Bio Ethanol Fireplace Fuel: A Comprehensive Guide
Bio ethanol fireplace fuel is a renewable liquid biofuel derived primarily from the fermentation of sugars and starches found in plants and agricultural byproducts. Its utilization in ventless fireplaces offers a clean and efficient heating solution, characterized by minimal environmental impact compared to traditional fossil fuel-based options. This article provides a detailed overview of bio ethanol fireplace fuel, explaining its composition, production, benefits, safety considerations, and comparisons with alternative fuels.
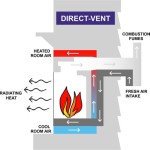
The increasing popularity of bio ethanol fireplaces stems from a confluence of factors including the desire for aesthetically pleasing heating solutions that are easy to install and operate, coupled with a growing awareness of environmental sustainability. Unlike traditional wood-burning fireplaces, bio ethanol fireplaces do not require a chimney or flue, making them suitable for a wide range of living spaces. Furthermore, the fuel itself burns cleanly, producing primarily carbon dioxide, water vapor, and a small amount of heat, minimizing smoke, soot, and ash production.
Understanding the Composition and Production of Bio Ethanol
Bio ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol, is a colorless, volatile, and flammable liquid. The chemical formula for ethanol is C2H5OH. Its production typically involves the fermentation of biomass rich in sugars and starches. Common feedstocks include corn, sugarcane, wheat, barley, and cellulosic materials such as wood chips and agricultural residues. The production process generally follows these steps:
1. Pretreatment: This step prepares the feedstock for fermentation. For starchy materials like corn, this involves grinding the grain and adding water to create a mash. Cellulosic materials require more complex pretreatment methods to break down the lignin and hemicellulose that encase the cellulose.
2. Hydrolysis: Starches and complex carbohydrates are broken down into simpler sugars. For starchy materials, this is achieved through enzymatic hydrolysis, where enzymes convert the starch into glucose. For cellulosic materials, acid or enzymatic hydrolysis is used to release sugars from the cellulose.
3. Fermentation: Sugars are fermented by yeast or bacteria to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide. The fermentation process typically takes several days, during which the microorganisms consume the sugars and generate ethanol as a byproduct.
4. Distillation: The resulting mixture, known as "beer" or "wash," contains ethanol, water, and other impurities. Distillation is used to separate the ethanol from the water and other components. The mixture is heated, and the ethanol, which has a lower boiling point than water, vaporizes and is collected and condensed.
5. Dehydration: The distilled ethanol typically contains a small amount of water. Dehydration is used to remove the remaining water to produce anhydrous ethanol, which is at least 99% pure. Molecular sieves or other drying agents are commonly used for this purpose.
6. Denaturing: To render the ethanol unfit for human consumption and avoid excise taxes, it is denatured by adding a small amount of denaturant, such as denatonium benzoate (Bitrex) or isopropyl alcohol. The denatured ethanol is then suitable for use as fuel.
The type and quality of the feedstock, as well as the efficiency of the production process, significantly influence the cost and environmental impact of bio ethanol. The production of bio ethanol from cellulosic materials is considered more sustainable than from food crops like corn, as it reduces competition with food production and utilizes waste materials.
Advantages of Using Bio Ethanol Fireplace Fuel
Bio ethanol fireplace fuel offers several advantages over traditional heating options, making it an increasingly popular choice for homeowners and businesses.
Environmental Friendliness: Bio ethanol is a renewable fuel source, derived from plant-based materials. When burned, it produces significantly fewer greenhouse gas emissions than fossil fuels. The carbon dioxide released during combustion is balanced by the carbon dioxide absorbed by the plants during their growth, creating a near-carbon-neutral cycle. While not strictly carbon neutral due to the energy inputs required for production and transportation, bio ethanol still boasts a lower carbon footprint compared to alternatives.
Clean Burning: Unlike wood-burning or gas fireplaces, bio ethanol fireplaces produce no smoke, soot, ash, or harmful emissions. The primary byproducts of combustion are carbon dioxide and water vapor. This clean burning characteristic eliminates the need for a chimney or flue, simplifying installation and reducing maintenance.
Ease of Use and Installation: Bio ethanol fireplaces are relatively easy to install and operate. They do not require gas lines, electrical connections, or chimney systems. Many models are freestanding and can be placed directly in a room, while others can be recessed into walls or integrated into furniture. Refueling is simple, involving pouring the bio ethanol fuel into the designated burner container.
Aesthetic Appeal: Bio ethanol fireplaces offer a modern and stylish aesthetic. They are available in a wide range of designs, from minimalist to ornate, and can complement various interior design styles. The visible flame provides a warm and inviting ambiance, enhancing the atmosphere of a room.
Cost-Effectiveness in Specific Scenarios: While the initial cost of a bio ethanol fireplace might be comparable to other options, the absence of installation costs related to venting and gas lines can make it more cost-effective, especially for apartments or homes where installing a traditional fireplace is impractical or expensive. The ongoing cost of fuel depends on usage and the price of bio ethanol in the local market.
No Requirement for Venting: Bio ethanol fireplaces do not require a chimney or flue, which is a significant advantage for apartments and homes where traditional fireplaces are not feasible. This also allows for greater flexibility in fireplace placement, as it is not constrained by existing venting systems.
Safety Precautions and Best Practices for Using Bio Ethanol Fuel
While bio ethanol fireplace fuel is generally considered safe, it is crucial to adhere to safety precautions and best practices to prevent accidents and ensure proper operation.
Use Only Approved Bio Ethanol Fuel: It is essential to use only bio ethanol fuel specifically designed for fireplaces. Avoid using other types of alcohol or flammable liquids, as they may not burn cleanly or safely. Check the label to ensure the fuel is specifically intended for indoor fireplace use.
Proper Ventilation: Although bio ethanol fireplaces produce minimal emissions, adequate ventilation is still important. Ensure that the room is well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of carbon dioxide. Opening a window or door periodically can help maintain air quality.
Refueling Safety: Never refuel a bio ethanol fireplace while it is burning or still hot. Allow the burner to cool completely before adding more fuel. Avoid overfilling the burner container, as this can lead to spills and potential fire hazards. Use a funnel to prevent spills during refueling.
Storage of Bio Ethanol Fuel: Store bio ethanol fuel in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from sources of heat, sparks, or open flames. Keep the fuel container tightly closed to prevent evaporation and spills. Store the fuel out of reach of children and pets.
Fire Safety Equipment: Keep a fire extinguisher or fire blanket nearby in case of an emergency. Familiarize yourself with the proper use of fire safety equipment.
Supervision: Never leave a burning bio ethanol fireplace unattended, especially if children or pets are present. Ensure that the fireplace is placed on a stable and non-flammable surface, away from curtains, furniture, and other combustible materials.
Read and Follow Manufacturer's Instructions: Always read and follow the manufacturer's instructions for your specific bio ethanol fireplace model. These instructions provide important information on installation, operation, maintenance, and safety precautions.
Carbon Monoxide Detectors: While bio ethanol fireplaces produce very little carbon monoxide compared to fossil fuel burning appliances, it's always a good safety practice to have working carbon monoxide detectors installed in your home, especially near sleeping areas. This adds an extra layer of protection in case of any incomplete combustion due to unforeseen issues.
Adhering to these safety precautions and best practices will minimize the risk of accidents and ensure the safe and enjoyable use of a bio ethanol fireplace.

Promo Regal Flame Prime Ventless Bio Ethanol Fireplace Fuel 6 Quarts Cicil 0 3x Jakarta Utara Home And Kitchen Usa Tokopedia

Unscented Bioethanol Fireplace Fuel 4 X 5 Litres

12l Bioethanol Fuel For Fireplaces 12x1l

E Nrg Bioethanol The Best Fuel For Your Ethanol Fire

Bio Ethanol Vs Isopropyl What S The Best Fireplace Fuel American

Liquid Bio Ethanol Fireplace Fuel Ignis Clean Burning

1l Bioethanol Fuel For Fireplaces

Liquid Bio Ethanol Fireplace Fuel Ignis Clean Burning

Bioethanol Fuel E Nrg Ecosmart Fire

Bioethanol Fires Chesneys
Related Posts