EPA Wood Burning Fireplaces: Efficiency, Regulation, and Benefits
Wood-burning fireplaces have long been a source of warmth and ambiance in homes, particularly in colder climates. However, traditional fireplaces have historically been inefficient and significant contributors to air pollution. In response to these concerns, regulatory bodies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have implemented stricter standards for wood-burning appliances, leading to the development and widespread adoption of EPA-certified wood-burning fireplaces. These fireplaces are designed to burn wood more cleanly and efficiently, reducing emissions and improving air quality. Understanding the features, benefits, and regulations surrounding EPA-certified wood-burning fireplaces is crucial for consumers considering installing or upgrading their heating systems.
The EPA's regulations are designed to reduce particulate matter emissions from residential wood heaters, including fireplaces, wood stoves, and fireplace inserts. Particulate matter, particularly PM2.5 (particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less), poses a significant threat to human health. These fine particles can penetrate deep into the lungs and bloodstream, contributing to respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues. By setting emission limits and requiring manufacturers to meet these standards, the EPA aims to mitigate the adverse health effects associated with wood smoke.
Understanding EPA Certification and Emission Standards
The EPA certification process for wood-burning fireplaces involves rigorous testing to ensure compliance with established emission limits. Manufacturers must submit their appliances to independent testing laboratories that are accredited by the EPA. These laboratories conduct standardized burn tests to measure the amount of particulate matter emitted during different stages of combustion. The test results are then submitted to the EPA for review and approval. If an appliance meets the EPA's emission standards, it is granted EPA certification and can be sold legally in the United States.
The emission standards for wood-burning fireplaces have evolved over time, with progressively stricter limits being implemented. The current EPA standards, often referred to as Phase 2 standards, represent a significant reduction in allowable particulate matter emissions compared to previous standards. These standards typically require fireplaces to emit no more than 2.0 grams of particulate matter per hour (g/hr) during the testing process. Some models can achieve even lower emissions, often below 1.0 g/hr, demonstrating the advancements in wood-burning technology.
Consumers can readily identify EPA-certified wood-burning fireplaces by looking for a permanent label affixed to the appliance. This label typically includes information about the manufacturer, model number, emission rate in grams per hour, and a statement confirming EPA certification. It is important to note that only fireplaces bearing this label are guaranteed to meet the EPA's emission standards. Purchasing a non-certified fireplace can result in increased air pollution and potential violations of local regulations.
Key Features of EPA-Certified Wood Burning Fireplaces
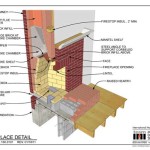
EPA-certified wood-burning fireplaces incorporate a variety of design features that contribute to cleaner and more efficient combustion. These features often include advanced combustion systems, air intake controls, and insulated fireboxes. The goal is to create a hotter, more complete burn, which reduces the amount of unburned particles and gases released into the atmosphere.
One common feature of EPA-certified fireplaces is the use of secondary combustion. This process involves introducing preheated air into the firebox above the primary combustion zone. This secondary air helps to burn off the gases and particles that would otherwise escape as smoke. Secondary combustion significantly reduces emissions and also increases the heat output of the fireplace.
Air intake controls are another important feature. These controls allow the user to regulate the amount of air entering the firebox, which in turn affects the rate of combustion. By carefully adjusting the air intake, users can optimize the burning process for maximum efficiency and minimal emissions. Some fireplaces feature automatic air controls that adjust the air intake based on the fire's temperature and combustion characteristics.
Insulated fireboxes are also common in EPA-certified fireplaces. Insulation helps to maintain a higher temperature within the firebox, which promotes more complete combustion. Insulated fireboxes also help to radiate heat into the room more efficiently, making the fireplace a more effective heating source.
Catalytic combustors represent another technology used in some EPA-certified wood-burning fireplaces. These devices are coated with a catalyst that helps to lower the ignition temperature of the gases and particles in the smoke. This allows them to burn at a lower temperature, further reducing emissions. Catalytic combustors require periodic maintenance and replacement, but they can significantly improve the efficiency and cleanliness of a wood-burning fireplace.
Benefits of Using EPA-Certified Wood Burning Fireplaces
Adopting EPA-certified wood-burning fireplaces offers a range of benefits for both the environment and the homeowner. These benefits include reduced air pollution, improved heating efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced safety.
The most significant benefit of EPA-certified fireplaces is their reduced impact on air quality. By emitting significantly less particulate matter than traditional fireplaces, these appliances help to improve air quality in both indoor and outdoor environments. This is particularly important in areas where wood burning is common and where air pollution levels are already elevated. Reducing particulate matter emissions can lead to fewer respiratory illnesses, improved cardiovascular health, and a reduced risk of other health problems.
EPA-certified wood-burning fireplaces are also more efficient than traditional fireplaces. The advanced combustion systems and insulated fireboxes in these appliances allow them to extract more heat from the wood, resulting in a higher heating efficiency. This means that homeowners can use less wood to achieve the same level of warmth, which can lead to cost savings on fuel expenses.
Beyond fuel savings, the improved efficiency of EPA-certified fireplaces can also translate into reduced maintenance costs. Because of the more complete combustion, there’s less creosote buildup in the chimney. Creosote is a flammable residue that can accumulate in chimneys and pose a fire hazard. Regular chimney cleaning is essential to prevent creosote buildup, and less buildup means less frequent and less costly cleanings.
Furthermore, EPA-certified wood-burning fireplaces often incorporate safety features that are not found in traditional fireplaces. These features may include spark arrestors to prevent embers from escaping the chimney, as well as better sealing around the firebox to prevent smoke from leaking into the room. These safety features can help to reduce the risk of chimney fires and other hazards associated with wood burning.
Finally, in some areas, using EPA-certified wood-burning appliances may be a requirement. Many municipalities and regions have regulations restricting or prohibiting the use of non-certified wood-burning devices during periods of high air pollution. Choosing an EPA-certified fireplace ensures compliance with these regulations and avoids potential fines or penalties.
In conclusion, EPA-certified wood-burning fireplaces represent a significant advancement in wood-burning technology. By meeting stringent emission standards and incorporating advanced design features, these appliances offer a cleaner, more efficient, and safer way to enjoy the warmth and ambiance of a wood-burning fire. Consumers considering a wood-burning fireplace should carefully evaluate their options and choose an EPA-certified model that meets their needs and contributes to a healthier environment. The available range of designs, from traditional to modern, allows integration into various home styles, making them a viable option for new construction and renovations alike.

Modern Wood Stove Emissions Regency Fireplace S

How Do The New 2024 Epa Wood Stove Regulations Impact Homeowners

Montecito Estate Epa Certified Wood Burning Fireplace F2845 Embers Home

Epa Wood Stove Regulations What You Need To Know

Epa Certified Wood Burning Fireplaces Canadian Chimney

Epa Iii Certified Wood Burning Superior Signature Series Fireplace Wct6940

Superior White Stacked Cf Trad Epa Cert Wood Fireplace Wrt3920 North Country Fire

Pacific Energy Fp30 Epa Wood Burning Fireplace For In Ottawa

2100 1 Timberwolf Wood Pellet Stoves Inserts

Wood Burning Epa Certified Fireplace With Powerful Catalytic Heating By Superior Wrt4826
Related Posts