Chimney Gas Fireplaces: A Comprehensive Overview
Chimney gas fireplaces represent a popular heating and aesthetic feature in many homes. They offer a convenient alternative to traditional wood-burning fireplaces, combining the visual appeal of a fire with the ease of gas fuel. Understanding the components, operation, maintenance, and safety aspects of chimney gas fireplaces is crucial for homeowners seeking to utilize this appliance effectively and responsibly.
A chimney gas fireplace typically consists of several key components working in conjunction. The gas burner assembly, fueled by natural gas or propane, produces the flames. Artificial logs, made from ceramic or refractory materials, are arranged to simulate the appearance of burning wood. A control valve regulates the gas flow, allowing for adjustment of the flame height and heat output. The venting system, connected to a chimney, expels combustion byproducts such as carbon dioxide and water vapor to the outside atmosphere. A glass enclosure, often tempered for heat resistance, provides a safety barrier and prevents drafts. Finally, a control system, which may include a remote control or wall switch, enables users to operate the fireplace remotely.
The operation of a chimney gas fireplace is relatively straightforward. When the control system is activated, the gas valve opens, allowing gas to flow to the burner. An ignition system, either a pilot light or electronic igniter, ignites the gas, producing flames. The flames heat the artificial logs, which radiate heat into the room. The combustion byproducts are drawn up the chimney by natural draft or a powered fan, depending on the venting system design. The heat output can be adjusted by regulating the gas flow using the control valve. To shut down the fireplace, the control system is deactivated, closing the gas valve and extinguishing the flames.
Key Point 1: Venting System Types and Requirements
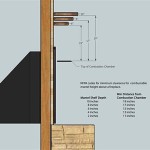
The venting system is a critical component of a chimney gas fireplace, ensuring the safe expulsion of combustion byproducts. There are two primary types of venting systems commonly used: natural vent and direct vent.
Natural vent systems rely on the natural buoyancy of hot gases to create a draft that pulls combustion byproducts up the chimney. These systems require a properly sized and constructed chimney that meets specific height and diameter requirements to ensure adequate draft. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to prevent obstructions or deterioration that could compromise the venting performance and create a safety hazard.
Direct vent systems, on the other hand, utilize a sealed combustion chamber and a coaxial vent pipe. The outer pipe draws in fresh air for combustion from outside the house, while the inner pipe expels the exhaust gases. This design eliminates the need for a conventional chimney and allows for more flexible installation options, as the vent pipe can be run horizontally through a wall or vertically through the roof. Direct vent systems offer improved energy efficiency and safety compared to natural vent systems, as they minimize the risk of backdrafting and reduce heat loss through the chimney.
Key Point 2: Maintenance and Safety Procedures
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a chimney gas fireplace. Neglecting maintenance can lead to performance issues, increased energy consumption, and potentially hazardous conditions.
Annual inspection and cleaning of the fireplace and venting system are highly recommended. A qualified technician should inspect the gas burner assembly, control valve, venting system, and other components for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. The burner should be cleaned to remove any debris or carbon buildup that could impede gas flow and flame quality. The venting system should be inspected for obstructions, such as bird nests or debris, and cleaned as necessary. The glass enclosure should be cleaned with a specialized cleaner to remove any soot or residue.
Gas leak detection is a critical safety precaution. Regularly test gas connections with a soapy water solution. Bubbles indicate a gas leak. A gas detector will alarm in the presence of gas. Never store flammable materials near the fireplace. Ensure carbon monoxide detectors are properly installed and maintained.
Key Point 3: Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Considerations
The fuel efficiency of a chimney gas fireplace can vary depending on several factors, including the venting system type, insulation levels, and usage patterns. Direct vent systems generally offer higher fuel efficiency compared to natural vent systems due to their sealed combustion chamber and reduced heat loss through the venting system.
Proper insulation of the fireplace surround and chimney can also help to improve fuel efficiency by reducing heat loss to the surrounding walls and attic. Using a programmable thermostat or remote control to regulate the fireplace operation can further optimize energy consumption by allowing users to adjust the heat output based on their comfort needs.
From an environmental perspective, chimney gas fireplaces produce fewer emissions compared to traditional wood-burning fireplaces. Natural gas and propane are cleaner-burning fuels than wood, resulting in lower levels of particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and other pollutants. However, it is important to note that burning fossil fuels still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Homeowners can consider purchasing carbon offsets or investing in renewable energy sources to mitigate the environmental impact of their gas fireplace.
Furthermore, proper maintenance and operation of the fireplace can help to minimize emissions. Ensuring that the burner is clean and properly adjusted, and avoiding over-firing the fireplace, can reduce the amount of unburned fuel and pollutants released into the atmosphere.
By understanding the components, operation, maintenance, safety aspects, and environmental considerations of chimney gas fireplaces, homeowners can make informed decisions regarding their use and ensure that they are operating safely and efficiently. Adhering to manufacturer's instructions and seeking professional assistance when necessary are crucial for maximizing the benefits of this versatile heating appliance.

Do Gas Fireplaces Need A Chimney Dreifuss

Do Gas Fireplaces Need A Chimney Dreifuss

Gas Wood Burning Chimneys Similarities Fireplace Chimney Experts

If You Have A Gas Fireplace It May Or Not Chimney Flue

The Types Of Gas Fireplaces Gaithersburg Md Fireplace Service
Understanding How Direct Vent Works Heat Glo

Do Gas Fireplaces Need A Chimney Dreifuss

Do Gas Fireplaces Have Chimneys The Chimney Doctor Ltd

Fireplaces Gas Fireplace Guidelines Maintenance

Venting A Gas Fireplace Through Existing Chimney Design Inserts