Fireplace Refractory Panel Repair: A Comprehensive Guide
Fireplaces, whether wood-burning or fueled by gas, offer warmth and ambiance to a dwelling. However, the intense heat generated during operation places significant stress on the internal components, particularly the refractory panels. These panels, also known as firebricks or fireboards, line the firebox and are crucial for protecting the surrounding structure from excessive heat. Understanding the function of refractory panels, the causes of their deterioration, and the methods for their repair are essential for maintaining a safe and efficient fireplace.
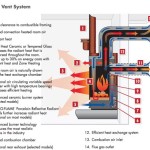
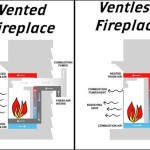
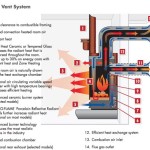
Refractory panels are specifically designed to withstand high temperatures without degrading or cracking. They are typically constructed from materials such as fireclay, vermiculite, or ceramic fiber. These materials possess excellent thermal resistance, preventing heat from transferring to the adjacent walls and chimney. Without functional refractory panels, the structural integrity of the fireplace and the surrounding building could be compromised, potentially leading to fires or other hazards. Furthermore, damaged panels reduce the fireplace's efficiency, causing heat loss and increased fuel consumption. Therefore, timely repair or replacement of these panels is paramount.
The lifespan of refractory panels varies depending on several factors, including the frequency of use, the type of fuel burned, and the quality of the materials used. Regular inspection is recommended to identify any signs of damage early on and prevent more extensive and costly repairs.
Identifying Damage to Refractory Panels
Recognizing the signs of damage to refractory panels is the first step in initiating the repair process. Several indicators suggest that panels may require attention. Cracks are a common sign of thermal stress. While hairline cracks may not immediately necessitate replacement, larger cracks or those that are widening over time indicate a weakening of the panel's structure. Crumbling or spalling, where pieces of the panel break off, is another significant sign of deterioration. This indicates that the panel is losing its structural integrity and its ability to effectively insulate the fireplace. Discoloration, such as excessive darkening or the appearance of white deposits (efflorescence), can also signify problems. Darkening might indicate soot buildup penetrating the panel, while efflorescence can suggest moisture intrusion which can weaken the panel. Warping or bulging of the panels is another indicator of heat-induced stress and necessitates immediate attention. Finally, if any panels are loose or have fallen out of place, they must be properly reinstalled or replaced to maintain the fireplace's safety and efficiency.
A thorough visual inspection, ideally performed annually before the heating season, is crucial. This inspection should include carefully examining all surfaces of the refractory panels for cracks, crumbling, discoloration, and any other signs of wear. A flashlight can be helpful for illuminating hard-to-reach areas. Any observed damage should be documented, including photographs, to track its progression over time. If the damage is extensive or if there is any uncertainty about the severity of the problem, consulting a qualified chimney sweep or fireplace professional is recommended.
In addition to visual inspection, other factors can contribute to the premature degradation of refractory panels. Overfiring the fireplace, burning inappropriate fuels (such as treated wood or trash), and allowing moisture to penetrate the firebox can all shorten the lifespan of the panels. Proper fireplace operation and maintenance are crucial for preserving the integrity of the refractory lining. The use of a fireplace grate can help promote proper airflow and prevent direct contact between the fuel and the panels, reducing the risk of damage. Regular cleaning of the firebox to remove ash and soot buildup is also essential.
Methods for Repairing Refractory Panels
The appropriate method for repairing refractory panels depends on the type and extent of the damage. Minor cracks, such as hairline fractures, can often be repaired using a high-temperature refractory mortar or sealant. These products are specifically formulated to withstand the extreme temperatures of a fireplace and create a durable, heat-resistant bond. Before applying the mortar, the damaged area should be thoroughly cleaned of any loose debris or soot. A wire brush can be used to prepare the surface and ensure proper adhesion of the mortar. The mortar should be applied according to the manufacturer's instructions, typically using a trowel or putty knife. It's crucial to allow the mortar to fully cure before using the fireplace.
For larger cracks or areas of crumbling, more extensive repairs may be necessary. In some cases, it may be possible to patch the damaged area using a refractory patching compound. These compounds are typically premixed and designed for filling larger voids and rebuilding damaged sections of the panel. As with mortar, proper surface preparation is essential for successful patching. The damaged area should be cleaned and any loose material removed. The patching compound should be applied in thin layers, allowing each layer to dry before applying the next. This prevents cracking and ensures a strong, durable repair.
If a panel is severely damaged, warped, or has lost a significant portion of its material, replacement is generally the best option. Replacing a refractory panel involves carefully removing the damaged panel and installing a new one in its place. The new panel should be of the same size and composition as the original to ensure a proper fit and optimal performance. Before installing the new panel, the surrounding area should be cleaned and any remaining mortar or adhesive removed. The new panel can be secured in place using refractory mortar or a high-temperature adhesive. It's important to ensure that the panel is properly aligned and flush with the surrounding panels.
When selecting repair materials, it's essential to choose products that are specifically designed for fireplace applications. These products are formulated to withstand the extreme temperatures and thermal cycling of a fireplace environment. Using generic mortars or sealants can lead to premature failure and require more frequent repairs. It is also crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully when applying these materials. Improper application can result in weak bonds, cracking, and reduced performance.
Safety Precautions and Considerations
Working with fireplaces and refractory materials involves certain safety precautions. Before beginning any repair work, ensure that the fireplace is completely cool and that the gas supply (if applicable) is turned off. Wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves, eye protection, and a dust mask. Refractory materials can be irritating to the skin and eyes, and the dust produced during repair work can be harmful if inhaled. Work in a well-ventilated area to minimize exposure to dust and fumes.
When removing damaged refractory panels, exercise caution to avoid damaging the surrounding structure. Use appropriate tools, such as a chisel and hammer, to carefully break the bond between the panel and the firebox. Avoid applying excessive force, which could crack or damage adjacent panels. Dispose of damaged refractory materials properly. These materials may contain harmful substances and should not be discarded in regular trash. Contact your local waste disposal authority for guidance on proper disposal methods.
If you are not comfortable performing fireplace repairs yourself, it is best to hire a qualified professional. Chimney sweeps and fireplace technicians have the experience and expertise to safely and effectively repair or replace refractory panels. They can also identify other potential problems with your fireplace and recommend appropriate solutions. Hiring a professional can ensure that the repairs are done correctly and that your fireplace is operating safely and efficiently.
Maintaining a functional fireplace requires diligent attention to detail, including regular inspection and timely repair of refractory panels. Neglecting these panels can lead to significant safety hazards and reduced heating efficiency. By understanding the signs of damage, the methods for repair, and the necessary safety precautions, homeowners can ensure the longevity and safe operation of their fireplaces. While minor repairs can often be handled by homeowners with appropriate tools and materials, more extensive damage or any uncertainties about the repair process should be addressed by a qualified professional.

Repair Your Fireplace Or Firebox Refractory Panel Replacement Parging

Fc Refractory Panel Replacement

What Causes Issues To Replace Fireplace Refractory Panels

Repair Ed Fireplace Panels Refectory Easy

Ed Refractory Panels Can Be A Major Safety Hazard In The Home Clean Sweep Chimney

Diy Fireplace Panel S Repair Of Firebrick Refractory

Repair Ed Fireplace Panels Refectory Easy

Repair Your Fireplace Or Firebox Refractory Panel Replacement Parging

Expert Manufactured Fireplace Panel Repair Replacement

Fireplace Panel Replacement Texan Residential Services
Related Posts