Gas Fired Fireplaces: A Comprehensive Overview
Gas fired fireplaces have become increasingly popular as a convenient and efficient alternative to traditional wood-burning fireplaces. They offer a variety of benefits, including ease of use, consistent heat output, and reduced maintenance. This article provides a comprehensive overview of gas fired fireplaces, covering their components, types, advantages, disadvantages, installation considerations, and maintenance requirements.
Components of a Gas Fired Fireplace
A gas fired fireplace comprises several key components that work together to generate and distribute heat. Understanding these components is crucial for proper operation and maintenance.
Gas Burner: The heart of the gas fireplace is the burner, which mixes natural gas or propane with air and ignites the mixture to produce a flame. Burners are typically constructed from stainless steel or cast iron for durability and longevity. They are designed to distribute the gas evenly across the flame pattern, optimizing heat output and visual appeal.
Gas Valve: The gas valve controls the flow of gas to the burner. It is typically a manual or automatic valve that responds to user input, such as a switch or a remote control. Automatic valves often include safety features, such as a thermocouple or thermopile, which shut off the gas supply if the pilot light is extinguished.
Pilot Light or Electronic Ignition: The pilot light (or electronic ignition system) initiates the burning process. A pilot light is a small, continuous flame that ignites the main burner when gas is supplied. Electronic ignition systems use a spark or hot surface igniter to light the burner, eliminating the need for a continuous pilot light and conserving energy. These systems are more common in newer models.
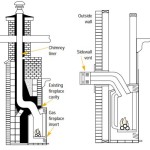
Firebox: The firebox is the enclosed chamber that houses the burner and the flames. It is typically constructed from steel or cast iron and is designed to withstand high temperatures. The interior of the firebox is often lined with refractory materials, such as ceramic fiber, to reflect heat and enhance the visual appearance of the flames.
Ventilation System: Gas fireplaces require a ventilation system to exhaust combustion byproducts safely outside the building. There are two primary types of venting systems: direct vent and B-vent. Direct vent systems draw combustion air from outside the building and exhaust combustion gases directly outside through a sealed system. B-vent systems use room air for combustion and vent exhaust gases through a chimney or flue that is connected to other appliances. Direct vent systems are often preferred due to their improved safety and efficiency.
Decorative Logs or Media: Gas fireplaces typically include decorative logs, stones, or glass media to enhance their aesthetic appeal. These materials are designed to withstand high temperatures and are strategically arranged to create a realistic and visually appealing flame pattern. They are often made from ceramic or refractory materials.
Control System: Most gas fireplaces have a control system that allows users to adjust the flame height, heat output, and other settings. The control system may consist of a simple on/off switch, a remote control, or a thermostat that automatically regulates the temperature.
Types of Gas Fired Fireplaces
Gas fireplaces come in various designs and configurations to suit different aesthetic preferences and installation requirements. Understanding the different types is crucial for selecting the right fireplace for a specific application.
Gas Inserts: Gas inserts are designed to be installed inside existing masonry fireplaces. They provide a convenient way to convert a traditional wood-burning fireplace to a gas-fueled appliance. Gas inserts typically include a sealed firebox, a gas burner, a ventilation system, and decorative logs or media. They offer improved efficiency and reduced emissions compared to open-hearth wood-burning fireplaces.
Gas Log Sets: Gas log sets consist of a burner and decorative logs that are placed inside an existing masonry fireplace. They offer a more affordable alternative to gas inserts but do not provide the same level of efficiency or safety. Gas log sets typically require an open damper for ventilation, which can result in heat loss and increased energy consumption. Vented and vent-free options are available, with vent-free options requiring careful consideration of room size and ventilation.
Direct Vent Fireplaces: Direct vent fireplaces are designed to be installed against an exterior wall, allowing for direct venting of combustion gases outside the building. They are highly efficient and safe, as they draw combustion air from outside and exhaust combustion gases directly outside. Direct vent fireplaces offer a wide range of design options, including traditional and contemporary styles.
Vent-Free Fireplaces: Vent-free fireplaces do not require a chimney or vent, as they burn gas very cleanly, producing minimal combustion byproducts. They are typically equipped with oxygen depletion sensors (ODS) that shut off the gas supply if the oxygen level in the room drops to an unsafe level. Vent-free fireplaces are subject to local building codes and are not permitted in all jurisdictions. They generally require larger room sizes to comply with safety standards.
Linear Fireplaces: Linear fireplaces are characterized by their long, horizontal flame pattern. They typically feature a contemporary design and are often used as a focal point in modern living spaces. Linear fireplaces are available in direct vent and vent-free configurations and can be installed in a variety of locations, including walls, corners, and islands.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gas Fired Fireplaces
Gas fired fireplaces offer several advantages over traditional wood-burning fireplaces, but they also have some potential drawbacks. A thorough understanding of these factors is vital for making an informed decision.
Advantages:
Convenience: Gas fireplaces are convenient to operate, as they can be turned on and off with the flip of a switch or the press of a button. They eliminate the need for storing and handling firewood, as well as the mess associated with wood-burning fireplaces.
Consistent Heat Output: Gas fireplaces provide consistent and predictable heat output, allowing users to maintain a comfortable temperature in their homes. They can be easily adjusted to meet changing heating needs.
Reduced Maintenance: Gas fireplaces require less maintenance than wood-burning fireplaces. There is no need to clean up ashes or sweep the chimney regularly. Routine maintenance typically involves inspecting the burner, gas valve, and ventilation system annually.
Improved Safety: Gas fireplaces are generally safer than wood-burning fireplaces, as they produce less smoke and creosote. They also eliminate the risk of sparks and embers escaping from the firebox.
Environmental Benefits: Gas fireplaces produce fewer emissions than wood-burning fireplaces, contributing to improved air quality. They burn gas more efficiently and cleanly, reducing their environmental impact.
Disadvantages:
Fuel Costs: The cost of natural gas or propane can fluctuate, potentially increasing the overall heating expenses. The expense directly depends on the frequency of use and local gas prices.
Reliance on Gas Supply: Gas fireplaces rely on a consistent supply of natural gas or propane. In the event of a power outage or gas supply interruption, the fireplace may not function.
Installation Costs: The initial installation cost of a gas fireplace can be higher than that of a wood-burning fireplace, especially if a new gas line or ventilation system is required.
Aesthetics: While gas fireplaces offer a realistic flame appearance, some individuals may prefer the aesthetics of a wood-burning fire, including the crackling sounds and the aroma of burning wood.
Complexity: Gas fireplaces involve complex components and systems, which can make repairs more challenging and require specialized expertise.
Installation Considerations for Gas Fired Fireplaces
Proper installation is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a gas fired fireplace. Installation should be performed by a qualified and licensed professional who is familiar with local building codes and safety regulations.
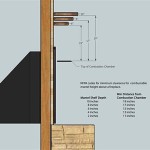
Location: The location of the fireplace should be carefully considered, taking into account factors such as the proximity to gas lines, ventilation requirements, and aesthetic preferences. The fireplace should be installed in a location that allows for adequate clearance from combustible materials.
Gas Line Connection: A gas line must be properly connected to the fireplace by a qualified gas fitter. The gas line should be sized appropriately to supply the required gas flow for the fireplace. Safety shut-off valves and pressure regulators should be installed as required by code.
Ventilation System Installation: The ventilation system should be installed in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions and local building codes. Direct vent systems should be properly sealed to prevent leaks. B-vent systems should be connected to a chimney or flue that is in good condition and free from obstructions.
Electrical Connections: Some gas fireplaces require electrical connections for features such as electronic ignition or blowers. These connections should be made by a qualified electrician in accordance with local electrical codes.
Clearances: Proper clearances from combustible materials must be maintained to prevent fire hazards. The manufacturer's instructions will specify the required clearances for different parts of the fireplace.
Maintenance of Gas Fired Fireplaces
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term performance and safety of a gas fired fireplace. Maintenance should be performed annually by a qualified technician.
Inspection: The fireplace should be inspected for any signs of damage or wear, such as cracks in the firebox, loose connections, or corrosion on the burner. The gas valve and pilot light should also be inspected for proper operation.
Cleaning: The burner and firebox should be cleaned to remove any debris or soot that may have accumulated. The decorative logs or media should also be cleaned to maintain their appearance.
Ventilation System Check: The ventilation system should be checked for any obstructions or leaks. The chimney or flue should be inspected for creosote buildup, which can pose a fire hazard.
Gas Leak Test: A gas leak test should be performed to ensure that there are no leaks in the gas line or connections. A soapy water solution can be used to detect leaks.
Pilot Light Adjustment: The pilot light may need to be adjusted to ensure that it is burning properly. The flame should be blue in color and should not be too small or too large.
Professional Servicing: It is recommended to have the fireplace professionally serviced annually by a qualified technician. The technician will perform a comprehensive inspection and maintenance check and address any potential issues. This servicing will ensure proper operation and will prolong the lifespan of the appliance.
By understanding the components, types, advantages, disadvantages, installation considerations, and maintenance requirements of gas fired fireplaces, consumers can make informed decisions and enjoy the benefits of a safe and efficient heating appliance.

Gas Burning Fireplaces Sierra Hearth And Home

Gas Fireplace Inserts Are Incredibly Easy To Use And Offer A Clean Burning Convenient Alternative Heat Insert

Napoleon Ascent Dx42 Direct Vent Gas Burning Fireplace

Convert To Gas Installing Fireplace Inserts Doctor Flue

Fireplaces Inserts Wood Gas Fireplace Xtrordinair
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ventless-gas-fireplaces-4160746-hero-f9d4bdcd9bd446eb84406de306f790ba.jpg?strip=all)
How To Pick Out A Ventless Gas Fireplace

Pros And Cons Of Gas Wood Electric Fireplaces Tripod International

Benefits Popularity Of Gas Fireplaces Stoves And Fireplace Inserts

Can A Wood Burning Fireplace Be Converted To Gas The Flame Company

Is A Gas Fireplace Worth It
Related Posts