Gas Indoor Fireplace: A Comprehensive Overview
A gas indoor fireplace offers an appealing combination of ambiance and convenience, making it a popular choice for homeowners seeking a supplemental heating source and a focal point for their living spaces. Unlike traditional wood-burning fireplaces, gas fireplaces eliminate the need for wood storage, chopping, and the associated mess of ash and soot. This article provides a comprehensive overview of gas indoor fireplaces, covering their types, benefits, installation considerations, maintenance requirements, and safety aspects.
Types of Gas Indoor Fireplaces
Gas indoor fireplaces are available in several distinct types, each offering different aesthetic styles and installation requirements. Understanding these variations is crucial when selecting the most appropriate fireplace for a specific home and individual preferences.
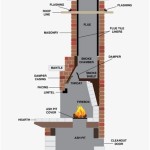
Gas Inserts: Gas inserts are designed to be installed directly into an existing wood-burning fireplace. They essentially convert the existing fireplace into a gas-burning appliance. This option is popular for homeowners who want to retain the look of a traditional fireplace without the hassle of wood. Gas inserts typically require a gas line connection and venting through the existing chimney. They are self-contained units, offering controlled burning and improved energy efficiency compared to open wood-burning fireplaces.
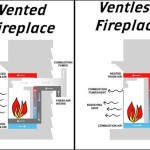
Gas Log Sets: Gas log sets are the simplest type of gas fireplace. They consist of ceramic or refractory logs placed within an existing fireplace opening or a designated firebox. These sets are connected to a gas line and create realistic-looking flames that mimic a wood fire. Gas log sets can be vented or vent-free, depending on the model and local regulations. Vented log sets require an open chimney flue for proper ventilation, while vent-free sets burn cleaner and do not require a chimney, but may have limitations on the size of the room they can be used in and may not be allowed in all jurisdictions. It is crucial to consult with a qualified professional to determine the appropriate venting option.
Gas Fireplace Stoves: These standalone units resemble traditional wood-burning stoves but operate on gas fuel. Gas fireplace stoves are often chosen for their aesthetic appeal and their ability to heat a specific area effectively. They are typically vented directly through a wall or the roof and can be installed in locations where a traditional fireplace is not feasible. Gas stoves are available in various styles, from classic designs to modern, minimalist looks.
Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces: Direct vent fireplaces are sealed units that draw combustion air from outside the home and vent exhaust gases directly outside through a dedicated venting system. This design ensures optimal efficiency and prevents the introduction of combustion byproducts into the living space. Direct vent fireplaces are versatile and can be installed on exterior walls, making them a popular choice for new construction and renovations.
Vent-Free Gas Fireplaces: Vent-free (also known as ventless) gas fireplaces do not require venting to the outside. They operate by burning gas very cleanly, minimizing the production of harmful emissions. While vent-free fireplaces offer installation flexibility, they are subject to stricter regulations and may not be permitted in all areas. They also require the use of an Oxygen Depletion Sensor (ODS) that will shut off the fireplace if the oxygen levels in the room decrease to a dangerous level. It is imperative to consult with local building codes and a qualified HVAC professional before considering a vent-free gas fireplace.
Benefits of Gas Indoor Fireplaces
Gas indoor fireplaces offer numerous advantages over traditional wood-burning fireplaces, contributing to their increasing popularity among homeowners.
Convenience and Ease of Use: One of the primary benefits of gas fireplaces is their convenience. They ignite instantly with the flip of a switch or the push of a button, eliminating the need to build and maintain a wood fire. The flame height and heat output can be easily adjusted with a control knob or remote control. Many modern units also feature programmable thermostats, allowing for precise temperature control and energy savings.
Cleanliness and Reduced Maintenance: Gas fireplaces produce significantly less ash, soot, and creosote compared to wood-burning fireplaces. This reduces the need for frequent cleaning and eliminates the risk of chimney fires associated with creosote buildup. The only regular maintenance required is an annual inspection by a qualified technician to ensure proper operation and safety.
Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness: Gas fireplaces can be more energy-efficient than traditional wood-burning fireplaces, especially direct vent models. They provide consistent heat and can be used as a supplemental heating source, reducing reliance on central heating systems. While the cost of gas may vary depending on location and market conditions, gas fireplaces can offer a cost-effective heating solution, particularly for zone heating specific rooms.
Environmental Friendliness: Gas fireplaces burn cleaner than wood-burning fireplaces, producing fewer emissions and contributing to improved air quality. Natural gas is a relatively clean-burning fossil fuel, and gas fireplace technology continues to advance, further reducing emissions. Using a gas fireplace can be a more environmentally responsible choice compared to burning wood, especially in areas with air quality concerns.
Safety: Gas fireplaces are designed with safety features such as flame sensors and automatic shut-off mechanisms to prevent gas leaks and ensure safe operation. They eliminate the risks associated with open fires, such as flying embers and the potential for uncontrolled burning. When properly installed and maintained, gas fireplaces offer a safe and reliable heating solution.
Installation, Maintenance, and Safety Considerations
Proper installation, regular maintenance, and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial for the safe and efficient operation of gas indoor fireplaces.
Professional Installation: Gas fireplace installation should always be performed by a qualified and licensed HVAC professional. Incorrect installation can lead to gas leaks, carbon monoxide poisoning, and other safety hazards. A professional installer will ensure that the fireplace is properly connected to the gas line, vented correctly (if required), and compliant with all local building codes. They will also conduct a thorough inspection and testing of the unit to ensure it is operating safely and efficiently.
Regular Maintenance: Annual maintenance is essential for gas fireplaces. A qualified technician should inspect the fireplace for any signs of damage or wear, clean the burner assembly, check the pilot light and ignition system, and ensure that the venting system (if applicable) is clear and unobstructed. Regular maintenance will prevent problems, extend the life of the fireplace, and ensure safe operation.
Carbon Monoxide Detection: Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and deadly gas produced by incomplete combustion. It is imperative to install carbon monoxide detectors in the home, especially near gas appliances. Regularly test the detectors to ensure they are functioning properly. If a CO alarm sounds, evacuate the premises immediately and call emergency services.
Venting Requirements: Proper venting is essential for vented gas fireplaces to ensure that combustion byproducts are safely exhausted outside the home. The venting system should be inspected regularly for any signs of damage or blockage. Never obstruct or alter the venting system in any way. For vent-free gas fireplaces, ensure adequate ventilation in the room by opening a window or door periodically.
Gas Leak Detection: If a gas odor is detected, immediately evacuate the premises and call the gas company or emergency services from a safe location. Do not use any electrical devices or open flames, as they could ignite the gas. Regular gas line inspections can help prevent gas leaks.
Local Codes and Regulations: Always comply with local building codes and regulations regarding gas fireplace installation, maintenance, and operation. These codes are in place to ensure safety and prevent hazards. Check with the local building department or fire marshal for specific requirements in the given area.
Choosing and owning a gas indoor fireplace requires careful consideration of various factors, including fireplace type, installation requirements, maintenance needs, and safety precautions. By carefully evaluating these aspects, homeowners can enjoy the warmth, ambiance, and convenience of a gas fireplace while ensuring its safe and efficient operation for years to come.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ventless-gas-fireplaces-4160746-hero-f9d4bdcd9bd446eb84406de306f790ba.jpg?strip=all)
How To Pick Out A Ventless Gas Fireplace

Freestanding High Efficiency Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces Inserts Stoves Godby Hearth And Home

An Indoor Gas Fireplace For The Home Lawn Leisure

Indoor Gas Fireplaces Capo Fireside

All Seasons Fireplace Blog Gas Fireplaces

A Guide To Choosing The Best Indoor Fireplace Increase Comfort

Majestic Indoor Outdoor See Through Gas Fireplace Mezzanine

Enclosed Gas Fireplaces Jetmaster

Freestanding Gas Fireplaces Fergus Fireplace

Stellar Transcend Indoor Outdoor Double Sided Gas Fireplace Fireside Hearth Home
Related Posts