Wood Burning Fireplace Gas Insert: A Comprehensive Overview
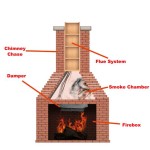
A wood burning fireplace gas insert represents a practical conversion solution for homeowners seeking to retain the aesthetic appeal of a traditional fireplace while gaining the convenience and efficiency of gas-fueled heating. It involves installing a self-contained gas appliance directly into an existing wood-burning fireplace opening. This conversion avoids the need for extensive reconstruction and offers a more user-friendly heating option.
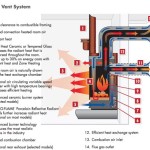
The core principle behind a gas insert is to provide controlled combustion of natural gas or propane within the confines of the existing fireplace structure. The insert is designed to vent exhaust gases safely through a chimney or direct vent system. The heat generated is then radiated or circulated into the room, providing supplemental heating. Choosing the right gas insert requires careful consideration of several factors, including fireplace size, venting options, fuel type availability, and desired aesthetic characteristics.
The modern gas insert is significantly more efficient than traditional wood-burning fireplaces. They are designed to minimize heat loss up the chimney and maximize heat transfer into the living space. Many models feature thermostatic controls, programmable timers, and remote operation, offering a level of control and convenience not possible with wood-burning fireplaces. Modern gas inserts also incorporate safety features such as oxygen depletion sensors (ODS) and automatic shut-off mechanisms, ensuring safe operation.
Advantages of Converting to a Gas Insert
Converting a wood-burning fireplace to a gas insert presents numerous benefits. One primary advantage is the enhanced convenience. Gas inserts eliminate the need for sourcing, storing, and manually loading wood. A simple flick of a switch or the press of a button ignites the fire, providing instant heat. The insert will then automatically adjust to maintain the user-defined settings, creating a consistent, comfortable temperature.
Another significant advantage is the increased efficiency. Wood-burning fireplaces are inherently inefficient, with a considerable amount of heat escaping up the chimney. Gas inserts, on the other hand, are designed for optimal heat transfer. Many models boast efficiency ratings of 70% or higher, meaning that a much larger percentage of the fuel's energy is converted into usable heat for the home. This improved efficiency can translate into lower heating costs, particularly when the gas insert is used as a supplemental heating source.
Environmental considerations also play a role in the decision to convert to a gas insert. Wood-burning fireplaces can contribute to air pollution through the release of particulate matter and other emissions. Gas inserts, particularly those using natural gas, produce significantly fewer emissions and have a smaller carbon footprint. This makes them a more environmentally friendly heating option.
Key Differences Between Gas Inserts and Gas Logs
While both gas inserts and gas logs are designed to be used in existing fireplaces, they function differently and offer distinct advantages. Gas logs are essentially decorative gas burners that are placed within the firebox. They provide the aesthetic appearance of a wood fire but do not offer the same level of heating efficiency or control as a gas insert. Gas logs typically vent up the existing chimney and are primarily intended for ambiance rather than significant heat production.
Gas inserts, in contrast, are fully enclosed appliances that are designed for both aesthetics and efficient heating. They are sealed units that vent directly to the outside, preventing heat loss and ensuring that all combustion gases are safely exhausted. The enclosed design allows for better insulation and heat transfer, resulting in higher efficiency ratings. Gas inserts also feature more advanced control systems, including thermostats, timers, and remote operation.
The installation process also differs significantly. Gas logs are relatively simple to install, typically requiring only a gas line connection. Gas inserts, however, require a more involved installation process, including the installation of a vent liner and connection to a gas supply. The installation should always be performed by a qualified professional to ensure safety and proper operation.
Considerations for Selecting a Gas Insert
Selecting the appropriate gas insert involves several key considerations. First, it is essential to determine the correct size of the insert for the fireplace opening. The dimensions of the firebox should be carefully measured to ensure a proper fit. An insert that is too small will not provide adequate heating, while an insert that is too large may not fit properly and can create safety hazards.
The available venting options are another crucial factor. Some gas inserts require a traditional chimney for venting, while others can be direct-vented through a wall or roof. Direct-vent inserts are generally more versatile and can be installed in homes without existing chimneys. The venting system must be properly installed and sized to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Fuel type availability is also a key consideration. Gas inserts are available for both natural gas and propane. The choice of fuel will depend on the availability of gas lines and the homeowner's preference. Natural gas is typically less expensive than propane, but propane may be a more suitable option for homes located in areas without natural gas service. The unit must be calibrated to the selected fuel type to ensure efficiency and safety.
Aesthetic preferences also influence the selection process. Gas inserts are available in a variety of styles and finishes, allowing homeowners to choose an insert that complements their home décor. Options include realistic log sets, contemporary glass media, and various flame patterns. The appearance of the insert should be carefully considered to ensure that it meets the homeowner's aesthetic expectations.
Installation Process and Safety Precautions
The installation of a gas insert should always be performed by a qualified professional. Improper installation can result in safety hazards, including gas leaks, carbon monoxide poisoning, and fire. A licensed technician will have the necessary expertise and training to ensure that the insert is installed correctly and safely.
The installation process typically involves several steps. First, the existing fireplace is thoroughly inspected to ensure that it is structurally sound and free of any damage. The chimney is then cleaned and inspected to ensure that it is properly ventilated. A vent liner is installed to provide a safe and efficient pathway for exhaust gases. The gas line is connected to the insert, and all connections are carefully tested for leaks.
Once the insert has been installed, the technician will perform a thorough safety check to ensure that it is operating properly. This includes verifying that the gas pressure is correct, that the venting system is functioning properly, and that all safety features are working as intended. The technician will also provide the homeowner with detailed instructions on how to operate and maintain the insert.
Carbon monoxide detectors should be installed in the home to provide an early warning of any potential carbon monoxide leaks. The detectors should be placed near sleeping areas and on each level of the home. The batteries in the detectors should be tested regularly and replaced as needed.
Maintenance and Care of Gas Inserts
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of a gas insert. The frequency of maintenance will depend on the model of the insert and the amount of usage. However, there are some general guidelines that should be followed to keep the insert in good working condition.
The glass front of the insert should be cleaned regularly to remove any soot or residue. A mild glass cleaner and a soft cloth should be used to avoid scratching the glass. The logs or media should also be cleaned periodically to remove any dust or debris. A vacuum cleaner with a soft brush attachment can be used for this purpose.
The venting system should be inspected annually to ensure that it is free of any obstructions. Birds, squirrels, and other animals can build nests in the chimney, which can block the flow of exhaust gases. A professional chimney sweep can inspect and clean the chimney to remove any obstructions.
The gas burner should be inspected annually by a qualified technician. The technician will check the burner for any signs of damage or wear and will clean the burner as needed. The gas pressure should also be checked to ensure that it is within the proper range.
The pilot light should be checked regularly to ensure that it is burning properly. A weak or flickering pilot light can indicate a problem with the gas supply or the burner. If the pilot light goes out, the homeowner should follow the manufacturer's instructions for relighting it.
Cost Considerations for Gas Insert Conversions
The cost of converting a wood-burning fireplace to a gas insert varies depending on several factors, including the size and type of insert, the complexity of the installation, and the geographic location. The cost of the insert itself can range from several hundred dollars to several thousand dollars, depending on the features and brand.
The installation cost will also vary depending on the complexity of the project. A simple installation that involves connecting to an existing gas line and venting system will typically cost less than a more complex installation that requires the installation of a new gas line or venting system. The cost of installation should always be factored into the overall cost of the conversion.
Ongoing operating costs should also be considered. Gas inserts consume natural gas or propane, which can add to the homeowner's monthly utility bills. However, the improved efficiency of a gas insert can often offset these costs, particularly when compared to the cost of purchasing and storing firewood.
Government rebates and tax incentives may be available to help offset the cost of converting to a gas insert. These incentives can vary depending on the location and the specific model of the insert. Homeowners should check with their local utility company and government agencies to see if any incentives are available.
Future Trends in Gas Insert Technology
The gas insert industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and features being introduced regularly. One emerging trend is the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly gas inserts. Manufacturers are focusing on reducing emissions, improving heat transfer, and incorporating smart home technology.
Smart home integration is another growing trend. Many gas inserts now offer connectivity to smart home systems, allowing homeowners to control the insert remotely using a smartphone or tablet. This integration can provide added convenience and energy savings.
Design innovations are also playing a role in the evolution of gas inserts. Manufacturers are creating more realistic log sets, innovative flame patterns, and sleek, modern designs to appeal to a wider range of homeowners.
The continued focus on efficiency, safety, and aesthetics will drive the future development of gas insert technology, making them an even more attractive option for homeowners seeking a convenient and efficient heating solution.

Convert To Gas Installing Fireplace Inserts Doctor Flue

Fireplace Insert Guide Fireplaces Direct Learning Center

Superior Dri2000 Gas Fireplace Insert Woodland Direct

Gas Fireplace Insert Vs Wood Burning Installation

Nordik 34i Kozy Heat Fireplaces
How To Install Gas Fireplace Insert Heat Glo

Fireplaces And Gas Inserts Fireplace West Grand Junction

A Step By Guide To Understanding Fireplace Inserts

How Fireplace Inserts Work We Love Fire

Can A Wood Burning Fireplace Be Converted To Gas The Flame Company
Related Posts