Direct Vent Gas Fireplace Inside Wall: An In-Depth Guide
Direct vent gas fireplaces have become increasingly popular as a convenient and efficient way to add supplemental heat and ambiance to a home. Unlike traditional wood-burning fireplaces or even vent-free gas models, direct vent fireplaces offer a sealed combustion system. This means they draw air from outside the home for combustion and vent exhaust gases directly outside, without relying on existing chimneys or compromising indoor air quality. One of the most common and aesthetically pleasing installation methods for these fireplaces is within an interior wall, which this article will explore in detail.
The concept of installing a direct vent gas fireplace inside an interior wall offers a multitude of advantages. It allows homeowners to introduce a fireplace feature virtually anywhere in the house, regardless of whether a pre-existing chimney is available. This flexibility opens up design possibilities, enabling the creation of focal points in living rooms, bedrooms, or even bathrooms, provided local building codes are met. Furthermore, due to their sealed combustion design, direct vent fireplaces are generally considered safer and more energy-efficient than traditional fireplaces.
This article will delve into the various aspects of installing a direct vent gas fireplace inside an interior wall, including planning considerations, fireplace selection, installation procedures, safety protocols, and maintenance tips. Understanding these elements is crucial for ensuring a successful and safe fireplace installation that enhances the comfort and aesthetic appeal of your home.
Key Point 1: Planning and Preparation for Interior Wall Installation
The first step in installing a direct vent gas fireplace inside an interior wall is meticulous planning. This phase encompasses several critical considerations that will dictate the feasibility and success of the project. A primary factor is determining the precise location for the fireplace. This decision should be based on both aesthetic preferences and practical limitations, such as the proximity to gas lines and the ability to vent directly to the exterior. Interior walls, while offering flexibility, may still present challenges in terms of framing and the routing of vent pipes.
Before any physical work commences, it is imperative to consult with local building codes and regulations. Fireplace installations are subject to stringent guidelines concerning clearances to combustible materials, venting requirements, and gas line connections. Obtaining the necessary permits is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues down the line. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in costly rework or even the fireplace being deemed unusable.
Selecting the appropriate fireplace model is another crucial aspect of the planning phase. Direct vent gas fireplaces come in various sizes, styles, and heat output capacities. It is essential to choose a model that is not only aesthetically pleasing but also appropriately sized for the room in which it will be installed. Overly large fireplaces can overheat a smaller space, while undersized models may not provide sufficient heat. The fireplace's BTU (British Thermal Unit) rating should be carefully considered in relation to the room's square footage and insulation levels.
Finally, a thorough inspection of the intended installation site is necessary. This includes assessing the existing wall framing, identifying any potential obstructions such as electrical wiring or plumbing pipes, and ensuring that the wall can structurally support the weight of the fireplace unit. If any modifications to the wall framing are required, it is advisable to consult with a qualified contractor or structural engineer to ensure that the changes are made safely and in accordance with building codes.
Key Point 2: Installation Procedures and Safety Protocols
Once the planning phase is complete, the installation process can begin. This typically involves several steps, including framing the fireplace opening, running the gas line, installing the venting system, and connecting the fireplace unit. Each of these steps requires adherence to specific safety protocols and manufacturer instructions.
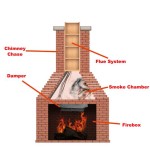
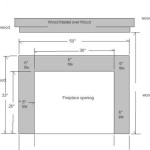
Framing the fireplace opening involves creating a rectangular enclosure within the wall to house the fireplace unit. This enclosure should be constructed using fire-resistant materials, such as non-combustible framing lumber or metal studs, to ensure adequate protection against heat. The dimensions of the opening should precisely match the specifications provided by the fireplace manufacturer, allowing for proper clearance and ventilation. It is crucial to maintain the required clearances to combustible materials as specified in the installation manual to prevent the risk of fire.
Running the gas line is a critical step that should only be performed by a qualified and licensed gas fitter. Improper gas line connections can lead to gas leaks, which pose a serious safety hazard. The gas line should be sized appropriately for the fireplace's gas consumption requirements, and all connections should be thoroughly tested for leaks using a gas leak detector. The gas line should also be properly supported and protected from physical damage.
The direct vent system is a key safety feature of these fireplaces. It requires careful installation to ensure that exhaust gases are safely vented outside the home. The vent pipe should be connected to the fireplace unit and extend through the wall to the exterior, terminating in a properly designed vent cap. The vent pipe should be installed with the correct slope to prevent condensation from accumulating inside the pipe. All connections should be sealed tightly to prevent leaks of exhaust gases into the home. The vent cap should be positioned in a location that prevents snow or debris from blocking the vent.
After the gas line and venting system are installed, the fireplace unit can be connected. This involves connecting the gas line to the fireplace's gas valve, wiring the electrical connections, and securing the fireplace unit to the framed opening. All electrical connections should be made in accordance with electrical codes, and the fireplace should be properly grounded. Once the installation is complete, a thorough inspection should be performed to ensure that all connections are secure and that the fireplace is operating correctly.
Key Point 3: Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a direct vent gas fireplace. This includes cleaning the fireplace glass, inspecting the venting system, and checking the gas connections. The frequency of maintenance will depend on the frequency of use and the specific recommendations of the fireplace manufacturer.
Cleaning the fireplace glass should be done periodically to remove soot and other deposits that can accumulate during operation. Use a commercially available fireplace glass cleaner and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. Avoid using abrasive cleaners, as these can scratch or damage the glass. A clean glass provides a clearer view of the flames and enhances the aesthetic appeal of the fireplace.
The venting system should be inspected annually for any signs of damage or blockage. Check the vent pipe for corrosion, cracks, or loose connections. The vent cap should be inspected to ensure that it is free of debris, such as leaves or snow. Any obstructions should be removed to ensure proper venting of exhaust gases. A blocked vent can lead to a buildup of carbon monoxide, which is a deadly gas.
The gas connections should be checked periodically for leaks using a gas leak detector. If a gas leak is detected, immediately shut off the gas supply and contact a qualified gas fitter to repair the leak. Never attempt to repair a gas leak yourself, as this can be extremely dangerous. It is also advisable to have the fireplace professionally inspected and serviced annually by a qualified technician. This will ensure that all components are functioning correctly and that the fireplace is operating safely.
Operational considerations include using the fireplace safely and efficiently. Always follow the manufacturer's instructions for operating the fireplace. Avoid placing combustible materials too close to the fireplace, as this can create a fire hazard. Never leave a burning fireplace unattended. Ensure that the room is adequately ventilated, especially if the fireplace is operated for extended periods. Familiarize yourself with the fireplace's safety features, such as the pilot light shut-off and the emergency shut-off valve. By following these operational guidelines, homeowners can enjoy the warmth and ambiance of their direct vent gas fireplace safely and responsibly.
In addition to regular maintenance, it is important to be aware of potential problems that can arise with direct vent gas fireplaces. These include issues such as pilot light problems, burner malfunctions, and venting problems. If you experience any of these issues, it is essential to have the fireplace inspected and repaired by a qualified technician. Do not attempt to diagnose or repair these problems yourself, as this can be dangerous.
Furthermore, considering the long-term energy efficiency of the fireplace is important. Some models are equipped with features such as electronic ignition and programmable thermostats that can help to reduce energy consumption. Using the fireplace only when needed and setting the thermostat at a comfortable temperature can also help to save energy. Investing in a high-efficiency model can result in significant energy savings over the lifespan of the fireplace.
Finally, remember to keep the area around the fireplace clean and free of clutter. This will help to prevent fires and ensure that the fireplace operates safely and efficiently. A well-maintained and properly operated direct vent gas fireplace can provide years of warmth, comfort, and aesthetic enjoyment.

How To Find The Most Efficient Direct Vent Gas Fireplace For Your Next Project

Guide To Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces
Gas Fireplace Venting Explained Heat Glo

Freestanding High Efficiency Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces Inserts Stoves Godby Hearth And Home
Have Your Fire Wherever You D Like Heatilator

Pros And Cons Of Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces Tarantin Industries

Fire Ribbon Direct Vent Slim Gas Fireplace Spark Modern Fires

Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces The Ultimate Guide Learning Center

Napoleon Gas Direct Vent Wall Mount Fireplace Whd31 Fireplaces Hvacdirect Com

12 Types Of Gas Fireplaces You Need To Know
Related Posts