Understanding Heat Glo Gas Fireplace Parts: A Comprehensive Guide
The Heat Glo gas fireplace is a popular choice for homeowners seeking efficient and aesthetically pleasing heating solutions. Maintenance and occasional repairs are essential to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of these fireplaces. Understanding the individual components that make up a Heat Glo gas fireplace is crucial for troubleshooting issues, performing routine maintenance, and ordering replacement parts when necessary. This article provides a detailed overview of the key components of a Heat Glo gas fireplace, their functions, and common issues.
Key Components of a Heat Glo Gas Fireplace System
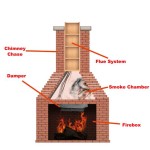
A Heat Glo gas fireplace comprises several interconnected parts, each playing a vital role in the safe and effective delivery of heat. These components can be broadly categorized into gas supply and control elements, the combustion chamber, the venting system, and the aesthetic features.
Gas Valve: The gas valve is arguably one of the most critical components. It regulates the flow of gas from the supply line to the burner. This valve is typically electronically controlled and responds to signals from the thermostat or remote control. Malfunctions of the gas valve can lead to a complete failure to ignite, inconsistent flame height, or gas leaks. Replacement of the gas valve often requires a qualified technician because it involves working directly with the gas supply.
Pilot Assembly: The pilot assembly provides a small, continuous flame used to ignite the main burner. It typically consists of a pilot burner, thermocouple or thermopile, and sometimes an igniter. The thermocouple/thermopile generates a small electrical current when heated by the pilot flame. This current is used to keep the gas valve open, ensuring a continuous gas supply to the pilot. If the pilot light goes out, the thermocouple cools down, shutting off the gas supply as a safety measure. Issues with the pilot assembly are a common cause of fireplace malfunctions, often manifesting as a pilot light that repeatedly extinguishes.
Burner: The burner is where the combustion of gas and air takes place, producing the heat and flames that characterize a gas fireplace. Burners are typically made of cast iron, stainless steel, or ceramic materials. They are designed with specific port configurations to distribute the gas evenly and create a visually appealing flame pattern. Over time, burners can become clogged with debris, corrode, or develop cracks, affecting their performance and potentially leading to incomplete combustion. Regular cleaning and inspection are crucial for maintaining burner efficiency.
Igniter: The igniter is responsible for initially lighting the pilot light or, in some models, directly igniting the main burner. There are two main types of igniters: spark igniters and hot surface igniters. Spark igniters generate a high-voltage spark that ignites the gas. Hot surface igniters use an electrically heated element to ignite the gas. Igniters can fail due to wear and tear, electrical issues, or physical damage. A faulty igniter will prevent the fireplace from starting.
Thermostat and Control System: The thermostat and control system regulate the fireplace's heat output and operation. This system can range from a simple manual control to a sophisticated electronic control with remote control capabilities. The thermostat monitors the room temperature and adjusts the gas flow accordingly to maintain the desired heat level. Electronic control systems often incorporate safety features, such as automatic shut-off in case of overheating or gas leaks. Malfunctions in the thermostat or control system can result in inaccurate temperature control, erratic operation, or complete failure of the fireplace.
Blower Motor: Many Heat Glo gas fireplaces are equipped with a blower motor, also known as a fan. The blower motor circulates heated air from the fireplace into the room, improving heating efficiency and distribution. The blower motor consists of a fan blade, an electric motor, and sometimes a speed control. Over time, the blower motor can accumulate dust and debris, causing it to become noisy or inefficient. Bearing wear and electrical problems can also lead to blower motor failure. Regular cleaning and lubrication can extend the life of the blower motor.
Glass Door: The glass door serves both aesthetic and functional purposes. It provides a clear view of the flames while also preventing drafts and containing sparks. The glass must be able to withstand high temperatures and is typically made of tempered or ceramic glass. Over time, the glass can become dirty or stained with soot. It is important to clean the glass regularly using a specialized fireplace glass cleaner. In cases of accidental breakage, the glass door must be replaced with a specific replacement part designed for the fireplace model to ensure proper fit and safety.
Log Set: The log set is a decorative element that mimics the appearance of a traditional wood-burning fireplace. Log sets are typically made of ceramic fiber or refractory cement and are designed to withstand high temperatures. The arrangement and design of the log set contribute significantly to the fireplace's aesthetic appeal. Over time, log sets can become cracked, chipped, or discolored due to prolonged exposure to heat. While minor damage may not affect the fireplace's function, severely damaged log sets may need to be replaced to maintain the fireplace's aesthetic value.
Venting System Components and Their Importance
The venting system is a critical safety component that removes combustion byproducts, such as carbon monoxide and unburned gases, from the fireplace and directs them safely outside the building. There are two main types of venting systems used with Heat Glo gas fireplaces: direct vent and B-vent.
Direct Vent Systems: Direct vent systems draw combustion air from outside the building and vent exhaust gases directly to the outside through a sealed pipe. This type of venting system is considered the safest option because it prevents indoor air from being used for combustion and eliminates the risk of backdrafting. Direct vent systems typically consist of two concentric pipes: one for intake air and one for exhaust. Proper installation and maintenance of the direct vent system are essential to prevent leaks and ensure proper ventilation.
B-Vent Systems: B-vent systems use indoor air for combustion and vent exhaust gases to the outside through a single-wall or double-wall pipe. B-vent systems are typically used in older homes where direct vent installation is not feasible. Because B-vent systems use indoor air, proper ventilation of the room is crucial to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. Regular inspection of the B-vent system is necessary to ensure it is free from obstructions and that it is properly sealed to prevent leaks.
Flue: The flue is the vertical pipe that carries exhaust gases from the fireplace to the outside. The flue must be properly sized and installed to ensure adequate draft and prevent backdrafting. Obstructions in the flue, such as bird nests or debris, can restrict airflow and lead to carbon monoxide buildup. Regular inspection and cleaning of the flue are essential for safe and efficient fireplace operation.
Vent Cap: The vent cap is located at the top of the flue and prevents rain, snow, and debris from entering the venting system. The vent cap also helps to create a draft, which draws exhaust gases out of the fireplace. A damaged or improperly installed vent cap can allow moisture and debris to enter the venting system, leading to corrosion and reduced airflow. Regular inspection of the vent cap is recommended to ensure it is in good condition.
Troubleshooting Common Heat Glo Gas Fireplace Problems
Understanding the function of each component allows for more effective troubleshooting. Common issues often point to specific parts needing attention.
Pilot Light Issues: Difficulty lighting or maintaining the pilot light are among the most common problems. Possible causes include a dirty pilot orifice, a faulty thermocouple or thermopile, or a malfunctioning gas valve. Cleaning the pilot orifice can often resolve the issue. If the thermocouple or thermopile is faulty, it will need to be replaced.
Fireplace Won't Ignite: If the fireplace fails to ignite, the problem could lie with the igniter, the gas valve, or the burner. Check the igniter for proper spark or heat. If the igniter is functioning correctly, the gas valve may be the issue. Ensure that the gas valve is receiving power and that it is opening properly. If the burner is clogged or corroded, it may need to be cleaned or replaced.
Inconsistent Flame Height: An inconsistent flame height can indicate a problem with the gas pressure, the gas valve, or the burner. Check the gas pressure to ensure it is within the recommended range. A malfunctioning gas valve can also cause inconsistent flame height. Cleaning the burner ports can also help to resolve this issue.
Unusual Noises: Unusual noises, such as clicking, hissing, or popping sounds, can indicate various problems. Clicking sounds may be caused by a faulty igniter. Hissing sounds may indicate a gas leak. Popping sounds can be caused by expanding metal or debris in the burner. Identifying the source of the noise can help pinpoint the cause and determine the necessary repair.
Soot Buildup: Excessive soot buildup on the glass door or the log set can indicate incomplete combustion. This can be caused by a dirty burner, improper gas pressure, or a malfunctioning venting system. Cleaning the burner and adjusting the gas pressure can help to reduce soot buildup. Inspect the venting system to ensure it is free from obstructions and that it is properly sized.
Odor: A noticeable odor, especially a gas smell, should be addressed immediately. Turn off the gas supply to the fireplace and ventilate the area. Contact a qualified technician to inspect the gas lines and connections for leaks. Never attempt to repair a gas leak yourself.
Regular maintenance, including cleaning the burner, inspecting the venting system, and checking the pilot assembly, can prevent many of these problems. Identifying the specific components and their functions within a Heat Glo gas fireplace empowers homeowners to understand the nature of potential problems and communicate effectively with qualified service technicians. Safety should always be the priority when dealing with gas appliances; any uncertainty warrants professional consultation.

Heat Glo St Trc See Thru Dv Gas Fireplace Parts Heatandgloparts Com

Heat Glo 8000cl Ift Lp 42 Dv Gas Fireplace Parts Heatandgloparts Com

Heat Glo Cbs 41 Woodburning Fireplace Parts Heatandgloparts Com
Heat Glo Supreme Gas Fireplace Insert Fireplaces Com

Heat Glo 6000gcf Ipi 36 Dv Gas Fireplace Parts Heatandgloparts Com

Heat Glo True 42 Indoor Gas Fireplace Black Glass Refractory Chadwicks S

Heat Glo Everest B Tall In The Wall Dv Gas Fireplace Parts Heatandgloparts Com

Heat Glo 6k

Heat Glo 6k Series Direct Vent Gas Fireplace Hechler S Mainstreet Hearth Home Troy Missouri

Heat Glo Escape Gas Fireplace Inserts Best Fire
Related Posts