Gas Fireplace Repair Parts: A Comprehensive Guide
Gas fireplaces offer a convenient and aesthetically pleasing alternative to traditional wood-burning fireplaces. However, like any appliance, they require regular maintenance and occasional repairs. Understanding the various components that make up a gas fireplace and recognizing the signs of wear and tear is crucial for ensuring its safe and efficient operation. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common gas fireplace repair parts, potential issues, and essential maintenance practices.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Gas Fireplace
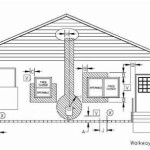
A gas fireplace is a complex system comprised of numerous interconnected components. These parts work in concert to deliver a controlled and consistent flame, providing both heat and ambiance. A thorough understanding of these components is essential for effective troubleshooting and repair.
The primary components of a gas fireplace include:
*Gas Valve:
The gas valve is the heart of the fireplace, controlling the flow of gas to the burner. It is typically an electrically operated valve that opens when signaled by the thermostat or control system. Malfunctions can result in no gas flow, inconsistent gas flow, or gas leakage. *Pilot Assembly:
The pilot assembly houses the pilot light, a small, continuously burning flame that ignites the main burner. It includes the pilot burner, thermocouple or thermopile, and igniter. A faulty pilot assembly can prevent the pilot light from staying lit, hindering the fireplace's ability to operate. *Burner:
The burner is the component responsible for producing the main flame. It is a metal tube or grate with numerous small holes through which gas flows and is ignited. Burner problems can result in uneven flames, insufficient heat output, or sooting. *Thermocouple/Thermopile:
These are safety devices that monitor the pilot flame. The thermocouple generates a small electrical current when heated by the pilot flame, which keeps the gas valve open. The thermopile generates a larger current that can power the entire gas valve. If the pilot flame goes out, the thermocouple or thermopile cools down, shutting off the gas supply to prevent gas leakage. *Igniter:
The igniter is used to light the pilot light. Modern fireplaces typically use electronic igniters, which produce a spark to ignite the gas. Older fireplaces may use a piezoelectric igniter, which generates a spark when a button is pressed. *Gas Lines and Fittings:
These components carry gas from the main gas supply to the gas valve and burner. Leaks in gas lines or loose fittings can pose a significant safety hazard and require immediate attention. *Vent System:
The vent system removes combustion byproducts from the fireplace and vents them outside the home. Proper venting is essential for preventing carbon monoxide poisoning. *Control Module/Board:
This electronic component controls the operation of the fireplace, including the gas valve, igniter, and blower. It receives signals from the thermostat or remote control and activates the appropriate components. *Blower (Optional):
Some gas fireplaces include a blower that circulates heated air into the room. The blower is typically a small fan powered by an electric motor. *Decorative Logs/Media:
These components are primarily aesthetic, designed to resemble real wood logs or other decorative materials like glass beads or stones. They do not directly contribute to the fireplace's functionality, but they can affect the flame pattern and heat distribution.Common Gas Fireplace Problems and Relevant Repair Parts
Several common issues can arise with gas fireplaces, necessitating the replacement of specific repair parts. Recognizing these problems early can prevent more significant damage and ensure the safe operation of the fireplace.
*Pilot Light Won't Stay Lit:
This is a frequent problem often attributed to a faulty thermocouple or thermopile. Over time, these components can degrade and fail to produce sufficient electrical current to keep the gas valve open. Replacement of the thermocouple or thermopile is typically the solution. Another possible cause is a dirty pilot orifice, which can be cleaned with a small wire or needle. *No Flame or Weak Flame:
A lack of flame or a weak flame can indicate a problem with the gas valve. The gas valve may be failing to open fully or may be clogged with debris. Replacement of the gas valve is often necessary. A clogged burner can also cause a weak or uneven flame. Cleaning the burner ports with a wire brush can often resolve this issue. *Gas Odor:
A gas odor is a serious safety concern requiring immediate attention. It may indicate a gas leak in the gas lines, fittings, or gas valve. Turn off the gas supply to the fireplace and contact a qualified gas technician to inspect and repair the system. Leak detection solutions can pinpoint the source of the leak, and replacement of the faulty component, such as a gas line or fitting, is essential. *Blower Not Working:
If the blower fails to operate, it may be due to a faulty motor or a damaged control module. Check the blower motor for any signs of damage or overheating. If the motor is faulty, it will need to be replaced. A malfunctioning control module can also prevent the blower from operating. Replacing the control module may be necessary. *Sooting:
Excessive sooting, or the accumulation of black carbon deposits, can indicate incomplete combustion. This is often caused by a blocked vent system, a dirty burner, or an improper air-to-gas ratio. Cleaning the burner and vent system can often resolve the problem. In some cases, adjusting the air shutter on the burner may be necessary to achieve the correct air-to-gas ratio. *Electronic Ignition Failure:
Electronic igniters can fail over time, preventing the pilot light from igniting. If the igniter is not producing a spark, it will need to be replaced. *Cracked or Damaged Logs/Media:
While primarily aesthetic, cracked or damaged logs can affect flame patterns and heat distribution. Replacement with compatible logs or media is necessary to maintain optimal performance and appearance.Essential Maintenance Practices for Longevity
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of a gas fireplace and ensuring its safe and efficient operation. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs and potentially dangerous situations.
*Annual Inspection:
A qualified gas technician should inspect the fireplace annually. The technician will inspect the gas lines, burner, vent system, and control system, ensuring all components are functioning correctly and safely. *Cleaning the Burner and Pilot Assembly:
The burner and pilot assembly should be cleaned regularly to remove dust, debris, and soot. Use a soft brush or vacuum cleaner to remove any buildup. A small wire or needle can be used to clean the pilot orifice. *Checking the Vent System:
The vent system should be inspected regularly for any obstructions or damage. Clear any debris from the vent outlet to ensure proper ventilation. *Replacing Batteries:
If the fireplace uses batteries for the remote control or control module, replace them regularly to ensure proper operation. *Inspecting Gas Lines and Fittings:
Regularly inspect gas lines and fittings for any signs of leaks or corrosion. Use a leak detection solution to check for leaks. *Cleaning the Glass Door:
The glass door should be cleaned regularly to remove soot and dust. Use a fireplace glass cleaner specifically designed for this purpose. *Following Manufacturer's Instructions:
Always follow the manufacturer's instructions for operation and maintenance. The manufacturer's manual provides specific recommendations for your fireplace model.When sourcing gas fireplace repair parts, it is crucial to opt for components specifically designed for the model and brand of the fireplace. Using generic or incompatible parts can lead to performance issues and safety hazards. Reputable suppliers specializing in fireplace components often provide detailed compatibility information and expert assistance.
Furthermore, safety should be paramount when undertaking any gas fireplace repair. If unsure about any aspect of the repair process, engaging a qualified gas technician is highly recommended. Working with gas appliances requires specific knowledge and expertise, and improper repairs can result in gas leaks, explosions, or carbon monoxide poisoning. Properly functioning repair parts combined with adequate maintenance practices will ensure the longevity and operability of the gas fireplace.

A Plus Inc Superior B800 Replacement Parts And Accessories

A Plus Inc Lennox Superior Marco Majestic Peterson

Gas Fireplace Natural Bdm35 The Cozy Cabin Lennox Hearth Parts

A Plus Inc Superior Vf 4000 Replacement Parts Accessoreis

A Plus Inc Lennox Edv4540 Replacement Pants And Accessories

A Plus Inc Lennox Ebvst Replacement Parts And Accessories

A Plus Inc Lennox Ebcr Replacement Parts And Accessories

A Plus Inc Superior Vf 5000 Replacement Parts Accessoreis

Majestic 36ldvr Ldvr Series Direct Vent Gas Fireplace Ereplacementparts Com

Cgcftn Fireplace Parts For Desa Comfortglow Partsfor Com
Related Posts