Coal Fireplace Inserts vs. Gas Fireplace Inserts: A Comparative Analysis
Fireplace inserts offer a practical and aesthetically pleasing solution for enhancing the efficiency and appearance of existing masonry fireplaces. Two prominent options are coal fireplace inserts and gas fireplace inserts, each possessing distinct characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. This article provides a comprehensive comparison between these two types of inserts, examining their operational mechanics, heating performance, fuel considerations, environmental impact, maintenance requirements, and cost implications.
A fireplace insert is essentially a self-contained heating appliance designed to be installed within an existing fireplace opening. It addresses the inherent inefficiency of traditional fireplaces, which often lose more heat than they generate. Inserts improve heat circulation and retention, resulting in a more comfortable and energy-efficient heating solution. Both coal and gas fireplace inserts aim to achieve this goal, but diverge significantly in their implementation.
Operational Mechanics and Installation
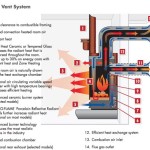
The fundamental difference between coal and gas fireplace inserts lies in the fuel they utilize and the method by which they convert this fuel into heat. A coal fireplace insert burns coal, a solid fossil fuel, to generate heat. The insert typically features a firebox designed to contain the burning coal, an air intake system to regulate combustion, and a flue to exhaust the resulting gases. Installation of a coal insert often involves reinforcing the existing chimney to accommodate the weight of the insert and the potentially corrosive byproducts of coal combustion. A stainless steel liner is usually recommended to protect the chimney from damage.
Gas fireplace inserts, conversely, burn natural gas or propane. These inserts are generally simpler to install than their coal counterparts, as they are lighter and produce cleaner emissions. Installation requires connecting the insert to a gas line and venting the exhaust gases through a chimney liner. The liner material can vary depending on the specific insert and local regulations.
Gas inserts typically offer more convenient operation, often featuring features such as remote control operation, automatic ignition, and thermostatic control. Coal inserts, on the other hand, require manual stoking and ash removal, demanding more active user involvement.
Heating Performance and Efficiency
Heating performance is a critical factor in selecting a fireplace insert. Both coal and gas inserts can provide substantial heat output, but their efficiency and heat distribution characteristics differ. Coal inserts are known for producing intense radiant heat, which can effectively warm a localized area. However, the efficiency of coal combustion can vary depending on the quality of the coal and the design of the insert. Some modern coal inserts incorporate advanced combustion technologies to improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
Gas inserts offer a more consistent and easily controllable heat output. They typically achieve higher efficiency ratings than coal inserts due to the cleaner and more complete combustion of gas. Gas inserts also often incorporate features such as blowers to circulate heated air throughout the room, promoting more even heat distribution.
The appropriate choice between coal and gas depends largely on the desired heating profile. If intense radiant heat is preferred for a specific area, a coal insert may be suitable. If a more consistent and easily controllable heat output with wider distribution is desired, a gas insert may be a better choice.
Fuel Considerations and Storage
The choice of fuel type significantly impacts the convenience, cost, and environmental implications of operating a fireplace insert. Coal, as a solid fuel, requires dedicated storage space and can be messy to handle. The availability and price of coal can also fluctuate depending on location and market conditions. Moreover, different types of coal vary in their heating value and ash content, requiring careful selection to optimize performance and minimize maintenance.
Gas, conversely, is typically delivered via a pipeline, eliminating the need for on-site storage. Propane, an alternative gas fuel, requires a tank for storage, but is readily available in most areas. The price of gas can also fluctuate, but is generally less volatile than coal prices. Gas is also cleaner to handle than coal, eliminating the mess and dust associated with solid fuel.
From a logistical perspective, gas offers significant advantages in terms of fuel handling and storage. However, the availability of a gas line and the associated connection costs may influence the decision.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
The environmental impact of fireplace inserts is primarily determined by the emissions produced during combustion. Coal combustion generates a variety of pollutants, including particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. Modern coal inserts often incorporate catalytic converters and other emission control technologies to reduce these pollutants, but they generally still produce higher emissions than gas inserts.
Gas combustion is significantly cleaner than coal combustion, producing primarily carbon dioxide and water vapor. Gas inserts typically meet stringent emission standards, making them a more environmentally friendly option. However, it's essential to consider the source of the gas. Natural gas is a fossil fuel, and its extraction and transportation can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
From an environmental perspective, gas inserts generally offer a lower environmental impact compared to coal inserts. However, it is important to consider the overall lifecycle emissions associated with both fuel types.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Both coal and gas fireplace inserts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and safety. Coal inserts require frequent ash removal, chimney cleaning to remove creosote buildup, and inspection of the firebox for corrosion or damage. The chimney liner also requires periodic inspection and replacement as needed.
Gas inserts require less frequent maintenance, typically involving annual inspection by a qualified technician. This inspection includes checking the gas lines for leaks, cleaning the burner assembly, and inspecting the venting system. Although less demanding than coal insert maintenance, regular servicing is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation.
The longevity of both types of inserts depends on the quality of the materials, the frequency of use, and the level of maintenance performed. With proper care, both coal and gas inserts can provide many years of reliable service.
Cost Implications
The cost of a fireplace insert encompasses several factors, including the initial purchase price, installation costs, fuel costs, and maintenance expenses. Coal inserts typically have a lower initial purchase price than gas inserts. However, installation costs can be higher due to the need for chimney reinforcement and liner installation. Fuel costs for coal can vary, but may be lower than gas in some regions.
Gas inserts generally have a higher initial purchase price, but installation costs may be lower due to their lighter weight and simpler venting requirements. Fuel costs for gas can vary depending on market conditions and the availability of a gas line. Maintenance costs for gas inserts are typically lower than those for coal inserts.
A comprehensive cost analysis should consider all these factors to determine the most cost-effective option over the lifespan of the insert. Factors like the frequency of use, local fuel prices, and the need for chimney modifications will significantly influence the overall cost.
Furthermore, rebates and tax credits may be available for installing energy-efficient fireplace inserts, which can help offset the initial cost. These incentives vary depending on location and government programs, so it is important to research available options.
Ultimately, the decision between a coal or gas fireplace insert depends on individual priorities and circumstances. Evaluating factors such as heating needs, budget constraints, fuel availability, environmental concerns, and maintenance preferences is crucial for making an informed choice. Careful consideration of these aspects will ensure that the selected insert provides years of comfortable and efficient heating.

Belmont Small Gas Insert

Gas Coal Baskets Natural And Propane

Gas Coal Baskets For Small Fireplaces

Valor 530icn Coal Fire Radiant Gas Fireplace And Insert Installed With Polished Windsor Arch In Mantel Antique Mantels

Coal Fireplace Restoration Atlanta Repair Burning Stove

Valor Fireplace Portrait

Valor Portrait Windsor Arch Gas Fireplace Bob S Intelligent Heating Decor

The Best Coal Effect Gas Electric Fires Direct Fireplaces

Gas Coal Baskets Natural And Propane

Gas Coals Coal Baskets
Related Posts