Fireplace Pellet Stoves: An Efficient Heating Alternative
Fireplace pellet stoves represent a modern and efficient alternative to traditional wood-burning fireplaces and stoves. They utilize compressed wood or biomass pellets as fuel, offering a consistent and controlled heating experience. These stoves are increasingly popular options for homeowners seeking energy-efficient and environmentally conscious heating solutions.
While sharing the visual appeal of a traditional fireplace, pellet stoves operate on different principles. Understanding their workings, benefits, and maintenance needs is crucial for making an informed decision when considering this heating appliance.
How Fireplace Pellet Stoves Work
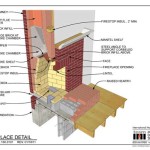
Unlike wood-burning fireplaces that rely on manually adding logs and controlling airflow, pellet stoves operate through an automated process. The process begins with the storage hopper, a container within the stove that holds a supply of pellets. These pellets are fed into a burn pot, a designated area for combustion, via an auger system. The auger, a screw-like mechanism, is controlled by an electric motor, delivering pellets at a pre-determined rate based on the desired heat output.
Once in the burn pot, the pellets are ignited. Most pellet stoves use an automatic igniter, an electric element that heats up to a high temperature, initiating combustion. Some older models may require manual ignition using a gel starter or similar product. Oxygen is crucial for the combustion process. A combustion fan (or blower) draws air into the burn pot, providing the necessary oxygen for efficient burning. The rate of airflow is often adjustable, allowing for control over the intensity of the flame and heat output.
The heat generated from burning the pellets radiates into the room. Many pellet stoves incorporate a convection fan to circulate the heated air more effectively, distributing warmth evenly throughout the space. This fan helps to reduce temperature stratification, preventing hot air from accumulating near the ceiling while the floor remains cold.
The exhaust produced during combustion is vented outside through a specialized vent pipe, typically made of stainless steel. This vent pipe differs from a traditional chimney and is designed for the lower temperatures and different properties of pellet stove exhaust. Regular cleaning of the vent pipe is essential to prevent creosote buildup and ensure proper exhaust flow.
Finally, the ash produced during combustion collects in an ash pan. This pan requires periodic emptying, typically every few days or weeks, depending on the stove's usage and the ash content of the pellets. Some higher-end models feature automatic ash removal systems, further simplifying the maintenance process.
Advantages of Fireplace Pellet Stoves
Pellet stoves offer several advantages over traditional wood-burning fireplaces, contributing to their increasing popularity among homeowners.
Efficiency: Pellet stoves are significantly more efficient than traditional wood-burning fireplaces. They typically achieve efficiencies of 75-90%, meaning that a larger percentage of the fuel's energy is converted into usable heat for the home. This is due to the controlled combustion process and the ability to precisely regulate airflow and fuel delivery. Traditional fireplaces, on the other hand, can have efficiencies as low as 10-20%, with much of the heat escaping up the chimney. The improved efficiency of pellet stoves translates to lower fuel costs and reduced environmental impact.
Convenience: Pellet stoves offer greater convenience compared to wood-burning fireplaces. The automated fuel feed system eliminates the need for manually loading logs, and the thermostat control allows for precise temperature regulation. Users can set the desired temperature, and the stove will automatically adjust the fuel feed rate to maintain a consistent level of warmth. Some models even offer programmable timers, allowing users to schedule heating cycles based on their needs. The reduced need for manual labor and increased control over the heating process make pellet stoves a convenient option for busy homeowners.
Environmental Considerations: Pellet stoves are generally considered to be more environmentally friendly than wood-burning fireplaces. Pellets are typically made from renewable biomass resources, such as wood waste from sawmills and furniture factories. Burning pellets produces significantly less smoke and particulate matter than burning wood, contributing to improved air quality. Many pellet stoves are EPA certified, meaning they meet stringent emission standards. While burning any fuel produces some emissions, pellet stoves offer a cleaner-burning alternative to traditional wood stoves and fireplaces, reducing their environmental footprint.
Safety: Pellet stoves can be inherently safer than traditional wood-burning fireplaces. The enclosed combustion chamber and controlled airflow reduce the risk of sparks escaping into the room. The exhaust is vented through a specialized pipe, minimizing the risk of creosote buildup in a traditional chimney. The self-contained nature of the stove also makes it less likely for flammable materials to come into contact with open flames. While safety precautions should always be taken when operating any heating appliance, pellet stoves offer enhanced safety features compared to open fireplaces.
Consistent Heat Output: Pellet stoves provide consistent and predictable heat output, unlike wood-burning fireplaces where heat fluctuates based on the type of wood used and how frequently it is added. Because the fuel is uniform and the feed rate is controllable, temperature fluctuations are minimized. This is especially helpful during periods when consistent room temperatures are desired.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Pellet Stove
Selecting the right pellet stove requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure it meets the specific heating needs and preferences of the homeowner.
Heating Capacity: The heating capacity of a pellet stove is measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units). The appropriate BTU rating depends on the size of the area to be heated, the insulation level of the home, and the climate. A larger space with poor insulation will require a stove with a higher BTU rating. Consulting with a heating professional can help determine the optimal BTU rating for the specific application.
Hopper Size: The hopper size determines how often the stove needs to be refilled with pellets. A larger hopper capacity means less frequent refills, but it may also take up more space. Consider the desired level of convenience and the amount of space available when choosing a stove with the appropriate hopper size. How readily available can you obtain pellets? Do you have room to store a large supply of pellets?
Features and Controls: Pellet stoves offer a range of features and controls, such as thermostat control, programmable timers, automatic ignition, and remote control operation. Evaluate which features are important and choose a stove that offers the desired level of functionality. Newer stoves may offer built-in Wi-Fi capabilities that enable remote access to adjust temperature or monitor the stove's status from afar via a mobile device. The level of sophistication of the controls can impact the cost of the stove.
Maintenance Requirements: All pellet stoves require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes emptying the ash pan, cleaning the burn pot, and inspecting the vent pipe. Some stoves are designed for easier maintenance than others. Consider the ease of maintenance when choosing a stove and be prepared to perform the necessary tasks or hire a professional to do so.
Pellet Quality: The quality of the pellets used in the stove can significantly impact its performance and efficiency. Look for high-quality pellets that are low in ash content and made from clean, dry wood. Avoid pellets that contain excessive amounts of bark or other contaminants. Pellet quality can vary even within the same brand from year to year, depending on the source of the raw materials.
Installation Requirements: Pellet stoves require proper installation to ensure safe and efficient operation. This typically involves venting the exhaust outside through a specialized vent pipe and connecting the stove to an electrical outlet. It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions and local building codes when installing a pellet stove. In many areas, a professional installation is required.
Cost: The initial cost of a pellet stove can vary depending on the size, features, and brand. Consider the long-term cost of ownership, including fuel costs, maintenance costs, and potential repair costs. Compare different models and brands to find a stove that fits within the budget and meets the heating needs.
Maintaining a Fireplace Pellet Stove
Proper maintenance is essential for the long-term operation and efficient performance of a fireplace pellet stove. Regular maintenance tasks help prevent malfunctions, ensure safe operation, and maximize the stove's lifespan.
Ash Removal: The ash pan should be emptied regularly, typically every few days or weeks, depending on the stove's usage and the ash content of the pellets. Allowing the ash pan to overfill can impede airflow and reduce heating efficiency. Empty the ash pan when the stove is cool, and dispose of the ashes properly.
Burn Pot Cleaning: The burn pot should be cleaned regularly to remove ash and clinkers (hardened ash deposits). A clogged burn pot can restrict airflow and reduce combustion efficiency. Use a scraper or brush to remove ash and clinkers from the burn pot.
Vent Pipe Inspection and Cleaning: The vent pipe should be inspected regularly for creosote buildup and cleaned as needed. Creosote is a flammable substance that can accumulate in the vent pipe, posing a fire hazard. Depending on usage, the vent pipe should be professionally cleaned at least once a year.
Hopper Cleaning: Periodically clean the hopper to remove any dust, debris, or fines (small pellet fragments) that may accumulate. These materials can clog the auger and interfere with the fuel feed system. Vacuum or wipe out the hopper to remove any debris.
Auger Maintenance: Inspect the auger for any signs of wear or damage. Lubricate the auger motor as needed, following the manufacturer's recommendations. A properly maintained auger ensures consistent fuel delivery.
Combustion and Convection Fan Maintenance: Clean the combustion and convection fans to remove any dust or debris that may accumulate. A dirty fan can reduce airflow and decrease heating efficiency. Use a vacuum cleaner or brush to clean the fan blades.
Gasket Inspection: Inspect the door gasket and other seals for any signs of wear or damage. A damaged gasket can allow air to leak into the combustion chamber, reducing efficiency and increasing emissions. Replace any worn or damaged gaskets promptly.
Professional Servicing: Schedule a professional servicing appointment at least once a year. A qualified technician can inspect the stove, clean all components, and make any necessary repairs. Professional servicing helps ensure that the stove is operating safely and efficiently.

Pellet Fireplace Inserts Lopi Stoves Made In Usa

P42i Tc Pellet Insert Forge Flame

Pellet Fireplace Inserts Lopi Stoves Made In Usa

Fireplace Insert Stoves Wood Gas Pellet Traditional Baltimore Maryland

Wood Stoves Pellet Gas Fireplace Inserts

Pellet Fireplace Inserts Lopi Stoves Made In Usa

Pellet Fireplace Inserts Complete Home Concepts

Gci60 Cast Iron Pellet Stove Insert Regency

Pellet Stove Inserts Turn Drafty Fireplaces Into Heaters Complete Home Concepts

Harman Xxv Tc Pellet Stove Fireside Hearth Home
Related Posts