Gas vs. Wood Burning Fireplaces: A Comparative Analysis
Fireplaces have long been a central feature in homes, providing warmth, ambiance, and a focal point for social gatherings. Two primary types of fireplaces dominate the market: gas and wood-burning. Each offers distinct advantages and disadvantages, making the choice dependent on individual preferences, lifestyle, and practical considerations.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between gas and wood-burning fireplaces, examining their functionalities, efficiency, environmental impact, aesthetic appeal, and maintenance requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for homeowners seeking to make an informed decision about which type of fireplace best suits their needs.
Heat Output and Efficiency
Heat output is a primary consideration for homeowners seeking a fireplace as a supplemental heating source. Wood-burning fireplaces, traditionally, have been associated with significant heat output. However, the actual efficiency of a wood-burning fireplace can vary considerably depending on factors such as the type of wood used, the design of the fireplace, and the presence of features like a damper.
Traditional open-hearth wood-burning fireplaces often suffer from low efficiency, with a substantial portion of the heat escaping up the chimney. This can lead to significant heat loss and increased energy consumption. Modern wood-burning fireplace inserts and stoves, designed with improved combustion technology, can significantly enhance efficiency, offering a more controlled burn and reduced heat loss.
Gas fireplaces, on the other hand, offer a more consistent and controllable heat output. They are typically rated for their BTU (British Thermal Unit) output, allowing homeowners to estimate the amount of heat they can expect. Gas fireplaces are generally more efficient than traditional wood-burning fireplaces, with some models achieving efficiency ratings of 70% or higher.
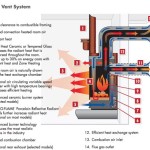
The efficiency of a gas fireplace hinges on the type of system employed. Direct vent gas fireplaces, which draw combustion air from outside and vent exhaust directly outside, are generally the most efficient. Vent-free gas fireplaces, which do not require a chimney, can also be efficient but require careful consideration of ventilation to avoid carbon monoxide buildup.
The choice between gas and wood based on heat output and efficiency depends on the homeowner's specific needs and priorities. Those seeking maximum heat output and willing to manage the intricacies of wood burning may find wood fireplaces suitable, particularly modern, high-efficiency models. Conversely, individuals prioritizing convenience, consistent heat, and higher efficiency may opt for gas fireplaces.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of fireplaces is an increasingly important consideration. Wood-burning fireplaces are known to contribute to air pollution, releasing particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and other harmful emissions into the atmosphere. The burning of wood can also contribute to deforestation if not sourced sustainably.
The type of wood burned also plays a significant role in the environmental impact. Softwoods, such as pine, tend to burn faster and produce more smoke than hardwoods, such as oak or maple. Burning seasoned wood, which has been properly dried, is also crucial for reducing emissions. Wet or unseasoned wood burns less efficiently and produces significantly more smoke.
Regulations regarding wood-burning fireplaces are becoming increasingly stringent in many areas. Some municipalities restrict the use of wood-burning fireplaces during periods of high air pollution or require the use of certified, low-emission appliances. These regulations aim to mitigate the negative environmental impacts associated with wood burning.
Gas fireplaces generally produce fewer emissions than wood-burning fireplaces. Natural gas and propane, the fuels used in gas fireplaces, burn more cleanly than wood, resulting in lower levels of particulate matter and carbon monoxide emissions. However, the combustion of natural gas and propane still releases greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change.
The environmental impact of gas fireplaces can be further mitigated by choosing energy-efficient models and ensuring proper maintenance. Regular servicing can help prevent gas leaks and ensure optimal combustion efficiency. Furthermore, the use of renewable natural gas or propane can reduce the carbon footprint associated with gas fireplaces.
Ultimately, the environmental impact of both gas and wood-burning fireplaces depends on various factors, including the type of fuel used, the efficiency of the appliance, and the user's practices. Homeowners seeking to minimize their environmental footprint should carefully consider these factors and choose the option that aligns with their sustainability goals.
Aesthetics and Maintenance
Aesthetics are a significant factor in the selection of a fireplace. Wood-burning fireplaces evoke a sense of tradition and rustic charm. The crackling sound of burning wood and the flickering flames create a unique ambiance that many find appealing. The visual appeal of a wood-burning fireplace is often considered a key advantage.
However, wood-burning fireplaces require significant effort to maintain. Fueling the fire involves sourcing, storing, and hauling wood. Ash removal is a regular task, and the chimney must be cleaned periodically to prevent creosote buildup, which is a fire hazard. The maintenance demands of wood-burning fireplaces can be time-consuming and physically demanding.
The aesthetics of gas fireplaces have evolved significantly in recent years. Modern gas fireplaces can mimic the appearance of wood-burning fireplaces with remarkable realism, utilizing ceramic logs and realistic flame patterns. Gas fireplaces offer a clean, modern aesthetic that complements a wide range of interior design styles.
Gas fireplaces are significantly easier to maintain than wood-burning fireplaces. They require minimal effort to operate, typically controlled by a switch or remote control. The only regular maintenance required is an annual inspection by a qualified technician to ensure proper functioning and safety. This ease of maintenance is a major advantage for many homeowners.
The choice between gas and wood based on aesthetics and maintenance hinges on personal preference and lifestyle. Those who value the traditional charm and ambiance of a wood-burning fire and are willing to invest the time and effort required for maintenance may find wood fireplaces appealing. Conversely, individuals prioritizing convenience, ease of use, and modern aesthetics may opt for gas fireplaces.
The installation costs for both types of fireplaces vary depending on the existing infrastructure. Installing a wood-burning fireplace typically requires a chimney, which can be expensive to build or repair. A gas fireplace requires a gas line, which can also add to the installation cost.
The operating costs also differ. Wood, while potentially cheaper in some regions if sourced locally, requires manual labor. Gas prices fluctuate, and the cost of running a gas fireplace depends on local gas rates. A thorough cost analysis, considering both installation and operating expenses, is crucial for making an informed decision.
Safety is paramount for both types of fireplaces. Wood-burning fireplaces pose a risk of chimney fires if not properly maintained. Gas fireplaces pose a risk of gas leaks or carbon monoxide poisoning if not installed and maintained correctly. Regular inspections and adherence to safety guidelines are essential for both types of fireplaces.
Ultimately, the decision between a gas and wood-burning fireplace is a personal one, based on individual priorities, lifestyle, and budget. Weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each type, considering factors such as heat output, environmental impact, aesthetics, and maintenance requirements, is crucial for making an informed decision that will provide years of warmth and enjoyment.

Gazco Huntingdon 30 Gas Stove Fireplace Supers

Gas Stoves Excellent Value To Buy From

Stoves Wood Gas Pellet Lopi

Yeoman Cl5 Contemporary Gas Stove Fireplace Supers

Can A Wood Burning Fireplace Be Converted To Gas The Flame Company

Fireplaces Inserts Wood Gas Fireplace Xtrordinair
Can I Convert My Wood Burning Fireplace To Gas Woodlanddirect Com

Free Standing Gas Fireplace Stoves For 30 On Now

Stoves Wood Gas And Pellet Sierra Hearth Home

Gas Stoves Made In Usa Lopi
Related Posts