Gas Fireplace Vent Clearance To Combustibles In Georgia, USA
In Georgia, USA, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of gas fireplaces necessitates a thorough understanding and strict adherence to vent clearance regulations regarding combustible materials. These regulations are designed to prevent fires and carbon monoxide poisoning, safeguarding occupants and property. Compliance involves not only following manufacturer instructions but also being aware of relevant state and local building codes. Failure to adhere to these clearance requirements can result in hazardous conditions and legal repercussions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of gas fireplace vent clearance regulations in Georgia, focusing on key areas that homeowners and installers must understand.
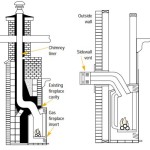
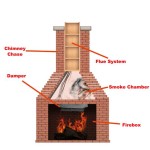
A "vent" in the context of gas fireplaces refers to the system designed to safely remove combustion byproducts, such as carbon monoxide, water vapor, and nitrogen oxides, from the living space and expel them into the atmosphere. These vents are typically constructed of metal materials, often aluminum or stainless steel, and are designed to withstand the heat and corrosive effects of flue gases. The specific type of venting required for a particular gas fireplace is determined by factors such as the fireplace's BTU input, the type of gas used (natural gas or propane), and the design of the fireplace itself. Common types of gas fireplace vents include: B-vent, direct vent and vent-free systems (although vent-free systems do not technically have a vent, their installation still requires adherence to specific safety guidelines related to clearances and ventilation).
The term "combustible materials" encompasses any material capable of igniting and burning. Common examples found in residential construction include wood framing, drywall, insulation, carpeting, curtains, furniture, and even some types of siding. The fire hazard presented by combustible materials is directly proportional to their proximity to heat sources, such as the surface of a gas fireplace vent. When combustible materials are placed too close to a vent, the radiant heat can cause them to gradually dry out and lower their ignition temperature, significantly increasing the risk of fire. This is why maintaining appropriate clearances is paramount.
Understanding the Importance of Vent Clearance
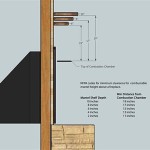
Vent clearance, in essence, dictates the minimum allowable distance between a gas fireplace vent and any combustible material. This distance is crucial because it mitigates the risk of fire caused by the radiant heat emitted from the vent during fireplace operation. Radiant heat is a form of energy that travels in waves and can heat objects from a distance. The amount of heat radiated by a gas fireplace vent depends on several factors, including the vent's surface temperature, the material it's made of, and the fireplace's heat output. When combustible materials are too close, they absorb this radiant heat, leading to a gradual increase in temperature. Over time, this can cause the material to reach its ignition point and ignite, potentially leading to a house fire. Proper vent clearance ensures that the radiant heat dissipates sufficiently before reaching any combustible surfaces, thereby preventing this dangerous scenario.
Beyond fire safety, maintaining adequate vent clearance is essential for the efficient and safe operation of the gas fireplace. Obstructed vents can impede the proper flow of combustion gases, leading to a build-up of carbon monoxide inside the home. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is highly toxic. Exposure to even small amounts can cause symptoms such as headache, dizziness, nausea, and confusion. In severe cases, carbon monoxide poisoning can be fatal. Proper vent clearance ensures that the combustion gases are properly exhausted from the home, preventing carbon monoxide build-up and protecting the health and safety of the occupants.
Furthermore, inadequate vent clearance can negatively impact the lifespan and performance of the gas fireplace itself. Excessive heat build-up around the vent can damage the vent material, leading to corrosion and deterioration over time. This can reduce the vent's effectiveness and increase the risk of leaks, further compromising safety. Overheating can also affect the fireplace's internal components, such as the gas valve and burner, potentially leading to malfunctions and costly repairs. By adhering to vent clearance requirements, homeowners can ensure the long-term reliability and efficiency of their gas fireplaces.
Key Regulations and Codes in Georgia
Georgia adheres to the International Residential Code (IRC), which provides comprehensive guidelines for building safety, including specific requirements for gas fireplace venting. Chapter 24 of the IRC addresses fuel gas provisions, which encompasses the installation and venting of gas appliances, including fireplaces. This chapter outlines the specific requirements for vent materials, sizing, termination, and clearances to combustibles. It is crucial to consult the latest version of the IRC as adopted by the state of Georgia, as amendments or modifications may exist. Local jurisdictions within Georgia may also have their own specific building codes and amendments that are stricter than the state-level IRC. These local ordinances often address specific concerns related to the unique characteristics of the region, such as high wind zones or areas prone to seismic activity. Therefore, it is essential to check with the local building department or fire marshal to determine the applicable regulations in your specific area.
Manufacturers play a significant role in determining vent clearance requirements. Every gas fireplace is designed with specific venting requirements based on its BTU rating, fuel type, and venting system design. The manufacturer's installation instructions provide detailed guidelines for proper vent installation, including the required clearances to combustibles. These instructions are considered an integral part of the appliance's listing and must be followed meticulously to ensure safe and compliant operation. In many cases, the manufacturer's recommended clearances will be stricter than the minimum requirements outlined in the IRC or local building codes. In such instances, the more stringent requirements must be followed. Installers and homeowners should always prioritize the manufacturer's instructions to ensure the fireplace is installed correctly and safely.
The vent type significantly influences the required clearances. Different types of gas fireplace vents have different radiating characteristics and require different clearance distances. B-vent, for instance, is commonly used for natural-draft gas fireplaces and typically requires greater clearances than direct vent systems. Direct vent systems are designed with two concentric pipes: one for intake air and one for exhaust gases. This design allows for closer clearances to combustibles compared to B-vent systems. Vent-free gas fireplaces, while not technically having a vent, require careful consideration of surrounding materials and ventilation within the room to ensure safe operation. The specific clearance requirements for each vent type are outlined in the IRC, the manufacturer's instructions, and any applicable local codes. Failure to use the correct vent type for the appliance and to adhere to the corresponding clearance requirements can create a significant fire hazard.
Practical Considerations for Compliance
Before installing a gas fireplace, it is crucial to carefully assess the surrounding area for combustible materials. This includes walls, ceilings, floors, framing members, insulation, and any decorative elements within the vicinity of the planned vent path. Pay particular attention to hidden combustibles, such as wiring or plumbing that may be concealed within walls or ceilings. If combustible materials are present within the required clearance zone, they must be either removed or adequately protected. Protection methods may include installing non-combustible shielding materials, such as metal or cement board, between the vent and the combustible material. The shielding material must be properly sized and installed to effectively block radiant heat transfer.
Proper shielding is critical when combustible materials cannot be removed. Shielding materials should be non-combustible and have a thermal resistance sufficient to prevent the combustible material from reaching its ignition temperature. Common shielding materials include sheet metal, cement board, and mineral wool insulation. The shielding must be installed with an air gap between the vent and the shielding material to allow for air circulation and further reduce heat transfer. The size and extent of the shielding must be sufficient to cover the entire area where the combustible material is within the required clearance zone. It is essential to consult the manufacturer's instructions and the IRC for specific requirements regarding shielding materials and installation techniques.
Regular inspections are vital for maintaining safety and compliance. Inspect the vent system regularly for any signs of damage, corrosion, or deterioration. Check for loose connections, gaps, or cracks in the vent pipes. Ensure that the clearances to combustibles remain intact and that no new combustible materials have been placed within the clearance zone. It is also important to have the gas fireplace professionally inspected and serviced annually by a qualified technician. The technician can assess the condition of the vent system, clean any debris buildup, and ensure that the fireplace is operating safely and efficiently. Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify and address potential problems before they escalate into serious hazards.
Furthermore, homeowner education plays a crucial role in fire safety. Homeowners should be educated on the proper operation of their gas fireplace, including the importance of maintaining vent clearances and avoiding the placement of combustible materials near the vent. They should also be instructed on how to recognize the signs of carbon monoxide poisoning and what to do in case of a suspected leak. Providing homeowners with clear and concise information about gas fireplace safety can empower them to take proactive steps to protect themselves and their families. Resources such as user manuals, informational brochures, and online tutorials can be valuable tools for educating homeowners about gas fireplace safety.

Chapter 10 Chimneys And Fireplaces Georgia State Minimum Standard One Two Family Dwelling Code 2024 Upcodes
Venting What Type Do You Need Heatilator

2024 International Fuel Gas Code Ifgc Chapter 5 Chimneys And Vents 503 8 Venting System Terminal Clearances

What Are The Best Ways To Vent A Gas Fireplace Zoroast

What Are The Best Ways To Vent A Gas Fireplace Zoroast

Fireplace Venting What Homeowners Need To Know
Install Document Template

Dri2027 27 Inch Direct Vent Gas Fireplace Insert By Superior

High Definition 35 Direct Vent Gas Fireplace

Fireplace Venting What Homeowners Need To Know
Related Posts