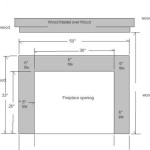
Gas Fireplace Insert Clearance To Combustibles Requirements
Gas fireplace inserts offer a convenient and efficient way to add warmth and ambiance to a home. They are designed to fit within existing masonry or prefabricated fireplace openings, providing a modern alternative to traditional wood-burning fireplaces. However, the installation of a gas fireplace insert requires careful attention to safety regulations, particularly regarding clearances to combustible materials. Failure to adhere to these requirements can lead to fire hazards, property damage, and potential injury.
Clearance to combustibles refers to the minimum distance required between the gas fireplace insert and any surrounding materials that can ignite and burn, such as wood framing, drywall, mantels, furniture, and even certain types of flooring. These clearances are specified by the manufacturer of the fireplace insert and are based on rigorous testing to ensure safe operation. Understanding and complying with these clearance requirements is paramount for a safe and code-compliant installation. This article will delve into the key aspects of gas fireplace insert clearance to combustibles, providing a comprehensive overview of the applicable standards and best practices.
Understanding Combustible Materials
The first step in ensuring a safe installation is understanding what constitutes a combustible material. Essentially, any material that can ignite and sustain a flame is considered combustible. Common examples in residential construction include wood framing, plywood, drywall, particleboard, paneling, wallpaper, fabrics, carpeting, furniture, and even certain types of insulation. The flammability of a material can vary depending on its composition, density, and moisture content. For instance, seasoned hardwood is more difficult to ignite than lightweight pine.
It's important to note that some materials, while not readily flammable, can still contribute to a fire hazard if placed too close to a heat source. These materials may smolder or char, eventually igniting or releasing toxic fumes. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain adequate clearances even for materials that might not seem immediately flammable. Furthermore, decorative items placed near the fireplace, such as candles, picture frames, and holiday decorations, are often made of combustible materials and should be kept well away from the heat source.
The manufacturer's installation manual will typically provide a detailed list of materials considered combustible in relation to their specific fireplace insert model. It is crucial to carefully review this list and identify any potential hazards in the surrounding area. In cases of uncertainty, it is always best to err on the side of caution and maintain a greater clearance distance.
Manufacturer's Specifications and Local Codes
The most critical source of information regarding clearance to combustibles is the manufacturer's installation manual for the specific gas fireplace insert being installed. This manual will contain detailed diagrams and instructions outlining the minimum clearances required for various components of the fireplace insert, such as the firebox, venting system, and facing materials. These specifications are based on rigorous testing conducted by independent laboratories to ensure that the fireplace insert operates safely under various conditions.
It is imperative to follow the manufacturer's instructions precisely. Deviations from these specifications can compromise the safety of the installation and potentially void the warranty. The manual will typically specify different clearance requirements for different sides of the fireplace insert, as well as for different types of combustible materials. For example, the clearance to the side walls may be different from the clearance to the mantel above the fireplace. The manual may also specify different clearances depending on the type of venting system used.
In addition to the manufacturer's specifications, local building codes and regulations also play a significant role in determining clearance requirements. These codes are designed to ensure the safety of buildings and their occupants, and they may impose stricter clearance requirements than those specified by the manufacturer. It is the responsibility of the installer to be familiar with and comply with all applicable local codes. A qualified building inspector can provide guidance on local code requirements and ensure that the installation is compliant.
Often, local codes will reference national standards such as those published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) or the International Code Council (ICC). These standards provide comprehensive guidance on the safe installation of gas appliances and may include specific requirements for clearance to combustibles. Consulting with a qualified professional, such as a licensed gas fitter or a building inspector, is highly recommended to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
Factors Affecting Clearance Requirements
Several factors can influence the clearance to combustibles requirements for a gas fireplace insert. These factors include the heat output of the fireplace insert, the type of venting system used, the type of combustible materials present, and the design and construction of the surrounding area.
The heat output of the fireplace insert, measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs), is a primary determinant of clearance requirements. Higher BTU ratings typically require greater clearances to combustible materials due to the increased heat generated. The manufacturer's installation manual will specify the clearance requirements for the specific BTU rating of the fireplace insert.
The type of venting system used also affects clearance requirements. Gas fireplace inserts can be vented in several ways, including direct vent, B-vent, and conventional vent systems. Direct vent systems draw combustion air from outside the building and exhaust flue gases directly to the outside, typically requiring less clearance than B-vent or conventional vent systems. The venting system must be installed according to the manufacturer's instructions to ensure proper operation and safety.
The specific type of combustible material present also influences clearance requirements. Some materials are more readily flammable than others and may require greater clearances. For example, a wood mantel above the fireplace may require a greater clearance than drywall. The manufacturer's installation manual will typically provide specific clearance requirements for different types of combustible materials.
Finally, the design and construction of the surrounding area can also affect clearance requirements. For example, if the fireplace insert is recessed into a wall, the clearance to the surrounding wall studs may need to be increased to prevent overheating. Similarly, if the fireplace insert is located near a corner, the clearance to the corner walls may need to be adjusted. It is crucial to carefully consider the specific design and construction of the surrounding area when determining clearance requirements.
Proper ventilation around the fireplace insert is also crucial for maintaining safe operating temperatures. Adequate airflow helps to dissipate heat and prevent the buildup of excessive temperatures near combustible materials. The manufacturer's installation manual will typically specify ventilation requirements for the fireplace insert.
Addressing Reduced Clearance Options
In some situations, meeting the standard clearance requirements may be challenging due to space limitations or design constraints. In these cases, it may be possible to use approved methods to reduce the clearance to combustibles. However, it is crucial to understand that these methods must be implemented correctly and in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions and local codes.
One common method for reducing clearance is to use a heat shield. Heat shields are non-combustible barriers that are installed between the fireplace insert and the combustible materials. They are designed to deflect heat away from the combustibles and reduce the surface temperature of the materials. Heat shields must be approved for use with the specific fireplace insert and must be installed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Another method for reducing clearance is to use a non-combustible facing material. Non-combustible facing materials, such as brick, stone, or tile, can be installed directly against the fireplace insert without requiring a clearance. However, it is important to ensure that the facing material is properly installed and that it does not trap heat behind it.
Another technique involves creating an air space between the fireplace insert and the combustible material. This air space allows for convective cooling, reducing the surface temperature of the combustible material. The air space must be properly ventilated to ensure adequate airflow. The size and configuration of the air space will be specified by the manufacturer of the fireplace insert.
It's important to note that reducing clearance to combustibles requires careful planning and execution. It is highly recommended to consult with a qualified professional to ensure that the chosen method is appropriate for the specific situation and that it is implemented correctly. Building inspectors will also require documentation and proof that the reduced clearances meet code requirements. Unauthorized or improperly installed clearance reduction methods can compromise the safety of the installation and potentially lead to fire hazards.
Inspection and Maintenance
Once the gas fireplace insert is installed, it is crucial to have it inspected by a qualified professional to ensure that it is operating safely and that all clearance requirements have been met. The inspector will examine the installation to verify that the fireplace insert is properly vented, that the gas connections are secure, and that the clearances to combustibles are adequate. The inspector will also check for any potential hazards, such as leaks or obstructions in the venting system.
Regular maintenance is also essential for ensuring the continued safe operation of the gas fireplace insert. The manufacturer's installation manual will provide a recommended maintenance schedule. This schedule may include tasks such as cleaning the burner, inspecting the venting system, and checking the gas connections. It is important to follow this schedule diligently to prevent problems from developing.
Homeowners should also be vigilant in monitoring the operation of the gas fireplace insert. If any unusual odors, noises, or flames are observed, the fireplace insert should be immediately turned off and a qualified professional should be contacted. It is also important to keep the area around the fireplace insert clear of combustible materials, such as furniture, curtains, and decorations.
A carbon monoxide detector should be installed in the vicinity of the gas fireplace insert to provide early warning of any potential carbon monoxide leaks. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that can be deadly. Regular inspections and maintenance, along with the use of a carbon monoxide detector, can help to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
Furthermore, ensure that anyone using the gas fireplace insert is familiar with its operation and safety features. Provide clear instructions on how to light the fireplace insert, how to adjust the flame, and how to turn it off in case of an emergency. This knowledge will help to ensure the safe and enjoyable use of the gas fireplace insert for years to come.

Fireplace Construction

Gas Fireplace Insert How To Choose For The French Country Mantel

Mantel Clearance For Masonry Versus Manufactured Fireplaces

Fireplace Chimney Clearances Information Canadian

Gas Fireplace Insert How To Choose For The French Country Mantel

How Fireplace Inserts Work We Love Fire

Fireplace Safety And Codes

Gas Fireplace Insert How To Choose For The French Country Mantel
Gas Fireplace Venting Explained Heat Glo

Advice For Gas Fireplaces Inserts Logs We Love Fire
Related Posts