Building Up A Fireplace Hearth: A Comprehensive Guide
The fireplace hearth serves as a crucial element in the overall design and function of a fireplace. It extends outward from the fireplace opening, providing a non-combustible surface that protects the surrounding flooring and safeguards against stray sparks and embers. Beyond its practical purpose, the hearth contributes significantly to the aesthetic appeal of the fireplace, serving as a focal point within the room. Constructing a fireplace hearth involves careful planning, selecting appropriate materials, and adhering to safety regulations.
This article provides a detailed guide to building up a fireplace hearth, covering essential aspects from planning and material selection to construction techniques and safety considerations. A well-constructed hearth not only enhances the visual appeal of a fireplace but also ensures its safe and efficient operation for years to come.
Planning and Preparation: Essential Steps for a Successful Hearth Build
Prior to commencing any construction, meticulously planning the hearth design and preparing the work area is essential for achieving a successful outcome. This planning phase involves several crucial considerations.
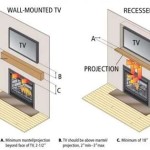
Determining Hearth Dimensions: The size of the hearth should be proportionate to the size of the fireplace opening and based on building codes. Local building codes specify minimum hearth extensions beyond the fireplace opening. These regulations often dictate the hearth's depth (distance extending outward from the fireplace) and width (distance spanning horizontally across the fireplace). Failure to adhere to these codes can result in safety hazards. Generally, larger fireplaces require larger hearths to provide adequate protection. A common rule of thumb is that the hearth should extend at least 16 inches in front of the fireplace and 8 inches beyond each side of the fireplace opening. For larger fireplaces with openings exceeding six square feet, these dimensions typically increase to at least 20 inches in front and 12 inches on each side.
Choosing the Right Materials: The selection of materials is crucial for both the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of the hearth. The materials chosen must be non-combustible to prevent fire hazards. Common materials include brick, stone, concrete pavers, and tile. Brick offers a classic and durable option, while stone provides a more natural and rustic appearance. Concrete pavers offer versatility in design and are often more cost-effective than natural stone. Tile provides a wide range of design possibilities but requires careful selection to ensure it is rated for high-temperature applications. Considerations should include the structural integrity of the chosen materials and their compatibility with the existing fireplace structure. The chosen materials should also complement the overall aesthetic of the room.
Preparing the Subfloor: The subfloor beneath the hearth must be structurally sound and capable of supporting the weight of the hearth materials. If the existing subfloor is wood, it may require reinforcement to prevent sagging or settling over time. This reinforcement might involve adding additional joists or increasing the thickness of the subfloor sheathing. Before proceeding, the construction professional usually removes any combustible materials, such as carpeting or wood flooring, from the area where the hearth will be constructed. Inspecting the subfloor for signs of damage or rot is also crucial, and any necessary repairs should be completed before proceeding with the hearth construction. If the existing subfloor is concrete, ensure it is clean and free of any debris that could interfere with the adhesion of the hearth materials.
Gathering Tools and Equipment: Before beginning the actual construction, gathering all necessary tools and equipment is essential. This includes tools for cutting and shaping the chosen materials, such as a wet saw for tile or stone and a masonry saw for brick. Mortar mixing equipment, such as a mixing tub and trowel, are needed for setting the hearth materials. Leveling tools, such as a spirit level and shims, are crucial for ensuring the hearth is level and even. Measuring tools, such as a tape measure and square, are necessary for accurate layout and cutting. Personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses, gloves, and a dust mask, is essential for protecting oneself from injury and harmful dust.
Construction Techniques: Building a Solid and Aesthetically Pleasing Hearth
Once the planning and preparations are complete, the actual construction of the hearth can begin. The construction process involves several key steps, requiring precision and attention to detail.
Creating a Mortar Bed: A mortar bed provides a stable and level base for the hearth materials. The mortar should be mixed according to the manufacturer's instructions, ensuring a consistent and workable consistency. The mortar bed should be applied evenly to the prepared subfloor, using a notched trowel to create ridges that will help the hearth materials adhere. The thickness of the mortar bed will vary depending on the type of materials being used and the desired height of the hearth. Ensuring the mortar bed is level and even is crucial for preventing uneven settling or cracking in the finished hearth.
Laying the Hearth Materials: Begin laying the hearth materials, starting from the fireplace opening and working outwards. Carefully position each piece, ensuring it is aligned and level. Use spacers to maintain consistent joint widths between the materials. Gently tap each piece into the mortar bed using a rubber mallet to ensure it is firmly seated. Periodically check the level of the hearth using a spirit level and make any necessary adjustments. If using multiple rows of materials, stagger the joints for added stability and visual appeal. For complex patterns or designs, consider creating a layout template beforehand to ensure accuracy.
Grouting and Finishing: Once the mortar has cured for the manufacturer's recommended time, typically 24-48 hours, the joints between the hearth materials can be grouted. Select a grout color that complements the chosen hearth materials and the overall aesthetic of the room. Apply the grout evenly to the joints, using a grout float to force it into the spaces. Remove any excess grout from the surface of the hearth materials using a damp sponge. Allow the grout to cure for the manufacturer's recommended time, typically 24-72 hours. Once the grout has cured, seal the hearth to protect it from stains and moisture. A sealant specifically designed for the chosen hearth materials should be used. Apply the sealant according to the manufacturer's instructions. Once the sealant is dry, the hearth is ready for use.
Integrating with Existing Flooring: Smoothing the transition between the hearth and the existing flooring is crucial for both aesthetics and safety. This can be achieved through various methods, such as using transition strips or feathering the edge of the hearth to create a gradual slope. The transition should be flush to prevent tripping hazards and ensure easy access for cleaning. Careful consideration should be given to the materials used for the transition to ensure they complement both the hearth and the existing flooring. For example, if the hearth is made of brick and the existing flooring is hardwood, a transition strip made of hardwood or a similar material can create a seamless transition.
Safety Regulations and Considerations: Ensuring a Safe and Compliant Hearth
Building a fireplace hearth requires strict adherence to safety regulations and consideration of potential hazards to ensure the safety of the occupants and the longevity of the structure.
Adhering to Building Codes: Local building codes dictate specific requirements for fireplace hearths, including minimum dimensions, material specifications, and clearance requirements. Consulting with the local building department or a qualified contractor is essential to ensure compliance with these codes. Failure to adhere to building codes can result in safety hazards and potential fines or legal issues. Building codes are designed to protect the health, safety, and welfare of the public, so it is crucial to follow them carefully.
Using Non-Combustible Materials: As previously mentioned, all materials used in the construction of the hearth must be non-combustible. This includes the hearth materials themselves, as well as any mortar or grout used. Using combustible materials can create a significant fire hazard and should be strictly avoided. Verify that all materials used are specifically rated for high-temperature applications. Consider using a fire-resistant sealant to further protect the hearth and surrounding areas.
Maintaining Proper Clearances: Maintaining proper clearances between the fireplace and combustible materials is crucial for preventing fires. Building codes typically specify minimum clearances between the fireplace opening and walls, ceilings, and other combustible materials. These clearances should be carefully observed during the construction of the hearth. Additionally, ensure that any curtains, furniture, or other combustible items are kept a safe distance from the fireplace opening. Regularly inspect the fireplace and surrounding areas to ensure that no combustible materials are too close.
Ensuring Adequate Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is essential for the safe and efficient operation of a fireplace. The fireplace should be properly vented to prevent the buildup of carbon monoxide and other harmful gases. Regular inspections of the chimney and flue are crucial to ensure they are free of obstructions and in good working order. Installing a carbon monoxide detector in the vicinity of the fireplace is highly recommended to provide an early warning of any potential carbon monoxide leaks. If any signs of carbon monoxide poisoning are detected, such as headaches, dizziness, or nausea, immediately evacuate the premises and seek medical attention.
By following these guidelines and exercising diligence throughout the planning, construction, and maintenance of a fireplace hearth, a homeowner can create a safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing addition to their home that provides warmth and enjoyment for years to come.

How To Build A Diy Built In Fireplace With An Electric Insert The Creative Mom

How To Build A Fireplace Red Cottage Chronicles

How To Build A Fireplace Surround Beneath My Heart

Updating Fireplace Hearth No Demolition Required Single Girl S Diy

How To Build A Concrete Fireplace Hearth

I Built A Fireplace Easier Than Thought

Easy Fireplace Mantel Diy

Diy Fireplace Makeover At Home With The Barkers

Building An Easy Modern Fireplace Mantel Young House Love

How To Build A Modern Fireplace Surround Hana S Happy Home
Related Posts