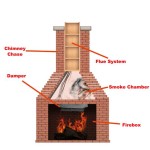
Fireplace Hearth Stone Thickness: A Comprehensive Guide
The fireplace hearth serves as a crucial safety component, protecting the surrounding flooring and combustible materials from sparks, embers, and radiant heat. Choosing the appropriate hearth material and, critically, the correct hearth stone thickness is paramount for ensuring both safety and aesthetic appeal. The thickness of the hearth stone directly impacts its ability to absorb and dissipate heat, as well as its structural integrity in withstanding the weight of the fireplace and the potential stresses of regular use.
Understanding the factors that influence the necessary fireplace hearth stone thickness involves considering building codes, manufacturer specifications, and the type of fireplace being installed. Ignoring these aspects can lead to safety hazards, property damage, and costly repairs. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the considerations involved in selecting the appropriate thickness for fireplace hearth stone.
Understanding Building Codes and Regulations
Local building codes and regulations play a significant role in determining the minimum acceptable fireplace hearth stone thickness. These codes are typically based on nationally recognized standards, such as those published by the International Code Council (ICC). The specific requirements can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the type of fireplace being installed. It is essential to consult with local building authorities or a qualified professional to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
These codes often specify minimum R-values (a measure of thermal resistance) for hearth extensions. The R-value requirement dictates the combined insulating properties needed to protect combustible materials. The thickness of the hearth stone contributes significantly to the overall R-value, and a thicker stone generally provides greater thermal resistance. If the fireplace is a zero-clearance model, the manufacturer's instructions will often specify the precise hearth requirements to maintain safe operation.
Failure to adhere to building codes can result in the rejection of a fireplace installation during inspection, requiring costly remediation work. Therefore, thorough research and consultation with relevant authorities are crucial steps in planning a fireplace installation project.
Factors Influencing Hearth Stone Thickness
Several factors beyond building codes influence the ideal hearth stone thickness for a given fireplace installation. These factors include the type of fireplace (wood-burning, gas, or electric), the fireplace's BTU (British Thermal Unit) output, and the material used for the hearth stone. Each of these elements plays a critical role in determining the necessary level of heat protection and structural support.
Wood-burning fireplaces typically require thicker hearth stones compared to gas or electric models due to the higher temperatures and potential for sparks and embers. The BTU output of the fireplace dictates the amount of heat generated, necessitating a thicker stone to absorb and dissipate the heat effectively. For example, a high-BTU wood-burning stove will generate significantly more heat than a small gas fireplace, requiring a correspondingly thicker hearth stone. The proximity of combustible materials also factors into this equation.
Furthermore, the type of stone used for the hearth affects the required thickness. Some stones, such as granite and slate, are denser and possess superior thermal conductivity compared to others. This means they can more effectively absorb and dissipate heat, potentially allowing for a slightly thinner hearth stone while still meeting safety requirements. Conversely, less dense stones may require a greater thickness to achieve the same level of protection.
Material Considerations and Thickness Guidelines
The choice of material for the hearth stone is critical. Natural stones like granite, slate, marble, and travertine are popular choices due to their aesthetic appeal, durability, and heat-resistant properties. However, each stone type possesses unique characteristics that influence the required thickness.
Granite, known for its high density and excellent heat resistance, is a common choice for fireplace hearths. For a wood-burning fireplace, a granite hearth stone thickness of at least 2 inches is generally recommended. This thickness provides ample protection against heat transfer and potential damage to the underlying flooring. For gas fireplaces, a slightly thinner granite slab, around 1.5 inches, may suffice.
Slate, another durable and heat-resistant option, is often used for hearths due to its natural beauty and relatively low porosity. A slate hearth stone thickness of at least 1.5 inches is typically recommended for wood-burning fireplaces, while a 1-inch thickness may be adequate for gas fireplaces. Marble, while aesthetically pleasing, is more porous than granite or slate and can be susceptible to staining. If using marble, it is recommended to seal it properly and consider a slightly thicker slab, around 2 inches, for added protection, particularly with wood-burning fireplaces.
Travertine, a type of limestone, is also a popular choice for hearths. However, it is more porous than granite or slate and may require sealing. A travertine hearth stone thickness of at least 2 inches is recommended for wood-burning fireplaces, with potentially a slightly thinner option for gas fireplaces if properly sealed and maintained. The specific thickness will depend on the specific type of stone and its properties.
In all cases, it is vital to consult with a qualified stone supplier or installer to determine the appropriate thickness based on the specific type of stone, the fireplace's heat output, and local building codes. Proper installation, including adequate support and appropriate grout or mortar, is crucial for ensuring the long-term stability and safety of the hearth.
Ultimately, selecting the appropriate fireplace hearth stone thickness is a multifaceted decision that requires careful consideration of building codes, fireplace type, material properties, and expert advice. A well-chosen and properly installed hearth not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the fireplace but also provides essential protection against fire hazards.

Fireplace Hearth Extension Rules Structure Tech Home Inspections

Fireplace Hearths Filler Panels

M Rock 24 In X Gray Concrete Hearth Cap Stone Mr24x24g The Home Depot

Slabs Hearths Terrazzo Stone Supply A Siteone Company

Stone Slabs Elite Blue Granite Natural Brick Depot

Stone Slabs Elite Blue Granite Natural Brick Depot

Guide To The Right Fireplace Hearth Direct Fireplaces

Slabs Hearths Terrazzo Stone Supply A Siteone Company

Schofield Stone Fireplace Hearths Mantles

Heritage Olive Limestone Hearth Mrs Stone
Related Posts