Adding a Gas Fireplace to a Finished Basement: A Comprehensive Guide
A finished basement can significantly expand the usable living space of a home, offering opportunities for recreation, relaxation, or even a home office. Adding a gas fireplace to this space can enhance its comfort and aesthetic appeal, transforming a potentially cold and underutilized area into a cozy and inviting environment. However, installing a gas fireplace in a finished basement requires careful planning, adherence to safety regulations, and a thorough understanding of the installation process. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the key considerations and steps involved in adding a gas fireplace to a finished basement.
Assessing the Suitability of the Basement for a Gas Fireplace
Before embarking on the installation process, it is crucial to determine whether the finished basement is suitable for a gas fireplace. Several factors need to be evaluated, including the availability of gas and ventilation, structural considerations, and local building codes. A comprehensive assessment can help prevent costly mistakes and ensure a safe and compliant installation.
The first consideration is the availability of a gas supply. Natural gas or propane is required to fuel the fireplace. If the home already has a natural gas line, extending it to the basement may be relatively straightforward. However, if natural gas is not available, a propane tank installation will be necessary. This involves additional planning and safety requirements, including proper tank placement and ventilation. A qualified gas technician should be consulted to assess the existing gas line capacity and determine the feasibility of extending it to the basement. The technician can also advise on the appropriate size of the propane tank if that is the chosen fuel source.
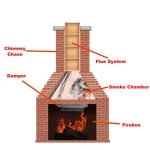
Ventilation is another critical factor. Gas fireplaces require a venting system to safely exhaust combustion byproducts, such as carbon monoxide, to the outside. There are two primary types of venting systems: direct vent and vent-free. Direct vent systems draw combustion air from outside and exhaust it outside through a sealed system, making them a safer and more efficient option. Vent-free systems, on the other hand, do not require venting to the exterior. However, they release combustion byproducts directly into the room, which can pose health risks if not properly managed. Many jurisdictions have restrictions or outright bans on vent-free gas fireplaces due to safety concerns. Therefore, direct vent systems are generally recommended for basement installations.
Structural considerations also play a role. The floor must be able to support the weight of the fireplace and any associated hearth materials. In some cases, reinforcement may be required. The location of the fireplace should also be chosen carefully, considering factors such as proximity to combustible materials and the overall layout of the basement. It is advisable to consult with a structural engineer to assess the load-bearing capacity of the floor and determine the best location for the fireplace. Furthermore, the framing around the fireplace must adhere to specific clearance requirements to prevent fire hazards.
Finally, understanding and complying with local building codes is essential. Building codes vary by jurisdiction and may specify requirements for gas line installation, venting, fire safety, and electrical connections. Obtaining the necessary permits before starting the installation is crucial to avoid fines and ensure compliance with regulations. A local building inspector can provide information on the specific codes that apply to the basement and the required permits.
Selecting the Right Gas Fireplace for the Basement
Choosing the appropriate gas fireplace model is a crucial step in the installation process. Several factors should be considered, including the size of the basement, the desired heat output, and the aesthetic style. Selecting a model that is both functional and visually appealing can enhance the overall comfort and ambiance of the finished basement.
The size of the basement is a primary consideration when determining the appropriate heat output. A gas fireplace that is too large for the space can overheat the room, while one that is too small may not provide adequate warmth. The heat output of a gas fireplace is measured in British thermal units (BTUs). Calculating the square footage of the basement and consulting with a fireplace specialist can help determine the appropriate BTU rating. Typically, a BTU rating of 30 to 40 BTUs per square foot is sufficient for heating a basement.
The venting system is another important factor to consider. As mentioned earlier, direct vent systems are generally recommended for basement installations due to their safety and efficiency. Direct vent fireplaces can be vented horizontally through an exterior wall or vertically through the roof. The choice of venting method will depend on the layout of the basement and the location of the fireplace. Horizontal venting is typically easier to install in basements, while vertical venting may be necessary if there are obstructions or if the fireplace is located in the center of the room.
The aesthetic style of the fireplace should also complement the overall design of the finished basement. Gas fireplaces are available in a wide range of styles, from traditional to contemporary. Some models feature realistic-looking logs and flames, while others have a more modern and minimalist design. Selecting a style that matches the existing décor and personal preferences can enhance the visual appeal of the basement. Consider the facing materials as well, such as brick, stone, or tile, as these can significantly impact the overall look of the fireplace.
Finally, energy efficiency is an important consideration. Look for gas fireplaces with high energy efficiency ratings, as these models will consume less gas and save money on heating costs. Some models also feature programmable thermostats and remote controls, which can further improve energy efficiency and convenience. Energy-efficient fireplaces not only reduce heating expenses but also minimize environmental impact.
The Installation Process and Safety Considerations
The installation of a gas fireplace in a finished basement is a complex process that should ideally be performed by a qualified professional. Proper installation is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and compliance with building codes. While some homeowners may attempt a DIY installation, it is generally recommended to hire a licensed gas fitter or HVAC technician with experience in gas fireplace installations.
The first step in the installation process is to prepare the area. This involves clearing the space around the fireplace location and protecting the surrounding surfaces. The gas line will need to be extended to the fireplace location, and the venting system will need to be installed. A qualified gas technician should perform the gas line installation to ensure that it is done safely and correctly. The venting system must be installed according to the manufacturer's instructions to prevent leaks and ensure proper ventilation.
Next, the fireplace unit is installed. This involves connecting the gas line to the fireplace and securing the unit in place. The framing around the fireplace must adhere to specific clearance requirements to prevent fire hazards. The hearth is then installed, which is a non-combustible surface that extends in front of the fireplace to protect the flooring from sparks and embers. The hearth must meet specific size and material requirements according to building codes.
Once the fireplace is installed, it needs to be tested and inspected. A qualified gas technician should perform a leak test to ensure that there are no gas leaks. The venting system should also be inspected to ensure that it is functioning properly. A building inspector will typically inspect the installation to ensure that it complies with all applicable building codes. This inspection is crucial for obtaining the necessary permits and ensuring the safety of the installation.
Safety considerations are paramount throughout the installation process. Carbon monoxide detectors should be installed in the basement to alert occupants of any dangerous levels of carbon monoxide. The fireplace should be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure that it is functioning properly. It is also important to educate all household members on the safe operation of the fireplace, including proper ventilation procedures and emergency shut-off procedures.
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the long-term safety and efficiency of the gas fireplace. This includes cleaning the fireplace, inspecting the venting system, and checking for any signs of damage or wear. A qualified technician should perform an annual inspection and maintenance service to ensure that the fireplace is functioning properly and safely. Neglecting maintenance can lead to malfunctions, reduced efficiency, and potential safety hazards.
Adding a gas fireplace to a finished basement can significantly enhance the comfort and value of the home. By carefully assessing the suitability of the basement, selecting the right gas fireplace model, and ensuring proper installation and maintenance, homeowners can enjoy the warmth and ambiance of a gas fireplace for years to come.

Netnewsledger Things To Consider When Adding A Fireplace Your Basement

Fireplace In Basement 101 Everything Homeowners Must Know

Will A Fireplace Heat Basements We Love Fire

Gas Fireplace For Your Basement

Basement Fireplaces Builders

Fireplace In Basement 101 Everything Homeowners Must Know

How To Install A Gas Fireplace With Tile Surround And Wood Mantel Sima Spaces

Factors To Consider Before Installing A Fireplace In Your Basement Elkstone Basements

Fireplace Basement Renovation Hamilton On Remodeling Design

How To Install A Gas Fireplace With Tile Surround And Wood Mantel Sima Spaces
Related Posts