be performed by homeowners, while more complex repairs should be handled by a qualified technician.
Cleaning: Regularly clean the glass front of the fireplace with a glass cleaner specifically designed for gas fireplaces. Dust and debris can accumulate on the glass, reducing visibility and potentially affecting performance. Remove any debris or obstructions from the burner area.
Pilot Light: Check the pilot light regularly to ensure it is burning properly. A weak or flickering pilot light may indicate a problem with the gas supply or the pilot assembly. If the pilot light frequently goes out, it may be necessary to clean or replace the pilot assembly.
Venting Inspection: Annually inspect the venting system for any signs of damage, corrosion, or blockages. Clear any debris or obstructions from the vent opening. For direct vent fireplaces, ensure that the vent termination is free from snow and ice during the winter months.
Gas Leak Testing: Periodically check for gas leaks around the fireplace and gas line connections using a soap and water solution. Apply the solution to the connections and look for bubbles, which indicate a leak. If a gas leak is suspected, immediately turn off the gas supply and contact a qualified gas fitter.
Professional Servicing: Schedule a professional inspection and servicing of the gas fireplace at least once a year. A qualified technician can inspect the burner, gas valve, venting system, and other components to ensure they are functioning properly. Professional servicing can help prevent costly repairs and ensure the safe operation of the fireplace.
```
Freestanding High Efficiency Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces Inserts Stoves Godby Hearth And Home

Indoor Gas Fireplaces Jetmaster
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ventless-gas-fireplaces-4160746-hero-f9d4bdcd9bd446eb84406de306f790ba.jpg?strip=all)
How To Pick Out A Ventless Gas Fireplace

Freestanding Gas Fireplaces Fergus Fireplace

All Seasons Fireplace Blog Gas Fireplaces

Enclosed Gas Fireplaces Jetmaster

Indoor Gas Fireplaces Planikafires

Ventless Gas Fireplace Propane
Custom Luxury Gas Fireplace Designs Stellar

All About Gas Fireplaces
Related Posts