Hearth Technologies Fireplace Parts: Understanding the Components for Optimal Performance
Hearth Technologies is a leading manufacturer of fireplaces and related heating appliances, providing a wide array of products under various brands. Maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of a Hearth Technologies fireplace requires understanding its constituent parts. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key components found within these fireplaces, focusing on their functionalities and importance in the overall heating system.
The complexity of a fireplace system varies depending on the type – gas, electric, or wood-burning. While the core principle of generating heat remains consistent, the specific parts involved differ significantly. This article will address components common across various Hearth Technologies fireplace models, as well as those specific to each fuel type.
Gas Fireplace Components: Ensuring Safe and Efficient Operation
Gas fireplaces offer convenience and efficiency, but rely on a complex system of parts to function safely and effectively. These components regulate gas flow, ignition, and flame characteristics, all critical for optimal performance.
One of the most critical components is the gas valve. This valve controls the flow of natural gas or propane into the fireplace. Modern gas valves are typically electronic, offering precise control over the gas pressure and flow rate. The valve is connected to a thermocouple or thermopile, which generates a small electrical current when heated by the pilot light. This current keeps the gas valve open, allowing gas to flow to the burner. If the pilot light goes out, the thermocouple cools down, cutting off the gas supply and preventing a dangerous buildup of unburned gas. Regular inspection and maintenance of the gas valve are crucial to ensure safe and reliable operation.
The burner is the component where the gas is actually combusted, producing the flames and heat. Burners come in various designs, including log sets, ribbon burners, and ceramic fiber burners. The design of the burner significantly affects the flame appearance and heat output. It's important to clean the burner regularly to remove any debris or soot that can obstruct the gas flow and alter the flame pattern. Blocked burners can lead to inefficient combustion and potentially dangerous carbon monoxide production.
The igniter is responsible for initiating the combustion process. In older models, a pilot light serves as a continuous flame source. However, many modern gas fireplaces employ electronic igniters, which use a spark or hot surface to ignite the gas. These igniters are more energy-efficient and safer than pilot lights, as they only use energy when the fireplace is in operation. If the igniter fails, the fireplace will not ignite, and troubleshooting the igniter system is often necessary.
A venting system is essential for safely expelling combustion byproducts from the fireplace. Gas fireplaces typically use direct vent or B-vent systems. Direct vent systems draw combustion air from outside the house and vent exhaust gases directly outside, creating a sealed system that prevents indoor air pollution. B-vent systems, on the other hand, rely on indoor air for combustion and vent exhaust gases through a chimney. Proper installation and maintenance of the venting system are crucial to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. Regular inspections should be conducted to ensure the vent is free of obstructions and properly sealed.
The glass door is a common feature on gas fireplaces, providing a barrier between the flames and the living space. The glass is typically tempered to withstand high temperatures. The glass door also helps to regulate the airflow and improve the efficiency of the fireplace. It is important to clean the glass regularly to maintain a clear view of the flames. Certain types of cleaners are specifically formulated for fireplace glass and should be used to avoid damaging the surface. Cracks or damage to the glass door require immediate replacement.
Electric Fireplace Components: Simplicity and Ease of Maintenance
Electric fireplaces offer a simpler alternative to gas and wood-burning fireplaces, requiring no venting or fuel supply. They primarily rely on electrical components to generate heat and simulate the appearance of flames.
The heating element is the core component responsible for generating heat in an electric fireplace. These elements are typically resistance coils that heat up when electricity passes through them. The heat is then circulated into the room by a fan. The wattage of the heating element determines the heat output of the fireplace. Over time, heating elements can degrade or burn out, requiring replacement.
The fan is crucial for distributing the heat generated by the heating element. It blows air across the heated coils, circulating warm air throughout the room. Regular cleaning of the fan is necessary to remove dust and debris that can impede airflow and reduce efficiency. A malfunctioning fan can lead to overheating and reduced heat output.
The flame effect generator is responsible for creating the visual illusion of flames. This can be achieved through various technologies, including rotating mirrors, LED lights, and holographic projections. The sophistication of the flame effect generator varies depending on the model. A failing flame effect generator will diminish the aesthetic appeal of the fireplace, and replacement may be necessary to restore the visual effects.
The control panel allows the user to adjust the heat output, flame intensity, and other settings. Modern electric fireplaces often feature remote controls for added convenience. The control panel may include buttons, switches, or a digital display. A malfunctioning control panel can limit the user's ability to adjust the fireplace settings and may require repair or replacement.
Wood-Burning Fireplace Components: Traditional Heat and Essential Safety Measures
Wood-burning fireplaces offer a classic and rustic heating experience, but also require a thorough understanding of their components and safety protocols.
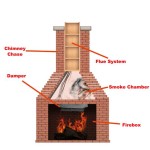
The firebox is the central chamber where wood is burned. It is constructed from heat-resistant materials such as firebrick or cast iron. The firebox must be properly insulated to prevent heat from escaping into the surrounding walls and potentially causing a fire hazard. Cracks or damage to the firebox require immediate repair to maintain its structural integrity and prevent heat transfer. Regular inspections are crucial to identify any signs of wear and tear.
The damper is a movable plate located in the chimney that controls the airflow through the fireplace. When the fireplace is in use, the damper should be fully open to allow smoke and exhaust gases to escape. When the fireplace is not in use, the damper should be closed to prevent drafts and heat loss. A malfunctioning damper can lead to inefficient combustion and potentially dangerous backdrafting of smoke into the room.
The chimney is a vertical structure that carries smoke and exhaust gases away from the fireplace. It is essential for maintaining proper draft and preventing smoke from entering the house. Regular cleaning of the chimney is crucial to remove creosote, a highly flammable byproduct of wood combustion. Creosote buildup can increase the risk of a chimney fire. Professional chimney sweeps should be hired to inspect and clean the chimney annually.
The grate is a metal structure that supports the wood within the firebox. It allows air to circulate around the wood, promoting more efficient combustion. The grate should be durable and heat-resistant to withstand the high temperatures within the firebox. A damaged or warped grate may need to be replaced to ensure proper airflow.
The fireplace screen is a protective barrier that prevents sparks and embers from escaping the firebox and potentially igniting nearby materials. It should be made of sturdy metal mesh and fit securely in front of the fireplace opening. A fireplace screen is an essential safety measure for preventing fire hazards.
In addition to these core components, Hearth Technologies fireplaces may incorporate decorative elements such as mantels, surrounds, and log sets. While these components do not directly affect the fireplace's heating performance, they contribute to its aesthetic appeal and overall design. Understanding the function and maintenance requirements of each component is essential for ensuring the safe, efficient, and long-lasting performance of a Hearth Technologies fireplace.

Service Parts Gbst4336i Hearth Amp Home Technologies

Astria Merit Plus Series Electric Fireplace Mpe 36 2 The Cozy Cabin Lennox Hearth Parts

Sl 750tv Ipi D Hearth Amp Home Technologies

Cb4842ir Hearth Amp Home Technologies

B Vent Gas Fireplace Slbv 40nm The Cozy Cabin Lennox Hearth Parts

Hearth Home Technologies Rcor Dv36in Direct Vent Gas Fireplace Owner S Manual

Drl6500 Series Direct Vent Gas Fireplace With Infini Flame Technology Drl6554ten The Cozy Cabin Lennox Hearth Parts

Hearth Home Technologies Brands

Direct Vent Gas Fireplace Drc3540dep The Cozy Cabin Lennox Hearth Parts

Hearth Home Technologies Brands