Gas Fireplace Vent Clearance to Combustibles: A Comprehensive Guide
Gas fireplaces offer a convenient and aesthetically pleasing heating solution for homes. However, their safe operation hinges on proper installation, particularly concerning vent clearances to combustible materials. Understanding and adhering to these clearances is crucial to prevent fires and ensure the long-term safety of a home and its occupants. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and managing vent clearance requirements for gas fireplaces.
Combustible materials refer to any substance capable of igniting and burning. This includes common building materials such as wood, drywall, framing lumber, insulation, fabrics, and even some types of plastics. When a gas fireplace is in operation, its vent system generates significant heat, which, if in close proximity to combustible materials, can raise their temperature to the point of ignition. This creates a fire hazard that can quickly escalate and cause significant damage.
Failure to comply with vent clearance regulations can have severe consequences, including property damage, injury, and even loss of life. Insurance companies may deny claims related to fires caused by improper fireplace installation, leaving homeowners financially responsible for the damages. Moreover, local building codes often mandate specific clearances, and failure to meet these requirements can result in fines and legal action. Ensuring proper clearances is therefore not just a matter of safety but also of legal compliance and financial responsibility.
Several factors influence the required vent clearance to combustibles, including the type of vent system, the fireplace model, and local building codes. It is essential to consult the manufacturer's installation instructions and local building codes to determine the specific clearance requirements for the chosen gas fireplace. These requirements are typically provided in detail and should be followed meticulously during installation.
Understanding Different Types of Vent Systems
Gas fireplaces utilize various types of vent systems, each with its own set of clearance requirements. The most common types of vent systems include:
B-Vent: B-vent systems are double-walled metal pipes designed primarily for venting natural gas appliances. They are typically used for appliances with lower operating temperatures. B-vent systems require specific clearances from combustible materials, generally ranging from 1 to 6 inches, depending on the manufacturer's specifications and local codes. It is crucial to maintain these clearances throughout the entire length of the vent system, including any elbows or transitions.
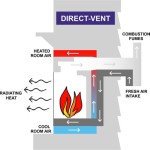
Direct Vent: Direct vent systems are sealed systems that draw combustion air from outside the home and exhaust combustion products directly to the outside. This type of system is generally considered safer than B-vent because it eliminates the need for indoor air for combustion and reduces the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Direct vent systems typically require tighter clearances to combustibles compared to B-vent systems, sometimes allowing for zero clearance in specific areas, provided the manufacturer's instructions are strictly followed.
Vent-Free: Vent-free fireplaces, also known as ventless fireplaces, do not require any venting system. They burn gas very efficiently and release combustion products directly into the room. While they are convenient, vent-free fireplaces are subject to strict regulations and are often prohibited in certain jurisdictions due to concerns about indoor air quality and carbon monoxide accumulation. Even though they lack a vent, clearances around the fireplace unit itself must still be adhered to, as the unit itself generates heat.
L-Vent: L-Vent systems are designed for appliances that burn oil or certain types of gas and operate at lower temperatures than appliances requiring B-Vent. However, their use is less common for modern gas fireplaces. Clearances for L-Vent systems must adhere to manufacturer's instructions and local building codes.
The selection of the appropriate vent system depends on the specific gas fireplace model, the building's construction, and local codes. Always consult with a qualified HVAC professional or gas fireplace installer to determine the most suitable vent system for a particular situation.
Determining the Required Clearance to Combustibles
The process of determining the required clearance to combustibles involves several steps. Ignoring any of these steps can create a potential safety hazard.
Consult Manufacturer's Instructions: The manufacturer's installation manual is the primary source of information regarding vent clearance requirements. This manual provides detailed diagrams and specifications indicating the minimum distances that must be maintained between the vent system and combustible materials. It is important to read and understand the entire manual before commencing any installation work. The manual will specify the clearance requirements for different sections of the vent, as clearances may vary depending on the proximity to the fireplace unit or the type of vent component (e.g., pipe section, elbow, or termination cap).
Review Local Building Codes: Local building codes often supplement or modify the manufacturer's recommendations. These codes may impose stricter clearance requirements based on local climate conditions, building practices, or other factors. It is essential to contact the local building department or consult with a qualified inspector to determine the applicable building codes and ensure compliance.
Identify Combustible Materials: Carefully assess the surrounding area where the vent system will be installed and identify all combustible materials. This includes not only visible materials such as wood framing and drywall but also hidden materials such as insulation and wiring. Ensure that these materials are adequately protected from the heat generated by the vent system.
Measure and Document Clearances: Use a measuring tape or laser distance meter to accurately measure the distances between the vent system and all combustible materials. Document these measurements and create a record for future reference. This documentation can be helpful during inspections or when performing maintenance on the fireplace system.
Use Approved Shielding: In some cases, it may be difficult to achieve the required clearances due to space constraints or other limitations. In these situations, it may be possible to use approved shielding materials to reduce the clearance requirements. Shielding materials, such as non-combustible insulation or metal heat shields, can create a barrier between the vent system and combustible materials, reducing the risk of ignition. The use of shielding materials must be approved by the manufacturer and comply with local building codes.
When using shielding, ensure it is properly installed and ventilated to prevent heat buildup. The shielding should extend beyond the vent system in all directions and be securely fastened to prevent movement. Regular inspection of the shielding is necessary to ensure it remains in good condition and continues to provide adequate protection.
Ensuring Proper Installation and Maintenance
Even with a thorough understanding of vent clearance requirements, proper installation and ongoing maintenance are critical to maintaining safety. Neglecting these aspects can compromise the integrity of the vent system and increase the risk of fire.
Professional Installation: It is strongly recommended that a qualified HVAC professional or gas fireplace installer perform the installation of the vent system. These professionals have the knowledge, skills, and experience to ensure that the installation is performed correctly and in compliance with all applicable codes and regulations. A professional installation also provides peace of mind, knowing that the system has been properly installed and tested.
Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections of the vent system to identify any potential problems, such as corrosion, damage, or obstructions. Look for signs of heat damage to surrounding materials, such as discoloration, charring, or warping. Inspect the vent system for leaks or gaps, which can allow combustion gases to escape into the home. Regular inspections should be conducted at least annually or more frequently if the fireplace is used extensively.
Proper Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance on the vent system to keep it in good working order. This includes cleaning the vent system to remove any debris or obstructions, such as bird nests or leaves. Check the connections between vent sections to ensure they are secure and airtight. Replace any damaged or worn components promptly. Proper maintenance not only ensures the safe operation of the fireplace but also extends the lifespan of the vent system.
Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Install carbon monoxide detectors in the home, particularly near sleeping areas, to provide an early warning of any carbon monoxide leaks. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that can be deadly if inhaled. Ensure that the detectors are properly installed and tested regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly. Replace the batteries in the detectors as recommended by the manufacturer.
Avoid Obstructions: Never obstruct the vent system or block the airflow around the fireplace. Avoid storing combustible materials near the fireplace or vent system. Keep the area around the fireplace clear of clutter and debris. Ensure that furniture, curtains, and other objects are kept at a safe distance from the fireplace and vent system. Obstructions can impede the flow of air and increase the risk of overheating or fire.
By adhering to these guidelines and consulting with qualified professionals, homeowners can ensure the safe and efficient operation of their gas fireplaces and protect their homes from the risk of fire.
Gas Fireplace Venting Explained Heat Glo
Venting

2024 International Fuel Gas Code Ifgc Chapter 5 Chimneys And Vents 503 8 Venting System Terminal Clearances
Venting

Combustibles Clearance Behind A Fireplace Greenbuildingadvisor

What Are The Best Ways To Vent A Gas Fireplace Zoroast

Valor Fireplace Portrait

Fireplace Chimney Clearances Information Canadian
Install Document Template

Empire Power Vent For Direct Gas Fireplaces
Related Posts