Gas Fireplace Logs: A Comprehensive Guide
Gas fireplace logs offer a convenient and aesthetically pleasing alternative to traditional wood-burning fireplaces. They provide the ambiance of a real fire without the associated mess, maintenance, and safety concerns. Understanding the different types, features, and installation considerations of gas fireplace logs is essential for homeowners seeking to enhance their living spaces with this increasingly popular heating solution.
This article provides a detailed overview of gas fireplace logs, covering various aspects from material composition to installation and maintenance. The goal is to equip readers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions when selecting and using gas fireplace logs.
Gas fireplace logs operate by burning natural gas or propane to create realistic-looking flames. They are typically arranged inside an existing fireplace, replacing the need for wood. The gas is fed through a burner system located beneath the logs, and the flames rise and flicker around the logs, creating a visually appealing effect.
One of the primary advantages of gas fireplace logs is their convenience. Unlike wood-burning fireplaces, they require no chopping, stacking, or storing of wood. Simply turn on the gas and ignite the burner, and the fire is ready. Similarly, turning off the fire is as easy as switching off the gas supply. This makes gas fireplace logs a user-friendly option for those who desire the ambiance of a fire without the hassle of wood.
Another significant benefit is reduced maintenance. Gas fireplace logs produce no ash, creosote, or other byproducts of combustion that require cleaning. This significantly reduces the amount of time and effort spent maintaining the fireplace. Regular inspections and occasional cleaning of the burner and logs are generally sufficient to keep the system in good working order.
Safety is also a key consideration. Gas fireplaces are generally safer than wood-burning fireplaces. They eliminate the risk of sparks, embers, and escaping flames that can cause fires. Additionally, gas fireplaces can be equipped with safety features such as oxygen depletion sensors (ODS) and automatic shut-off valves, which further enhance their safety.
However, it is important to acknowledge some potential drawbacks. Gas fireplaces do not produce the same level of radiant heat as wood-burning fireplaces. While they can effectively heat a room, they may not provide the same intense warmth as a traditional fire. This is an important consideration for those who prioritize heating performance.
Furthermore, gas fireplace logs are dependent on a gas supply. This means that they will not function during power outages unless a backup power source is available. This can be a disadvantage in areas prone to frequent power disruptions. The initial cost of installation can also be higher than setting up for a traditional wood-burning fireplace, though the long-term cost savings on wood and maintenance may offset this initial expense.
Types of Gas Fireplace Logs
Gas fireplace logs are broadly categorized into two main types: vented and vent-free (or ventless). Each type has its own set of characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
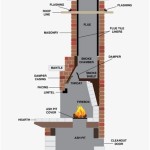
Vented Gas Logs: Vented gas logs are designed to be used in fireplaces with a functioning chimney. They produce a more realistic flame and higher heat output than vent-free logs. However, they also require a larger amount of gas to operate and are less energy-efficient. Vented logs must be used with the fireplace damper fully open to allow for proper ventilation of combustion gases. This also means that a significant amount of heat escapes up the chimney.
The primary advantage of vented gas logs is their realistic appearance. They produce a dynamic and flickering flame that closely resembles a real wood fire. This makes them a popular choice for those who prioritize aesthetics. Additionally, vented logs typically produce more heat than vent-free logs, making them a better choice for heating larger rooms.
However, vented gas logs are less energy-efficient than vent-free logs. A significant portion of the heat generated by the fire escapes up the chimney, reducing the overall heating efficiency. They require a larger amount of gas to operate, resulting in higher fuel costs. They also require a functioning chimney, which can be an added expense for homes that do not already have one.
Vent-Free Gas Logs: Vent-free gas logs, also known as ventless gas logs, are designed to be used in fireplaces without a chimney. They burn cleaner than vented logs and are more energy-efficient. However, they produce a less realistic flame and lower heat output. Vent-free logs are equipped with an oxygen depletion sensor (ODS) that shuts off the gas supply if the oxygen level in the room drops to a dangerous level.
The primary advantage of vent-free gas logs is their energy efficiency. They burn cleaner than vented logs and do not require a chimney, which eliminates heat loss through the chimney. This makes them a more cost-effective option for heating a room. They can be installed in homes without a chimney, providing greater flexibility in placement.
However, vent-free gas logs produce a less realistic flame than vented logs. The flame is typically smaller and less dynamic, which may be a drawback for those who prioritize aesthetics. They produce lower heat output than vented logs, making them less suitable for heating larger rooms. They also require careful monitoring of oxygen levels to ensure safe operation. Regular inspections of the ODS and proper ventilation are essential to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
Material and Construction
The materials used in the construction of gas fireplace logs play a significant role in their appearance, durability, and performance. The most common materials include ceramic fiber, refractory cement, and concrete.
Ceramic Fiber Logs: Ceramic fiber logs are lightweight and porous, allowing for excellent flame distribution. They are typically less expensive than other types of logs but may be less durable. Ceramic fiber provides a realistic texture and retains heat well, contributing to the efficiency of the fireplace. This material is also easy to mold, allowing manufacturers to create logs with intricate details and realistic wood grain.
However, ceramic fiber logs are more prone to damage than other types of logs. They can crack or break if mishandled or exposed to excessive heat. They may also degrade over time, requiring replacement. Their lightweight nature, while convenient for installation, can also make them susceptible to displacement if not properly secured within the firebox.
Refractory Cement Logs: Refractory cement logs are more durable and heat-resistant than ceramic fiber logs. They are heavier and more expensive but offer a longer lifespan. Refractory cement provides a strong and stable base for the flames, ensuring even heat distribution. This material is also less prone to cracking or breaking, making it a more reliable option for long-term use.
The increased durability of refractory cement logs comes at the cost of weight and price. These logs are heavier to handle and potentially more expensive than ceramic-fiber alternatives. They also tend to retain heat more slowly, extending the warm-up period of the fireplace.
Concrete Logs: Concrete logs are the most durable and heat-resistant option. They are very heavy and expensive but offer the longest lifespan. Concrete logs provide a solid and stable base for the flames, ensuring even heat distribution. This material is virtually indestructible and can withstand extremely high temperatures without damage.
However, the increased durability of concrete logs comes at a significant cost. They are extremely heavy and difficult to handle, requiring professional installation. They are also the most expensive type of gas fireplace logs. Concrete logs may also take longer to heat up than other types of logs, reducing their overall efficiency.
Beyond the base material, the construction of the logs also involves meticulous detailing to achieve a realistic appearance. Manufacturers often use molds and hand-painting techniques to replicate the texture, color, and grain of real wood. This attention to detail significantly enhances the aesthetic appeal of gas fireplace logs.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of gas fireplace logs. It is highly recommended to have a qualified professional install gas fireplace logs to ensure that all connections are secure and that the system is functioning properly.
Installation: The installation process typically involves connecting the gas line to the burner system, placing the logs in the firebox according to the manufacturer's instructions, and testing the system for leaks. A professional installer will ensure that the gas pressure is correct, that the burner is properly adjusted, and that all safety features are functioning correctly.
Before installation, it is important to inspect the fireplace and chimney (if applicable) to ensure that they are clean and in good working order. Any necessary repairs should be made before installing the gas fireplace logs. It is also important to ensure that the fireplace meets all local building codes and regulations.
For vent-free gas logs, it is essential to ensure that the room is properly ventilated. A carbon monoxide detector should be installed in the room to monitor oxygen levels and provide an early warning of any potential hazards.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential for maintaining the performance and safety of gas fireplace logs. This includes regular inspections of the burner system, cleaning the logs, and checking for leaks.
The burner system should be inspected regularly for any signs of damage or corrosion. The burner ports should be cleaned periodically to ensure proper flame distribution. Any debris or buildup should be removed to prevent clogging.
The logs should be cleaned periodically to remove any dust or soot. A soft brush or vacuum cleaner can be used to clean the logs. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasives, as these can damage the logs. It is important to consult the manufacturer's instructions for specific cleaning recommendations.
The gas line and connections should be checked regularly for leaks. A soap and water solution can be used to check for leaks. If any leaks are detected, the gas supply should be shut off immediately, and a qualified professional should be called to repair the leak.
In addition to regular maintenance, it is important to have the gas fireplace logs professionally inspected and serviced annually. A professional technician can identify and address any potential problems before they become serious. This will help to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the system.
By following these installation and maintenance guidelines, homeowners can enjoy the convenience and ambiance of gas fireplace logs for many years to come. Careful attention to detail and adherence to safety precautions are essential for ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.

The Best Gas Log Sets For 2024 Fireplaces Direct Learning Center

Napoleon Fiberglow 30 Gas With Burner Log Sets Gl30ne North Country Fire

What You Need To Know About Gas Fireplace Logs Fireplaces Direct Learning Center

Gas Logs What You Need To Know Before More

Gas Fireplace Log Bundle Woodstack 18 Harvest Exclusive Masters Services Chimney Sweep And Masonry

How Long Do Gas Logs Last To Replace Fireplace

Warming Trend Update Gas Logs To Improve Performance And Appearance Walton

Majestic Vdy Duzy Series Vented Gas Log Set

Hearth Home Realwood Gas Log Set Fireside

Rasmussen Wb White Birch Gas Logs Only
Related Posts