Energy Efficient Electric Fireplace Heater: A Comprehensive Guide
Electric fireplace heaters have emerged as a popular alternative to traditional fireplaces, offering a combination of aesthetic appeal and supplemental heating capabilities. Their ease of installation, lack of venting requirements, and diverse design options contribute to their widespread adoption. However, a key consideration for potential buyers is energy efficiency. Understanding the factors that influence the energy consumption of electric fireplace heaters is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions and minimizing operating costs.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of energy-efficient electric fireplace heaters, exploring their operating principles, efficiency determinants, available technologies, and strategies for optimizing energy use. The aim is to equip readers with the knowledge necessary to select and utilize electric fireplace heaters in a cost-effective and environmentally responsible manner.
Understanding How Electric Fireplace Heaters Work
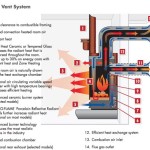
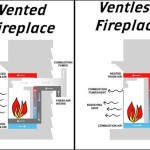
Electric fireplace heaters operate by converting electrical energy into heat. This process typically involves passing electricity through a heating element, such as a resistance coil or a ceramic plate. The element heats up due to the electrical resistance, and the generated heat is then circulated into the room using a fan or convection currents. The visual effect of flames is often achieved through simulated flames projected onto a screen or reflected using mirrors and LED lighting. These visual effects operate independently of the heating function and consume a relatively small amount of electricity.
The effectiveness of an electric fireplace heater is measured by its ability to raise the temperature of a room to a comfortable level while consuming minimal electricity. Several factors contribute to this efficiency, including the type of heating element, the insulation of the unit, and the effectiveness of the fan or convection system used to distribute the heat.
Key Factors Influencing Energy Efficiency
Several factors directly impact the energy efficiency of an electric fireplace heater. Understanding these factors is essential for comparing different models and making an informed purchase.
Heating Element Type: The type of heating element significantly influences energy efficiency. Resistance coils are the most common type, but they can be less efficient than other options. Ceramic heating elements, for instance, are known for their rapid heating and even heat distribution, potentially leading to energy savings. Infrared heaters, which directly heat objects and people in the room rather than the air itself, can also be more efficient in certain situations, as they require less energy to achieve a comfortable level of warmth.
Wattage Rating: The wattage rating of an electric fireplace heater indicates the rate at which it consumes electricity. Higher wattage heaters generate more heat but also consume more energy. It is important to select a wattage rating appropriate for the size of the room being heated. Overly powerful heaters will consume unnecessary energy, while underpowered heaters may struggle to maintain a comfortable temperature.
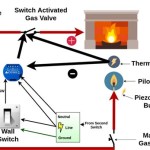
Thermostat Control: Accurate thermostat control is crucial for maintaining a consistent room temperature and preventing energy waste. A well-designed thermostat will cycle the heating element on and off as needed to maintain the desired temperature, minimizing energy consumption. Some models feature programmable thermostats that allow users to set different temperature schedules for different times of the day or week.
Fan Efficiency: If the electric fireplace heater uses a fan to circulate heat, the efficiency of the fan is an important consideration. A more efficient fan will circulate the heat more effectively, allowing the heater to operate at a lower wattage setting. Look for models with adjustable fan speeds, allowing users to optimize airflow for different heating needs.
Insulation: The insulation of the electric fireplace heater unit itself can also affect energy efficiency. Adequate insulation will prevent heat loss from the unit, ensuring that more of the generated heat is directed into the room. Some manufacturers use reflective materials within the unit to further enhance insulation and minimize heat loss.
Zone Heating: Electric fireplace heaters are particularly well-suited for zone heating, which involves heating only the rooms that are being used. This is a more energy-efficient approach than heating an entire house, especially in larger homes. By focusing the heat on specific areas, users can significantly reduce their overall energy consumption.
Energy-Efficient Technologies and Features
Manufacturers are continually developing new technologies and features to improve the energy efficiency of electric fireplace heaters. Some of the most promising advancements include:
LED Flame Technology: Modern electric fireplaces use LED lighting to create realistic flame effects. LEDs are highly energy-efficient compared to traditional light bulbs, consuming significantly less electricity while providing bright and vibrant lighting. The use of advanced algorithms and projection techniques further enhances the realism of the flame effects, creating a visually appealing and energy-efficient ambiance.
Infrared Heating Technology: Infrared heaters utilize infrared radiation to directly heat objects and people in the room. This is a more efficient heating method compared to conventional heaters that heat the air, as it minimizes heat loss and provides more targeted warmth. Infrared heaters are particularly effective in well-insulated rooms.
Smart Thermostats and Wi-Fi Connectivity: Many electric fireplace heaters are now equipped with smart thermostats and Wi-Fi connectivity. These features allow users to control the heater remotely using a smartphone or tablet. Smart thermostats can learn user preferences and automatically adjust the temperature to optimize energy efficiency. Wi-Fi connectivity also enables integration with other smart home devices and platforms, allowing for seamless control and automation.
Eco Modes: Some electric fireplace heaters feature an "eco mode" that automatically adjusts the heating output to minimize energy consumption. This mode typically operates at a lower wattage setting and prioritizes maintaining a comfortable temperature over rapid heating. Eco modes are useful for maintaining a consistent temperature without wasting energy.
Timer Functionality: Programmable timers allow users to set specific on and off times for the heater. This feature is useful for preheating a room before it is occupied or for automatically turning off the heater when it is no longer needed. Timers can significantly reduce energy consumption by preventing the heater from operating unnecessarily.
Strategies for Optimizing Energy Use
Even with an energy-efficient electric fireplace heater, proper usage practices are essential for maximizing energy savings. Consider the following strategies to optimize energy use:
Proper Sizing: Selecting an electric fireplace heater with the appropriate wattage rating for the room size is crucial. Overly powerful heaters will consume excessive energy, while underpowered heaters may struggle to maintain a comfortable temperature.
Proper Insulation: Ensure that the room being heated is well-insulated to minimize heat loss. Seal any drafts around windows and doors, and consider adding insulation to walls and ceilings if necessary. Good insulation will allow the electric fireplace heater to operate more efficiently and maintain a consistent temperature.
Strategic Placement: Position the electric fireplace heater in a location that allows for optimal heat distribution. Avoid placing it near doorways or windows where heat can easily escape. Consider placing it in a central location in the room to ensure even heating.
Thermostat Settings: Set the thermostat to the lowest comfortable temperature. Lowering the thermostat by just a few degrees can significantly reduce energy consumption. Use a programmable thermostat to set different temperature schedules for different times of the day or week.
Supplemental Heating: Use the electric fireplace heater as a supplemental heating source rather than relying on it as the primary heating system for the entire house. This approach allows for zone heating and reduces overall energy consumption.
Regular Maintenance: Keep the electric fireplace heater clean and free of dust. Dust accumulation can reduce the efficiency of the heating element and fan. Regularly clean the unit according to the manufacturer's instructions.

Lifeplus Small Electric Fireplace Heater Tabletop 13 5 Energy Efficient Indoor Space Portable Wood Cabinet 3d Flame For Home Decor Com

Are Electric Fireplaces Energy Efficient We Love Fire

Lifeplus Small Electric Fireplace Heater Tabletop 13 5 Energy Efficient Indoor Space Portable Wood Cabinet 3d Flame For Home Decor Com

Comfort Glow Electric Quartz Mobile Fireplace Indoor Heater With 3 Energy Efficient Heating Elements White Target

Eco Friendly Hearth Embrace Efficiency With Electric Fireplace Arttoreal

Electric Fireplace Heater Are They Effective Types And Specs

Electric Fireplace Stove 23 Inches Freestanding Infrared He Grillpartsreplacement Bbq Parts Retailer

Lifeplus Small Electric Fireplace Heater Tabletop 13 5 Energy Efficient Indoor Space Portable Wood Cabinet 3d Flame For Home Decor Com

Comfort Glow Electric Quartz Mobile Fireplace Indoor Heater With 3 Energy Efficient Heating Elements Target

Energy Saving Small Good Quality Decorative Electric Fireplace China Heater Made In Com
Related Posts