Gas Burning Stove Fireplaces: An Overview
Gas burning stove fireplaces represent a popular heating alternative and aesthetic addition to residential and commercial spaces. They offer a blend of visual appeal reminiscent of traditional wood-burning stoves with the convenience and efficiency of gas fuel. Understanding the functionality, benefits, types, and maintenance aspects of these appliances is crucial for informed decision-making.
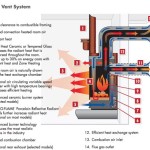
A gas burning stove fireplace operates by combusting natural gas or propane within a sealed firebox. This firebox typically contains ceramic logs or other decorative media designed to replicate the look of a real wood fire. The combustion process generates heat, which is then distributed into the room through convection, radiation, or a combination of both. The stove is connected to a venting system that safely exhausts combustion byproducts, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor, to the outside.
The ignition system of a gas stove fireplace can vary. Older models often rely on a pilot light, a continuously burning small flame that ignites the main burner when needed. Modern stoves commonly use electronic ignition systems, which employ a spark to ignite the gas, eliminating the need for a standing pilot light and potentially saving on fuel costs. Thermostats or remote controls allow for precise temperature regulation, enhancing user convenience and energy efficiency.
Gas stove fireplaces offer various advantages over traditional wood-burning fireplaces. They eliminate the need for wood storage, chopping, and handling. They produce significantly less particulate matter and smoke, contributing to cleaner air quality both indoors and outdoors. The ease of starting and stopping the fire, along with precise temperature control, provides added convenience and safety.
While gas stove fireplaces offer several benefits, responsible operation and regular maintenance are crucial for safe and efficient performance. Improper installation or maintenance can lead to gas leaks, carbon monoxide poisoning, and fire hazards. Proper ventilation is essential to ensure the safe removal of combustion gases.
Key Advantages of Gas Burning Stove Fireplaces
One of the most significant advantages of a gas burning stove fireplace is its ease of use and convenience. Unlike wood-burning fireplaces, which require manual loading and tending to the fire, gas stoves can be ignited and extinguished with the flip of a switch or the press of a button. This level of automation allows for effortless temperature control and eliminates the need for constant monitoring. The absence of wood handling also contributes to a cleaner and more convenient heating experience.
Energy efficiency is another key benefit. Modern gas stoves are designed with advanced combustion technology and heat exchange systems, resulting in higher thermal efficiency compared to traditional wood-burning fireplaces. The ability to precisely control the flame height and heat output allows for optimized energy consumption and reduced heating costs. Many gas stoves also feature thermostats or remote controls, enabling users to program desired temperatures and further improve energy efficiency.
Furthermore, gas burning stove fireplaces offer significant environmental advantages. They produce far fewer emissions than wood-burning fireplaces, contributing to improved air quality both indoors and outdoors. The combustion of natural gas or propane generates significantly less particulate matter, smoke, and other pollutants, reducing the risk of respiratory problems and other health issues. By opting for a gas stove fireplace, homeowners can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Types of Gas Burning Stove Fireplaces
Direct vent gas stove fireplaces are sealed combustion systems that draw combustion air from outside the home and vent exhaust gases directly outside through a dedicated vent pipe. This type of stove offers the highest level of safety and efficiency, as it eliminates the risk of backdrafting and prevents indoor air pollution. Direct vent stoves are typically more expensive than other types of gas stoves but offer superior performance and safety features.
Vent-free gas stove fireplaces, also known as ventless stoves, do not require a chimney or vent. They burn gas very cleanly, producing minimal combustion byproducts that are released directly into the room. However, vent-free stoves are subject to certain regulations and restrictions due to concerns about indoor air quality. It is essential to ensure adequate ventilation in the room where a vent-free stove is installed and to follow all manufacturer's instructions for safe operation.
B-vent gas stove fireplaces rely on an existing chimney or flue to vent combustion gases. They draw combustion air from the room and vent exhaust gases up the chimney. B-vent stoves are an option for homes with existing chimneys, but they require careful installation and inspection to ensure proper venting and prevent backdrafting. They are generally less efficient than direct vent stoves due to heat loss through the chimney.
Maintaining a Gas Burning Stove Fireplace
Regular inspection and cleaning are essential for maintaining the safe and efficient operation of a gas burning stove fireplace. At least annually, a qualified technician should inspect the stove's components, including the burner, gas lines, venting system, and control mechanisms. The technician should also check for gas leaks and carbon monoxide emissions.
Cleaning the burner and decorative logs or media is important for maintaining optimal performance and visual appeal. Dust and debris can accumulate on these components, affecting the flame quality and heat output. The logs or media can be carefully removed and cleaned with a soft brush or vacuum cleaner. The burner should be cleaned with a specialized gas appliance cleaner to remove any deposits or corrosion.
The venting system should be inspected regularly for obstructions or damage. Birds' nests, leaves, and other debris can block the vent, preventing proper exhaust of combustion gases. Any obstructions should be removed promptly. The vent pipe should be inspected for corrosion, cracks, or leaks. Damaged vent pipes should be replaced immediately to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.

Huntingdon 30 Gas Stoves Gazco Traditional

Freestanding Gas Burning Stoves Sierra Hearth And Home

Gas Burning Stove Installation Service Provider More In Wi

Free Standing Gas Fireplace Stoves For 30 On Now

Rais Gabo Gas Ii Stove For

Gas Stoves Made In Usa Lopi

Gas Stoves Fireplace And Stove The Hearth Doctor Inc

Benefits Popularity Of Gas Fireplaces Stoves And Fireplace Inserts

Stoves Wood Gas And Pellet Sierra Hearth Home

Guide To Gas Stoves Direct
Related Posts