Gas Fireplace Freestanding Direct Vent: A Comprehensive Overview
Gas fireplaces have become increasingly popular as a convenient and aesthetically pleasing heating solution for homes. Among the various types available, the freestanding direct vent gas fireplace offers a unique combination of advantages, including ease of installation, efficient heating, and versatile placement options. This article provides a detailed exploration of freestanding direct vent gas fireplaces, covering their operation, benefits, installation considerations, and maintenance requirements.
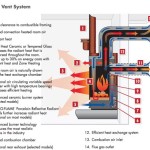
A freestanding direct vent gas fireplace is a self-contained heating unit designed to resemble a traditional wood-burning stove or fireplace. Unlike traditional fireplaces, which require a chimney for venting exhaust gases, a direct vent system utilizes a sealed combustion chamber and a dual-pipe vent system. One pipe draws fresh air from outside the home for combustion, while the other expels exhaust gases back outside. This sealed system enhances safety and efficiency by preventing indoor air from being used for combustion and minimizing heat loss.
The "freestanding" aspect refers to the fireplace's ability to be placed virtually anywhere in a room, as long as venting requirements are met. This contrasts with built-in fireplaces that are integrated into a wall structure. Freestanding models often rest on a pedestal or legs, adding to their visual appeal and creating a focal point in the room.
Key Point 1: Operational Principles and Efficiency
The efficient operation of a freestanding direct vent gas fireplace hinges on its sealed combustion system. The direct vent system utilizes two concentric or coaxial pipes. The inner pipe expels exhaust gases generated during combustion, while the outer pipe draws fresh air from outside the home. This process ensures that the fireplace does not draw air from within the living space, preventing drafts and maintaining consistent indoor air quality. Because the system is sealed, there is reduced risk of carbon monoxide entering the home, making them safer than traditional wood-burning fireplaces or ventless gas fireplaces.
Furthermore, the sealed combustion process maximizes heating efficiency. By drawing fresh air from outside, the fireplace avoids cooling the existing warm air inside the room. The heated air is then circulated into the room, providing supplemental heat. Many models incorporate fans to further enhance heat distribution, ensuring even warmth throughout the space. Energy efficiency ratings vary among different models, but direct vent systems generally offer higher efficiency compared to other types of gas fireplaces, minimizing energy consumption and reducing heating costs.
The fuel source for these fireplaces is typically natural gas or propane. Natural gas is often a more cost-effective option if a gas line is readily available, while propane provides flexibility for homes without access to natural gas. The size and BTU (British Thermal Units) output of the fireplace should be carefully considered to match the heating needs of the room. Over sizing can lead to discomfort, while under sizing may not sufficiently heat the space.
Key Point 2: Installation Requirements and Considerations
Proper installation is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of a freestanding direct vent gas fireplace. While the installation process is generally simpler than installing a traditional fireplace with a chimney, it still requires careful planning and adherence to building codes and manufacturer instructions. A qualified and licensed professional should be consulted to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
The most critical aspect of installation is the venting system. The direct vent pipes must be properly routed to the exterior of the home, ensuring a secure and weatherproof seal. The vent termination point must also meet specific requirements, such as minimum distances from windows, doors, and other air intakes, to prevent exhaust gases from re-entering the home. Horizontal venting is the most common configuration, where the vent pipes run horizontally through an exterior wall. Vertical venting is also possible, where the vent pipes extend upward through the roof, although this is less common for freestanding models.
Gas line installation is another key consideration. If a gas line is not already present in the desired location, a qualified plumber must install one. This involves connecting the fireplace to the main gas supply and ensuring proper gas pressure and leak-free connections. Electrical connections may also be required for features like the blower fan, electronic ignition, or remote control.
Clearance requirements around the fireplace must be strictly observed to prevent fire hazards. The manufacturer's instructions will specify the minimum distances from combustible materials, such as walls, furniture, and curtains. A non-combustible hearth pad may also be necessary to protect the floor beneath the fireplace.
Key Point 3: Maintenance and Longevity
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the continued safe and efficient operation of a freestanding direct vent gas fireplace. Proper maintenance can also extend the lifespan of the unit and prevent costly repairs.
One of the most important maintenance tasks is cleaning the glass front of the fireplace. Over time, deposits can accumulate on the glass, reducing visibility of the flames. A specialized glass cleaner designed for gas fireplaces should be used to remove these deposits without damaging the glass. Regular cleaning will keep the flames visible and ensure optimal aesthetics.
The burner assembly should also be inspected and cleaned periodically. Dust, debris, and spider webs can accumulate in the burner ports, affecting the flame pattern and potentially causing malfunctions. A soft brush or vacuum cleaner can be used to remove these obstructions. Professional servicing is recommended on a yearly basis to ensure all components are functioning properly and to check for any potential issues.
The vent system should also be inspected regularly to verify that it is free of obstructions and that all connections are secure. Look for any signs of damage or deterioration, such as corrosion or leaks. If any issues are detected, a qualified technician should be contacted immediately to make repairs.
Regularly inspect the pilot light and thermocouple. A faulty thermocouple can prevent the pilot light from staying lit, rendering the fireplace inoperable. If the pilot light frequently goes out, the thermocouple may need to be replaced. It is important to shut off the main gas supply to the fireplace during maintenance.
By understanding the operational principles, installation requirements, and maintenance procedures for freestanding direct vent gas fireplaces, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of efficient and aesthetically pleasing supplemental heating while ensuring the safety and longevity of their investment.

Lennox Visions Elite Series Direct Vent Freestanding Stove

Kozy Birchwood 20 Gas Stove Fireplace S Hearth Home

Direct Vent Gas Stoves In Dc

Kozy Birchwood 20 Gas Stove Fireplace S Hearth Home

Heat N Glo Paloma Direct Vent Gas Stove

Gas Direct Vent Stoves S Service Whole Main Street Fireplace Suffolk Long Island

Gas Propane Free Standing Stoves

Gas Fireplace Stand Alone 75x65 Curve Ortal Usa Contemporary Closed Hearth Floor Mounted

Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces Best Fire Hearth Patio

Marquis Titan Friendly Fires
Related Posts