How To Put Ceramic Logs in a Gas Fireplace
The process of arranging ceramic logs in a gas fireplace is a crucial step in achieving both aesthetic appeal and optimal performance. Proper log placement contributes to a realistic flame pattern, maximizes heat output, and ensures safe operation of the appliance. Incorrectly positioned logs can impede gas flow, leading to incomplete combustion, carbon monoxide production, and potential damage to the fireplace components. Therefore, understanding the principles of log placement is paramount for any gas fireplace owner. This article provides a comprehensive guide to safely and effectively installing ceramic logs.
Prior to commencing any work on a gas fireplace, safety precautions are of utmost importance. The gas supply to the fireplace must be completely shut off to prevent accidental activation of the burner. Locate the gas shut-off valve, typically situated near the fireplace or in an adjacent room, and turn it to the "off" position. Allow the fireplace to cool completely before proceeding with any adjustments. Wearing gloves is recommended to protect hands from dirt and potential sharp edges on the ceramic logs. Also, ensure adequate ventilation in the room during the installation process.
The majority of gas fireplace models come with a specific log placement diagram provided by the manufacturer. This diagram serves as the primary guide for arranging the ceramic logs correctly. This diagram is often found in the fireplace's user manual, or it may be affixed to the inside of the firebox. Deviating from the manufacturer's recommended arrangement can lead to inefficient combustion, excessive soot production, and potential safety hazards. Always consult the diagram before beginning the installation. If the diagram is missing or unclear, contacting the manufacturer or a qualified fireplace technician is advisable. The diagram will illustrate the precise location of each log, specifying its orientation and relationship to the burner and other logs.
Ceramic logs are designed with a specific purpose in mind: to mimic the appearance of real wood burning in a fireplace. These logs are made from a heat-resistant ceramic material that can withstand the high temperatures produced by a gas flame. The logs are not all identical; each has a unique shape, size, and texture that contributes to the overall realistic aesthetic. The surface of each log is often textured to simulate bark, wood grain, and charred areas. The color variations in the ceramic material also add to the realism. Some logs are even designed with hollowed-out sections to allow the flames to flicker through, creating a more dynamic and visually appealing fire. Understanding the design intent of each log assists in placing it correctly according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Key Point 1: Understanding the Burner and Pilot Light Relationship
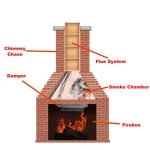
The proper placement of ceramic logs is directly related to the position of the burner and the pilot light in the gas fireplace. The burner is the component that releases the gas, which is then ignited to produce the flames. The pilot light is a small, continuous flame that ignites the main burner when the fireplace is turned on. Ceramic logs should never directly cover or obstruct the burner or the pilot light. Doing so can impede gas flow, leading to incomplete combustion and the production of carbon monoxide. Furthermore, obstructing the pilot light can prevent the main burner from igniting, rendering the fireplace inoperable. The manufacturer's diagram will clearly indicate the areas around the burner and pilot light that must remain unobstructed. Pay close attention to these areas when arranging the logs.
The burner itself can take on various forms depending on the model of the gas fireplace. Some burners are linear, extending across the width of the firebox. Others are circular or oval-shaped. The design of the burner will influence the optimal log placement. For example, a linear burner may require logs to be arranged in a staggered formation to allow the flames to spread evenly. A circular burner may require logs to be arranged around it in a concentric pattern. Regardless of the burner design, the goal is always to ensure that the flames can reach all areas of the logs, creating a realistic and visually appealing fire.
The pilot light's role is crucial in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the gas fireplace. It provides a constant ignition source for the main burner. If the pilot light is extinguished, the gas supply to the main burner will automatically shut off, preventing the build-up of unburned gas. Therefore, it is essential to keep the area around the pilot light clear of any obstructions, including ceramic logs. Some gas fireplaces have a pilot light shield that helps protect the pilot light from drafts and debris. This shield should also be kept clear of any obstructions. Regularly inspecting the pilot light to ensure that it is burning properly is a simple but important safety precaution.
The position of the thermocouple, a safety device that monitors the pilot light, must also be considered. The thermocouple senses the heat from the pilot light and, if the pilot light is burning properly, allows the gas valve to remain open. If the pilot light is extinguished, the thermocouple cools down, causing the gas valve to close. Obstructing the thermocouple with a ceramic log can prevent it from sensing the heat of the pilot light, causing the gas valve to close prematurely. This can lead to the fireplace shutting off unexpectedly. The manufacturer's diagram will typically indicate the location of the thermocouple and the surrounding area that must remain unobstructed.
Key Point 2: Following the Manufacturer's Log Placement Diagram
As previously mentioned, meticulous adherence to the manufacturer's log placement diagram is essential for safe and efficient operation. The diagram provides a detailed guide to the specific arrangement of each log in the fireplace. The diagram typically includes a numbered or lettered designation for each log, as well as an illustration showing its correct position and orientation. It is important to identify each log according to its designation and place it in the corresponding location in the firebox. The diagram may also include specific instructions for how to orient each log, such as which side should face up or which end should be closest to the burner.
The diagram may also indicate the order in which the logs should be placed. In some cases, it is necessary to place certain logs before others to ensure that they are properly supported and aligned. For example, the diagram may specify that the base logs should be placed first, followed by the smaller logs that rest on top of them. Following the correct order of placement will help ensure that the logs are stable and secure.
If the log placement diagram is unclear or ambiguous, consult the manufacturer's user manual for further clarification. The user manual may contain additional details about the log placement process, including troubleshooting tips and diagrams. If the user manual is not available, contact the manufacturer directly or consult a qualified fireplace technician. Attempting to guess the correct log placement without proper guidance can lead to inefficient combustion, soot production, and potential safety hazards.
Furthermore, it is crucial to ensure that the ceramic logs are not touching the glass enclosure of the fireplace. Direct contact between the logs and the glass can cause the glass to overheat and potentially crack or shatter. The manufacturer's diagram will typically indicate the minimum distance that the logs should be kept from the glass enclosure. Maintaining this distance will help prevent damage to the glass and ensure the safe operation of the fireplace.
Key Point 3: Inspecting Flame Pattern and Adjusting as Needed
Once the ceramic logs have been placed according to the manufacturer's diagram, it is important to inspect the flame pattern to ensure that it is burning properly. After turning the gas supply back on and igniting the fireplace, observe the flames carefully. The flames should be evenly distributed and should not be impinging directly on any of the logs. The flames should also be a consistent color, typically blue or yellow. If the flame pattern is uneven, erratic, or producing excessive soot, adjustments may be necessary.
If the flames are impinging directly on a log, it may be necessary to reposition the log slightly to allow for better airflow. Try shifting the log a small distance to the left or right, or rotating it slightly. Observe the flame pattern after each adjustment to see if it improves. It is also possible that the log is too close to the burner, restricting gas flow. In this case, it may be necessary to move the log further away from the burner. Remember to turn off the gas supply and allow the fireplace to cool completely before making any adjustments.
Soot production is a sign of incomplete combustion. Soot is a black, powdery substance that is produced when the gas is not burning completely. Excessive soot can accumulate on the logs, the firebox, and the glass enclosure, making the fireplace look dirty and unattractive. It can also clog the burner and other components, leading to inefficient operation. If the fireplace is producing excessive soot, it may be necessary to adjust the log placement to improve airflow and combustion. It is also possible that the burner is dirty or clogged. In this case, it may be necessary to clean the burner or have it professionally serviced.
If after making adjustments to the log placement, the flame pattern is still not optimal, or if there are any other concerns about the operation of the fireplace, consult a qualified fireplace technician. A technician can diagnose the problem and make the necessary repairs or adjustments to ensure that the fireplace is operating safely and efficiently. Regular maintenance and inspection by a qualified technician is recommended to prolong the life of the fireplace and ensure its safe operation.
Following these guidelines will ensure that the ceramic logs are properly placed in the gas fireplace, leading to a safe, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing fire. Always prioritize safety, consult the manufacturer's instructions, and seek professional assistance when needed.

How To Install Gas Logs 13 Steps With S Wikihow
How To Arrange Gas Logs Howstuffworks

Vented Gas Logs Heater Or Decorative Bart Fireside

How To Select And Install A Gas Fireplace Log Set Fireplaces Direct Learning Center

How To Put In A Gas Log Set For Fireplace

How To Install Gas Logs 13 Steps With S Wikihow

How Long Do Gas Logs Last To Replace Fireplace

Gas Fireplace Logs The Ultimate Guide

What You Need To Know About Gas Fireplace Logs Fireplaces Direct Learning Center

Barton 10 Piece Fireplace Logs Ceramic Wood Fire Place Log Gas Heat Resistant Realistic Stackable Indoor Or Outdoor Set
Related Posts