Can An Electric Fireplace Heat A House Without Electricity?
The question of whether an electric fireplace can heat a house without electricity is a common one, particularly in situations involving power outages or when seeking alternative heating solutions. The short answer is no. Electric fireplaces, by their very nature, require electricity to operate their heating elements and fan systems. However, a deeper exploration of this topic reveals nuances regarding backup power options, alternative heating methods, and the general functionality of electric fireplaces.
Electric fireplaces are essentially space heaters that mimic the appearance and ambiance of traditional wood-burning fireplaces. They consist of a heating element, typically a coil or infrared heater, a fan to circulate the heated air, and a display screen that simulates flames. All these components rely on a consistent electricity supply to function. Without electricity, an electric fireplace is simply a decorative piece.
The heating capacity of an electric fireplace is generally measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs) or watts. A typical electric fireplace might produce around 5,000 BTUs, which is sufficient to heat a room of approximately 400 square feet. However, this output is entirely dependent on a stable electrical connection. Disrupt this connection, and the fireplace ceases to generate heat.
The dependence on electricity is what differentiates electric fireplaces from other heating methods. For example, a traditional wood-burning fireplace can continue to provide heat as long as there is wood to burn. Similarly, a furnace powered by natural gas or propane can often operate with a backup generator during a power outage. An electric fireplace lacks this inherent resilience to power interruptions.
Backup Power Solutions for Electric Fireplaces
While an electric fireplace cannot function without electricity in its standard configuration, there are ways to provide backup power. These solutions invariably involve providing an alternative source of electricity to power the unit. Several options are available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Generators: Portable generators are a common solution for providing emergency power. These generators can run on gasoline, propane, or diesel fuel and can supply enough electricity to power essential appliances, including an electric fireplace. However, generators require careful operation, including proper ventilation to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. They also necessitate a readily available fuel supply.
The size of the generator needed depends on the wattage of the electric fireplace and other appliances that need to be powered simultaneously. Overloading a generator can damage both the generator and the connected devices. It is crucial to calculate the total wattage requirements and choose a generator with sufficient capacity.
Battery Backup Systems: Battery backup systems, also known as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), can provide a limited amount of electricity to an electric fireplace. These systems typically consist of a battery bank and an inverter that converts the battery's direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity compatible with household appliances. The runtime of a battery backup system depends on the battery capacity and the power consumption of the connected devices.
Battery backup systems are generally more expensive than generators and have a shorter runtime. However, they are quieter, cleaner, and require less maintenance. They are also a better option for short-term power outages or when noise is a concern.
Solar Power: Solar panels can be used to generate electricity and power an electric fireplace, either directly during daylight hours or by charging a battery bank for later use. This option is environmentally friendly but requires a significant initial investment in solar panels, inverters, and batteries. The amount of electricity generated by solar panels depends on sunlight availability, which can be a limiting factor in some regions.
Furthermore, the efficiency of solar panels can vary depending on factors such as panel angle, shading, and weather conditions. A well-designed solar power system can provide a sustainable source of electricity for an electric fireplace, but it requires careful planning and installation.
Alternative Heating Methods for Homes Without Electricity
Given the reliance of electric fireplaces on electricity, exploring alternative heating methods that do not require electricity is prudent, particularly in regions prone to power outages. These methods offer varying levels of effectiveness and convenience, but they provide essential warmth and comfort during emergencies.
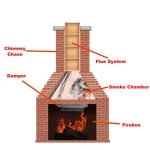
Wood-Burning Fireplaces and Stoves: Traditional wood-burning fireplaces and stoves are a reliable source of heat during power outages. They require a supply of wood, which can be stored in advance. However, wood-burning appliances require proper ventilation to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. Regular chimney cleaning is also essential to reduce the risk of chimney fires.
The efficiency of wood-burning fireplaces and stoves varies considerably. Open fireplaces are generally less efficient than closed stoves, as a significant amount of heat escapes up the chimney. Modern wood-burning stoves are designed to burn wood more efficiently and produce less smoke.
Propane or Kerosene Heaters: Propane and kerosene heaters are portable and relatively inexpensive heating options. They do not require electricity and can provide a significant amount of heat. However, these heaters produce exhaust fumes and require adequate ventilation to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully when operating these heaters.
Propane heaters are generally cleaner-burning than kerosene heaters, but they require a supply of propane tanks. Kerosene heaters are more readily available in some areas, but kerosene fuel can have a strong odor.
Passive Solar Heating: Passive solar heating involves designing a building to capture and store solar energy. This can be achieved through large south-facing windows, thermal mass materials such as concrete or brick, and proper insulation. Passive solar heating can reduce the need for supplemental heating, but it requires careful planning during the building design phase.
The effectiveness of passive solar heating depends on factors such as climate, building orientation, and window size. A well-designed passive solar home can significantly reduce energy consumption for heating.
Emergency Preparedness: Beyond alternative heating methods, it is crucial to have a comprehensive emergency preparedness plan in place. This includes having a supply of warm clothing, blankets, and sleeping bags. Insulating windows and doors can help to retain heat inside the home. A well-stocked emergency kit should also include food, water, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
Regularly practicing emergency drills and ensuring that all family members are aware of the emergency plan can help to minimize the impact of power outages and other emergencies.
Understanding Electric Fireplace Functionality
A clear understanding of how electric fireplaces operate is essential to appreciate their reliance on electricity. The core components of an electric fireplace are the heating element, the fan, and the flame effect display. Each of these components requires electricity to function properly.
The heating element is responsible for generating heat. This element can be a coiled wire, an infrared heater, or a ceramic heater. When electricity flows through the heating element, it heats up and radiates heat into the surrounding air. The fan then circulates this heated air throughout the room.
The flame effect display is typically an LED screen that projects a realistic-looking flame image. The brightness and movement of the flames can often be adjusted to create a desired ambiance. The flame effect consumes a relatively small amount of electricity compared to the heating element, but it is still dependent on a consistent power supply.
Some electric fireplaces also include additional features such as thermostats, timers, and remote controls. These features enhance the convenience and functionality of the fireplace, but they also require electricity to operate.
The power consumption of an electric fireplace can vary depending on its size and features. A typical electric fireplace might consume between 1,000 and 1,500 watts when the heating element is turned on. The flame effect display typically consumes only a few watts. Understanding the power consumption of an electric fireplace is important for calculating the required capacity of backup power systems.
In summary, while electric fireplaces offer a convenient and aesthetically pleasing heating solution, their inherent reliance on electricity means they cannot function without a power source. Backup power options and alternative heating methods are essential considerations for maintaining warmth and comfort during power outages. A comprehensive understanding of electric fireplace functionality and emergency preparedness can help to mitigate the impact of power interruptions.

ᑕ❶ᑐ Free Standing Electric Fireplaces All You Need To Know

ᑕ❶ᑐ Are Electric Fireplaces Energy Efficient

ᑕ❶ᑐ Electric Fireplace And Entertainment Stands The Best Fit

How To Choose A Home Fireplace Ask This Old House

ᑕ❶ᑐ Electric Stove Heat Does It Better Than An Fireplace

ᑕ❶ᑐ Why Does Electric Fireplace Smell Like Burning

How To Choose A Home Fireplace Ask This Old House

How To Choose A Home Fireplace Ask This Old House

Portable Electric Fireplace Stove Heater Remote Control Indoor Winter Heating

Electric Fireplace Stove Freestanding Portable Indoor Space Heater 3 Side Fire House Decor Tv Home Appliances Air Conditioners Heating On Carou