Basement Gas Fireplace: A Comprehensive Guide
A basement gas fireplace presents a compelling option for supplementing heating, enhancing ambiance, and increasing the overall value of a home. Unlike traditional wood-burning fireplaces, gas fireplaces offer convenience, efficiency, and cleaner operation, making them particularly well-suited for the unique environment of a basement. However, selecting, installing, and maintaining a gas fireplace in a below-ground space requires careful consideration of factors such as ventilation, safety regulations, and proper sizing to ensure optimal performance and safety. This exposition will explore the key aspects of basement gas fireplaces, offering a comprehensive overview of the technology, its advantages, and the critical considerations for a successful installation.
Advantages of a Gas Fireplace in the Basement
The installation of a gas fireplace in a basement offers several distinct advantages compared to other heating solutions or alternative fireplace types. These advantages contribute to the growing popularity of gas fireplaces as a desirable feature in modern homes. These perks include ease of use and improved energy efficiency.
Convenience and Ease of Use: Gas fireplaces provide unparalleled convenience. With the simple push of a button or flick of a switch, a gas fireplace ignites, providing instant warmth and ambiance. There is no need to gather, stack, or kindle wood, eliminate ash disposal, and offer thermostat-controlled operation for consistent heat. The convenience factor makes gas fireplaces an attractive option for homeowners seeking supplemental heating without the hassle of traditional wood-burning stoves.
Improved Energy Efficiency: Modern gas fireplaces are designed for optimal energy efficiency. Direct vent models, in particular, draw combustion air from outside the house and vent exhaust gases directly outdoors. This sealed system minimizes heat loss and prevents the introduction of potentially harmful combustion byproducts into the living space. Many gas fireplaces also feature programmable thermostats and remote controls, allowing for precise temperature control and energy savings. The efficiency of gas fireplaces translates to lower heating bills and a reduced environmental footprint.
Cleanliness and Reduced Maintenance: Unlike wood-burning fireplaces, gas fireplaces produce minimal soot, ash, and creosote. This cleanliness translates to reduced maintenance requirements, eliminating the need for frequent chimney cleaning and ash disposal. Gas fireplaces also contribute to improved indoor air quality by reducing the emission of particulate matter and other pollutants associated with wood-burning. The clean-burning nature of gas fireplaces makes them a healthy and environmentally responsible heating option.
Aesthetic Versatility: Gas fireplaces are available in a wide variety of styles, sizes, and finishes, allowing homeowners to customize the look and feel of their basement living space. From traditional log sets to contemporary glass media options, gas fireplaces can be tailored to complement any décor. The aesthetic versatility of gas fireplaces makes them a valuable addition to any basement renovation or remodeling project, enhancing the visual appeal and overall value of the home.
Critical Considerations for Basement Gas Fireplace Installation
Installing a gas fireplace in a basement presents unique challenges that necessitate careful planning and execution. Several critical considerations must be addressed to ensure a safe, efficient, and code-compliant installation. These considerations encompass ventilation, safety, and adherence to local building codes. Failure to address these aspects can lead to serious consequences, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire hazards, and property damage.
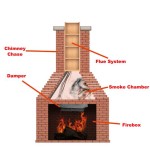
Ventilation Requirements: Adequate ventilation is paramount when installing a gas fireplace in a basement. Unlike above-ground installations, basements often have limited natural airflow. Direct vent gas fireplaces are typically recommended for basement installations because they draw combustion air from outside the house and vent exhaust gases directly outdoors. These systems minimize the risk of carbon monoxide buildup and ensure optimal combustion efficiency. It is crucial to select a direct vent system that is properly sized for the basement space and that meets all applicable building codes.
Carbon Monoxide Detection: Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and deadly gas produced by incomplete combustion. Since gas fireplaces rely on combustion, it is essential to install functioning carbon monoxide detectors in the basement and on every level of the home. CO detectors should be located near sleeping areas and in areas where the fireplace is used. Regular testing and maintenance of CO detectors are crucial to ensure their proper function and to protect the occupants of the home. Hardwired CO detectors with battery backup are recommended for maximum safety.
Gas Line Installation and Safety: A qualified and licensed gas fitter must perform the gas line installation for a basement gas fireplace. The gas line must be properly sized and installed to meet the fireplace's gas pressure requirements. All connections must be leak-tested to ensure that there are no gas leaks. It is essential to follow all applicable gas piping codes and regulations to prevent gas leaks and potential explosions. A gas shut-off valve should be readily accessible near the fireplace for emergency shut-off purposes.
Building Codes and Permits: Before installing a gas fireplace in a basement, it is essential to obtain the necessary building permits from the local municipality. Building codes vary by location and may specify requirements for ventilation, clearances, and fire safety. It is the homeowner's responsibility to ensure that the installation complies with all applicable building codes to avoid potential fines or legal issues. A building inspector may need to inspect the installation to verify compliance with the code requirements.
Clearance to Combustibles: Gas fireplaces generate significant heat, and it is essential to maintain adequate clearance to combustible materials, such as wood framing, drywall, and furniture. The fireplace manufacturer's instructions will specify the minimum clearance requirements for different types of combustible materials. Failure to maintain adequate clearances can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. It is crucial to carefully follow the manufacturer's instructions and to ensure that the installation complies with all applicable clearance requirements.
Types of Gas Fireplaces Suitable for Basements
The market offers various types of gas fireplaces, each with distinct characteristics and suitability for basement installations. The choice of fireplace type depends on factors such as space availability, venting options, and aesthetic preferences. Understanding the different types of gas fireplaces is crucial for making an informed decision that meets the specific needs of the basement environment. Three common types are direct vent, vent-free, and B-vent fireplaces.
Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces: Direct vent gas fireplaces are the most popular and safest type for basement installations. These fireplaces draw combustion air from outside the house and vent exhaust gases directly outdoors through a sealed venting system. The sealed system prevents the introduction of combustion byproducts into the living space and minimizes heat loss. Direct vent fireplaces can be vented horizontally through an exterior wall or vertically through the roof. They offer greater flexibility in terms of placement and venting options compared to other types of gas fireplaces.
Vent-Free Gas Fireplaces: Vent-free gas fireplaces, also known as ventless fireplaces, do not require a chimney or venting system. They burn gas very efficiently and release combustion byproducts directly into the living space. While vent-free fireplaces offer convenience and ease of installation, they are not recommended for basements due to concerns about indoor air quality. Vent-free fireplaces can produce carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and water vapor, which can accumulate in poorly ventilated basements and pose health risks. Many jurisdictions prohibit the installation of vent-free fireplaces in confined spaces such as basements.
B-Vent Gas Fireplaces: B-vent gas fireplaces, also known as natural vent fireplaces, use a chimney or B-vent pipe to vent exhaust gases to the outside. They draw combustion air from the room in which they are installed. B-vent fireplaces are generally less efficient than direct vent fireplaces and require a dedicated chimney or vent pipe. They are typically not recommended for basements unless a suitable chimney or vent can be installed. The installation of a B-vent fireplace in a basement can be complex and expensive, requiring significant modifications to the home's structure.
In summary, selecting a gas fireplace for a basement involves a careful evaluation of various factors, including ventilation requirements, safety regulations, and aesthetic preferences. Direct vent gas fireplaces are generally the preferred choice due to their safety, efficiency, and flexibility. Vent-free and B-vent fireplaces may not be suitable for basement installations due to concerns about indoor air quality and venting limitations. Consulting with a qualified HVAC professional and adhering to local building codes is essential to ensure a safe and code-compliant installation.

Netnewsledger Things To Consider When Adding A Fireplace Your Basement

Will A Fireplace Heat Basements We Love Fire

Fireplace In Basement 101 Everything Homeowners Must Know

Check Out The Five Reasons Of Installing A Linear Fireplace

Factors To Consider Before Installing A Fireplace In Your Basement Elkstone Basements

Cozy Up With Fireplaces Electric Vs Gas Sheffield Homes Finished Basements And More

Heating Your Basement

How To Install A Gas Fireplace With Tile Surround And Wood Mantel Sima Spaces

Fireplace Insert Guide Fireplaces Direct Learning Center

Basement Fireplace Ideas Photos Houzz
Related Posts