Understanding Ventless Gas Fireplaces
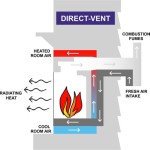
Ventless gas fireplaces, also known as vent-free gas fireplaces, present a heating alternative for residential and commercial spaces. Unlike traditional wood-burning fireplaces or vented gas fireplaces that require a chimney or flue to expel combustion byproducts, ventless models are designed to burn cleanly enough to be operated without external venting. This characteristic offers installation flexibility and potential energy efficiency benefits. However, it also introduces specific considerations regarding safety, air quality, and regulatory compliance.
The operation of a ventless gas fireplace relies on a carefully engineered combustion process that aims to minimize the production of harmful emissions. These fireplaces are typically equipped with oxygen depletion sensors (ODS) that monitor the oxygen level in the room. If the oxygen level drops below a safe threshold, the ODS automatically shuts off the gas supply to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. This safety mechanism is a standard feature in most ventless gas fireplaces sold today.
The fuel source for ventless gas fireplaces can be either natural gas or liquid propane (LP). The choice of fuel depends on the availability of gas lines and local regulations. Natural gas is generally considered a more economical option where available, while LP offers portability and independence from gas lines. The fireplace manufacturer will specify the appropriate fuel type for each model, and it is crucial to adhere to these specifications for safe and efficient operation.
Installation of a ventless gas fireplace is typically simpler than installing a vented fireplace, as it eliminates the need for extensive ductwork. However, it is still essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions meticulously. The fireplace must be placed on a non-combustible surface and maintain adequate clearance from combustible materials. Professional installation is often recommended, particularly when dealing with gas line connections, to ensure safety and compliance with local building codes.
Key Point 1: Safety Considerations and Carbon Monoxide
The primary concern surrounding ventless gas fireplaces is the potential for carbon monoxide (CO) buildup. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless, and toxic gas produced by incomplete combustion. While ventless fireplaces are designed to burn cleanly, malfunctions, improper maintenance, or inadequate ventilation can lead to elevated CO levels. Therefore, adherence to safety guidelines and routine maintenance are paramount.
It is imperative to install and maintain a working carbon monoxide detector in the same room as the ventless gas fireplace. The detector should be tested regularly and replaced according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Carbon monoxide detectors provide an early warning system, alerting occupants to the presence of dangerous CO levels before they reach harmful concentrations.
Proper ventilation is also crucial, even with ventless fireplaces. While they do not require external venting, they do require adequate airflow within the room to ensure sufficient oxygen for combustion and to dilute any combustion byproducts. The manufacturer's instructions will specify the minimum room size and ventilation requirements for each fireplace model. Regularly opening a window or door, even slightly, can help maintain adequate ventilation.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of a ventless gas fireplace. This includes cleaning the burner assembly, inspecting the ODS, and checking for any signs of damage or wear. Any malfunctions or unusual odors should be addressed promptly by a qualified technician. Failure to maintain the fireplace properly can increase the risk of carbon monoxide buildup and other safety hazards.
The use of a ventless gas fireplace in sleeping rooms or confined spaces is generally discouraged or prohibited by local codes. These areas are particularly vulnerable to carbon monoxide buildup due to the lack of ventilation and the potential for prolonged exposure. Consult local building codes and manufacturer's recommendations before installing a ventless gas fireplace in any room.
Key Point 2: Air Quality and Indoor Pollutants
Besides carbon monoxide, ventless gas fireplaces produce other combustion byproducts that can affect indoor air quality. These include nitrogen dioxide (NO2), water vapor, and small amounts of unburned hydrocarbons. While these emissions are generally low under normal operating conditions, they can contribute to indoor air pollution, particularly in poorly ventilated spaces.
Nitrogen dioxide is a respiratory irritant that can exacerbate asthma and other respiratory conditions. It can also contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain. While ventless gas fireplaces produce less NO2 than vented fireplaces, prolonged exposure to even low levels can be problematic for sensitive individuals, such as children, the elderly, and those with respiratory illnesses.
Water vapor is another byproduct of combustion. Ventless gas fireplaces release moisture into the air, which can increase humidity levels. Excessive humidity can promote the growth of mold and mildew, which can trigger allergic reactions and respiratory problems. Monitoring humidity levels and using a dehumidifier, if necessary, can help mitigate this issue.
Unburned hydrocarbons are volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can contribute to indoor air pollution. VOCs can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat, and some are known carcinogens. While ventless gas fireplaces are designed to minimize unburned hydrocarbons, proper maintenance and ventilation can further reduce their emissions.
To minimize the impact on indoor air quality, it is important to use the ventless gas fireplace sparingly and to ensure adequate ventilation. Air purifiers with HEPA filters can also help remove particulate matter and VOCs from the air. Additionally, consider choosing a ventless gas fireplace model with low emission certifications, such as those meeting ANSI standards.
Key Point 3: Regulations and Building Codes
The use of ventless gas fireplaces is subject to regulations and building codes that vary by location. These regulations are designed to ensure the safe and responsible use of these appliances and to protect public health. It is crucial to consult local building codes and obtain any necessary permits before installing and operating a ventless gas fireplace.
Some jurisdictions may prohibit the use of ventless gas fireplaces altogether, particularly in certain types of buildings or occupancies. Other jurisdictions may impose restrictions on the size and type of ventless gas fireplaces that can be installed, as well as requirements for ventilation and carbon monoxide detection.
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) has developed standards for ventless gas fireplaces that address safety, performance, and emissions. These standards are often referenced in building codes and regulations. Look for ventless gas fireplaces that are certified to meet ANSI standards to ensure that they have been tested and evaluated for safety and performance.
Local fire marshals and building inspectors are responsible for enforcing building codes and regulations related to ventless gas fireplaces. They may require inspections to ensure that the fireplace is installed and operated in compliance with applicable codes. Failure to comply with these codes can result in fines or other penalties.
It's crucial to research and comply with local codes pertaining to ventless gas fireplaces before purchasing and using one. Consult with local building officials, fire departments, or qualified HVAC professionals to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
In addition to the considerations above, users of ventless gas fireplaces should be aware of the potential impact on overall energy consumption. While ventless fireplaces can provide supplemental heat, they are not typically designed to be the primary heating source for a home. Over-reliance on a ventless fireplace can lead to higher energy bills. Understanding the limitations and appropriate use of a ventless gas fireplace is important for both safety and efficiency.
Finally, it is important to remember that ventless gas fireplaces, while convenient, are not a substitute for responsible safety practices. Regular maintenance, proper ventilation, and functional carbon monoxide detectors are essential for safe operation. Always prioritize safety and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ventless-gas-fireplaces-4160746-hero-f9d4bdcd9bd446eb84406de306f790ba.jpg?strip=all)
How To Pick Out A Ventless Gas Fireplace

Duluth Forge Dual Fuel Ventless Gas Fireplace 32 000 Btu Remote Control Antique White Finish 170107 The Home Depot

Ventless Gas Logs Vent Free Fireplace Experts

What Is A Ventless Gas Fireplace Dorr Oil

Duluth Forge Dual Fuel Ventless Gas Fireplace 26 000 Btu Remote Control Antique White Finish 170105 The Home Depot

Ventless Gas Fireplace Vent Free Modern

Ventless Gas Fireplace Propane

Vent Free Archives SÓlas Contemporary Fireplaces

Considering A Ventless Gas Fireplace Here S What You Need To Know Bob Vila

Vermont Castings Vent Free Stoves Main Street Fireplace Fall
Related Posts