Understanding Coal Burning Fireplaces: A Comprehensive Guide
Coal burning fireplaces represent a historical and practical heating solution, offering a distinct alternative to traditional wood-burning systems. While less common today due to environmental concerns and the rise of alternative heating technologies, understanding the nuances of coal fireplaces remains relevant for historical preservation, specific heating needs, and informed decision-making when considering various fuel options.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of coal burning fireplaces, exploring their operation, benefits, drawbacks, maintenance needs, and safety considerations. It aims to present a balanced and informative perspective, enabling readers to understand the complexities associated with this type of heating appliance.
Fuel Characteristics and Combustion Process
The primary differential between coal and wood fireplaces lies in the fuel itself. Coal, a sedimentary rock formed from compressed plant matter over millions of years, possesses a significantly higher energy density than wood. This means that a smaller volume of coal can produce a greater amount of heat compared to an equivalent volume of wood. Anthracite coal, the type typically used in residential fireplaces, is particularly desirable due to its high carbon content, low sulfur content, and clean-burning characteristics relative to other coal varieties. Bituminous coal, while containing more energy, produces more smoke and pollutants, making it less suitable for domestic use.
The combustion process in a coal fireplace differs from that of a wood fireplace. Coal requires a higher ignition temperature than wood and benefits from a strong draft to facilitate complete combustion. Once ignited, coal burns at a higher temperature and for a longer duration. This extended burn time translates to fewer refueling intervals, offering a convenience factor for users. However, achieving and maintaining proper combustion is crucial for maximizing heat output and minimizing the emission of harmful pollutants.
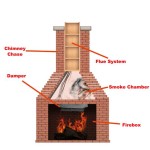
The efficiency of coal combustion is also dependent on the fireplace design. Specialized coal-burning fireplaces often incorporate features such as grates designed specifically for coal, air vents positioned to optimize airflow, and ash collection systems to manage the byproduct of combustion. These design elements contribute to a more controlled and efficient burning process.
Advantages of Coal Burning Fireplaces
Despite their declining popularity, coal burning fireplaces offer several advantages that warrant consideration. First, the high energy density of coal results in a significant heat output per unit of fuel. This characteristic makes coal fireplaces particularly effective for heating large spaces or maintaining consistent warmth over extended periods. Users often report needing to refuel less frequently compared to wood-burning alternatives, which translates to reduced effort and greater convenience.
Second, anthracite coal, when burned correctly, produces relatively little smoke. While all combustion processes generate some level of air pollution, anthracite coal's low sulfur content minimizes the emission of sulfur dioxide, a significant contributor to acid rain. Modern coal-burning appliances often incorporate advanced combustion technologies to further reduce emissions and improve air quality. However, these technologies may require significant upfront investment.
Third, the availability and cost of coal can be advantageous in certain regions. In areas with readily accessible coal reserves, the fuel may be more affordable than wood, propane, or other heating alternatives. Furthermore, coal's relatively stable pricing can provide a degree of predictability in heating costs, allowing users to better manage their budgets.
Finally, many older homes already possess existing coal fireplaces, often dating back to the early 20th century. Restoring and utilizing these fireplaces can be more cost-effective than installing a completely new heating system. Historical preservation enthusiasts may also find value in maintaining and operating these historically significant appliances.
Disadvantages of Coal Burning Fireplaces
The use of coal burning fireplaces also presents several disadvantages that must be carefully considered. Perhaps the most significant concern is the environmental impact associated with coal combustion. While anthracite coal produces less smoke than bituminous coal, it still emits particulate matter and greenhouse gases, contributing to air pollution and climate change. Regulations regarding coal burning fireplaces are becoming increasingly strict in many jurisdictions, reflecting growing concerns about air quality and public health.
Another drawback is the handling and storage of coal. Coal is a heavy and bulky fuel, requiring significant physical effort to transport and load into the fireplace. It also necessitates a dedicated storage space, typically a basement, shed, or covered outdoor area. The storage space must be dry and well-ventilated to prevent the coal from absorbing moisture and degrading its burning properties.
Furthermore, the ash produced by coal combustion is more voluminous and contains different chemical properties compared to wood ash. Coal ash often contains higher concentrations of heavy metals and other pollutants, requiring careful disposal in accordance with local regulations. Improper disposal of coal ash can contaminate soil and water resources.
Finally, coal-burning fireplaces require specialized knowledge and skills to operate safely and efficiently. Achieving optimal combustion requires precise control of airflow and fuel loading. Mistakes in operation can lead to incomplete combustion, resulting in increased emissions and reduced heat output. Users must also be vigilant in maintaining the fireplace and chimney to prevent the buildup of creosote and other flammable deposits, which can pose a fire hazard.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a coal burning fireplace. Regular chimney inspections are essential to identify and address any potential problems, such as cracks, blockages, or creosote buildup. A qualified chimney sweep should conduct thorough inspections and cleaning at least once a year, or more frequently if the fireplace is used extensively.
The fireplace itself should also be inspected regularly for signs of damage or deterioration. Cracks in the firebox, damaged grates, or loose bricks can compromise the fireplace's structural integrity and pose a safety hazard. These issues should be repaired promptly by a qualified professional.
Proper ventilation is paramount for preventing carbon monoxide poisoning. Carbon monoxide is a colorless and odorless gas produced by incomplete combustion. It is highly toxic and can be fatal if inhaled in high concentrations. Carbon monoxide detectors should be installed in the home, particularly near sleeping areas, and tested regularly to ensure they are functioning properly.
When operating a coal burning fireplace, it is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. Avoid overloading the firebox with coal, as this can lead to incomplete combustion and increased emissions. Use a poker or other tool to stir the coal bed periodically, ensuring that all of the coal is burning evenly. Never leave a coal fire unattended, and extinguish the fire completely before leaving the house or going to bed.
The disposal of coal ash should be handled with care. Allow the ash to cool completely before removing it from the fireplace. Place the ash in a metal container with a tight-fitting lid to prevent it from spreading. Contact your local waste management authority for guidance on proper disposal methods. In some areas, coal ash may be classified as hazardous waste and require special handling.

Can You Burn Wood In A Coal Fireplace

Can You Burn Wood In A Coal Stove What Need To Knows Legacy Stoves

Valor 530icn Coal Fire Radiant Gas Fireplace And Insert Installed With Polished Windsor Arch In Mantel Antique Mantels

Coal Fireplace Restoration Atlanta Repair Burning Stove

Can You Burn Wood In A Coal Fireplace

Ontario Victorian

Blazing Coal Fire Burning In Victorian Fireplace Stock Photo Adobe

Victor Gas Coal Burner Victorian Fireplace Home Small Farmhouse Decor

Anthracite Coal Simply Flooring Fireplace

Belmont Small Gas Insert