```html
Gas or Wood Fireplace: A Comprehensive Comparison
The choice between a gas or wood fireplace is a significant decision for homeowners seeking to add warmth and ambiance to their living spaces. Both options offer unique advantages and disadvantages, making the selection process dependent on individual priorities, lifestyle, and budget. This article provides a comprehensive overview of gas and wood fireplaces, examining their key features, benefits, drawbacks, and operational considerations to assist in making an informed decision.
Key Point 1: Installation and Cost Considerations
Installation costs are a primary factor influencing the decision between gas and wood fireplaces. Wood-burning fireplaces typically require a chimney, which can be a significant expense if one is not already present. The construction or renovation of a chimney involves structural work, masonry, and potentially roofing modifications, contributing to higher initial costs.
Gas fireplaces, conversely, often require a gas line installation, which can be less expensive than chimney construction, particularly if a gas line is already accessible near the desired fireplace location. The installation process involves connecting the fireplace to the gas supply, ensuring proper ventilation, and testing for leaks. The complexity and cost of gas line installation depend on the distance to the existing gas meter and any necessary permitting requirements.
Beyond the initial installation, ongoing costs also differ significantly. Wood-burning fireplaces necessitate the purchase of firewood, which can fluctuate in price depending on the type of wood, quantity, and geographical location. The storage of firewood also requires dedicated space and protection from the elements. Gas fireplaces, on the other hand, incur natural gas or propane costs, which are typically lower than the ongoing expenses associated with firewood. However, gas prices can fluctuate based on market conditions and regional availability.
Maintenance costs should also be considered. Wood fireplaces require regular cleaning to remove ash and creosote buildup, which can pose a fire hazard if left unattended. Chimney sweeping is a necessary service to prevent creosote accumulation and ensure proper ventilation. Gas fireplaces, while requiring less frequent cleaning, may need occasional maintenance by a qualified technician to inspect gas lines, burners, and venting systems.
Key Point 2: Operational Efficiency and Environmental Impact
The operational efficiency of gas and wood fireplaces impacts both heating performance and environmental consequences. Wood-burning fireplaces, while providing a traditional ambiance, tend to be less efficient than gas fireplaces. A significant portion of the heat generated by a wood fire is often lost through the chimney, resulting in lower overall heating efficiency. Moreover, wood-burning fireplaces produce smoke, particulate matter, and other pollutants that contribute to air pollution.
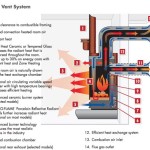
Modern gas fireplaces, particularly those with sealed combustion systems, offer significantly higher energy efficiency. These fireplaces draw combustion air from outside the home and vent exhaust gases directly outside, minimizing heat loss and improving indoor air quality. Gas fireplaces also offer precise temperature control, allowing homeowners to adjust the heat output to their desired level.
The environmental impact of each type of fireplace is a crucial consideration. Wood-burning fireplaces contribute to deforestation if firewood is not sourced sustainably. Burning wood releases carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. While wood is considered a renewable resource, the rate of deforestation and the carbon footprint associated with harvesting, transporting, and burning wood can offset its renewable benefits.
Gas fireplaces, while burning fossil fuels, generally produce fewer pollutants than wood-burning fireplaces. Natural gas is a relatively clean-burning fuel, and modern gas fireplaces are designed to minimize emissions. However, the extraction, processing, and transportation of natural gas can have environmental consequences, including methane leakage, which is a potent greenhouse gas. The overall environmental impact of gas fireplaces depends on the source of the gas and the efficiency of the combustion system.
Key Point 3: Aesthetics, Maintenance, and Safety
Aesthetics play a crucial role in the choice between gas and wood fireplaces. Wood-burning fireplaces offer a traditional, rustic ambiance with the crackling sounds and flickering flames that many find appealing. The authentic look and feel of burning wood can create a cozy and inviting atmosphere. However, maintaining a wood fire requires constant tending, adding wood, and managing the ashes.
Gas fireplaces offer a more convenient and low-maintenance alternative. They can be ignited with the flip of a switch or the press of a button, providing instant warmth and ambiance. Modern gas fireplaces offer realistic-looking flames and log sets, mimicking the appearance of a wood fire. The convenience and ease of use make gas fireplaces a popular choice for homeowners seeking a hassle-free heating solution.
Maintenance requirements differ significantly between the two types of fireplaces. Wood-burning fireplaces require regular cleaning to remove ash and creosote buildup. Chimney sweeping is essential to prevent chimney fires and ensure proper ventilation. The periodic maintenance of wood-burning fireplaces can be physically demanding and time-consuming.
Gas fireplaces require less frequent cleaning and maintenance. However, it is important to have the fireplace inspected annually by a qualified technician to ensure proper operation and safety. Gas leaks, faulty burners, and venting problems can pose safety hazards if left unaddressed. Regular maintenance helps prevent these issues and ensures the safe and efficient operation of the gas fireplace.
Safety considerations are paramount when choosing between gas and wood fireplaces. Wood-burning fireplaces pose a risk of sparks, embers, and smoke entering the home. A properly installed and maintained chimney is essential to prevent chimney fires and carbon monoxide poisoning. A fire screen or door is necessary to contain sparks and prevent accidental burns.
Gas fireplaces also require safety precautions. Carbon monoxide detectors are essential to alert homeowners to any potential gas leaks or incomplete combustion. Proper ventilation is crucial to prevent the buildup of carbon monoxide inside the home. Regular inspections and maintenance by a qualified technician help ensure the safe operation of the gas fireplace and minimize the risk of gas leaks or explosions.
```Converting A Wood Burning Fireplace Into Gas Heat Glo

Wood Fireplaces Gas Conversion That Counts
Can I Convert My Wood Burning Fireplace To Gas Woodlanddirect Com

Pros And Cons Of Gas Wood Electric Fireplaces Tripod International

Want To Convert Gas Wood Fireplace Full Service Chimney

Fireplaces Inserts Wood Gas Fireplace Xtrordinair

Pros And Cons Of Gas Wood Electric Fireplaces Tripod International

Gas Logs Vs Wood Burning Outdoor Fireplaces Green Okie

Gas Logs Vs Wood Burning Who Wins Vertical Chimney Care
.aspx?strip=all)
How To Diffeiate Inserts Fireplaces Regency
Related Posts