Fireplace Mantel Measurements: A Comprehensive Guide
The fireplace mantel serves as a prominent focal point within a room, contributing significantly to its overall aesthetic appeal. Accurate measurements are crucial for ensuring a harmonious and functional integration of the mantel into the surrounding space. This article provides a detailed exploration of fireplace mantel measurements, encompassing key considerations, standard dimensions, and best practices for achieving optimal results.
Before delving into specific measurements, it's important to understand the role of the mantel within the overall fireplace design. The mantel serves both decorative and functional purposes. Decoratively, it provides a surface for displaying artwork, photographs, or other cherished items, enhancing the visual appeal of the fireplace. Functionally, it acts as a heat shield, protecting combustible materials above the fireplace opening from excessive heat. Furthermore, the mantel can serve as a structural element, supporting the weight of decorative overmantels or extending shelving systems.
Understanding the different types of mantels is also essential. Mantels can range from simple shelves to elaborate, multi-piece structures. Common types include floating mantels, which appear to be suspended from the wall, traditional mantels with corbels and detailed moldings, and contemporary mantels with clean lines and minimalist designs. The style of the mantel significantly influences its measurements and installation requirements.
Determining Optimal Mantel Height
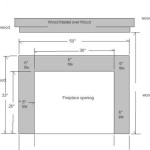
Mantel height is arguably the most critical measurement to consider. An improperly positioned mantel can detract from the overall aesthetic and potentially pose a safety hazard. The primary factor influencing mantel height is the fireplace opening's height and the type of fireplace. Building codes and safety standards often dictate minimum clearances between the top of the fireplace opening and the underside of the mantel.
Generally, a clearance of at least 12 inches is recommended between the top of the fireplace opening and the bottom of a wood mantel. This clearance helps prevent the mantel from overheating and potentially igniting. However, this is a general guideline, and the specific requirements may vary depending on the type of fireplace (wood-burning, gas, or electric) and the mantel material. Check local building codes and manufacturer specifications for accurate guidelines.
For gas fireplaces, the required clearance often depends on the BTU output of the fireplace. Higher BTU ratings typically necessitate greater clearances. Similarly, electric fireplaces, while generally producing less heat, may still have specific clearance requirements to prevent damage to the mantel or surrounding wall. Consultation with a qualified fireplace installer or building inspector is highly recommended to ensure compliance with all relevant regulations.
Beyond safety considerations, aesthetic factors also play a role in determining ideal mantel height. A mantel that is too high can feel visually disconnected from the fireplace opening, while a mantel that is too low can appear cramped and obstruct the view of the fire. A balanced approach, considering both safety and aesthetic principles, is essential. A common rule of thumb is to position the mantel so that it is approximately 4 to 6 inches above the keystone or upper edge of the fireplace opening surround. This placement allows for a visual connection between the fireplace and the mantel, creating a cohesive and balanced design.
Consider the overall room height and proportions when determining mantel height. In a room with high ceilings, a higher mantel may be appropriate to maintain visual balance. Conversely, in a room with low ceilings, a lower mantel may be preferable. The height of other furniture in the room, such as sofas and chairs, should also be taken into account. The mantel should complement the surrounding furniture and contribute to a harmonious overall design.
Calculating Mantel Width and Depth
In addition to height, mantel width and depth are crucial dimensions to consider. Mantel width refers to the overall horizontal span of the mantel, while mantel depth refers to the distance the mantel projects out from the wall. These measurements influence the mantel's visual impact and its ability to accommodate decorative items. Fireplace size and wall dimensions are key considerations during this process.
The optimal mantel width typically extends several inches beyond the width of the fireplace surround on each side. This overhang creates a visual frame around the fireplace opening, drawing attention to the focal point. A common guideline is to extend the mantel approximately 6 to 12 inches beyond the surround on each side. However, the specific amount of overhang may vary depending on the overall design and the desired aesthetic.
Consider the width of the surrounding wall and any architectural features that may influence the mantel's placement. If the fireplace is located on a relatively narrow wall, a wider mantel may appear disproportionate. Conversely, if the fireplace is located on a large wall, a narrower mantel may be visually insignificant. It is important to strike a balance between the mantel's width and the surrounding space to create a harmonious design.
Mantel depth is primarily determined by functional and aesthetic considerations. A deeper mantel provides more surface area for displaying decorative items, but it can also protrude further into the room, potentially obstructing traffic flow. A shallower mantel may be less obtrusive, but it may also offer limited display space. A common range for mantel depth is between 6 and 12 inches. This depth provides sufficient surface area for most decorative items while minimizing the risk of obstruction.
The desired style and the type of items to be displayed also influence mantel depth. A minimalist mantel with a clean, streamlined design may require a shallower depth, while a traditional mantel with intricate moldings may require a greater depth. If the mantel is intended to support heavy items, such as large vases or sculptures, a deeper and more structurally robust mantel is necessary.
Considering Structural Support and Installation
Accurate measurements are not just about aesthetics; they are also critical for ensuring proper structural support and safe installation. The mantel's weight, the type of wall construction, and the chosen installation method all influence the structural requirements and the necessary measurements. A poorly installed mantel can be unstable and potentially dangerous.
The weight of the mantel is a primary factor to consider. Mantels made from solid wood or stone can be significantly heavier than mantels made from lighter materials such as MDF or composite. The wall must be capable of supporting the mantel's weight without deflection or failure. It is crucial to identify the wall's structural components, such as studs or concrete blocks, to ensure that the mantel is securely anchored. Use a stud finder to locate wall studs and plan accordingly.
The type of wall construction (drywall, plaster, brick, or stone) influences the choice of fasteners and installation methods. Drywall and plaster walls typically require specialized anchors that can distribute the mantel's weight over a larger surface area. Brick and stone walls require masonry anchors that are specifically designed to grip these materials. Always consult with a qualified contractor or building supply professional to select the appropriate fasteners for the specific wall type.
Installation methods vary depending on the mantel's design and the desired aesthetic. Floating mantels, for example, typically require hidden brackets or supports that are securely attached to the wall studs. Traditional mantels may be attached with screws or nails, supplemented with construction adhesive for added stability. Carefully follow the manufacturer's instructions for installation, and do not hesitate to seek professional assistance if needed.
In some cases, it may be necessary to reinforce the wall structure to adequately support the mantel. This may involve adding additional studs or installing a header beam above the fireplace opening. Structural modifications should only be performed by qualified professionals who can ensure that the work is done safely and in compliance with all applicable building codes.
Precise measurements are also crucial for ensuring a seamless fit between the mantel and the surrounding wall. Any gaps or imperfections can detract from the overall aesthetic and potentially compromise the mantel's structural integrity. Use a level and a tape measure to ensure that the mantel is installed square and plumb. Caulk or filler can be used to conceal minor gaps, but excessive gaps may indicate an underlying structural issue.
By carefully considering these factors and taking accurate measurements, homeowners can ensure that their fireplace mantel is not only visually appealing but also structurally sound and safely installed. Remember to always consult with qualified professionals when necessary, and prioritize safety and compliance with building codes.

Mantel Dimensions Fireplacepro

Fireplace Mantel Worksheet How To Measure For A

Fireplace Mantel Installation Tips How To Antique Woodworks

How To Build Install A Fireplace Mantel We Love Fire

Measuring Your Fireplace For A Mantel

Average Fireplace Dimensions

Types Of Fireplaces And Mantels The Home Depot

Best Fireplace Mantel Proportions How Not To Muck It Up Shelf Dimensions Surrounds

Danielle Fireplace Mantel Siteworks Mantels

A Plus Inc Candler 36
Related Posts