Gas Fireplace Hearth Code: Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Gas fireplaces offer a convenient and aesthetically pleasing alternative to traditional wood-burning fireplaces. However, their installation and use are governed by strict safety codes designed to prevent fires, carbon monoxide poisoning, and other hazards. These codes, often referencing national standards like those from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and local building codes, particularly focus on the hearth area surrounding the fireplace. Compliance with these regulations is not only a legal requirement but also crucial for ensuring the safety of the occupants and the structural integrity of the building.
The hearth, the non-combustible area directly in front of and around the fireplace opening, plays a vital role in protecting combustible flooring and nearby materials from the intense heat and potential sparks emitted by the gas fireplace. The specific requirements for the hearth's size, material, and construction vary depending on the fireplace model, BTU output, and local building codes. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is paramount for a safe and compliant installation.
Hearth Extension Requirements: Size and Material
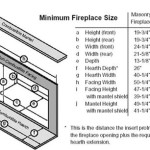
One of the most important aspects of gas fireplace hearth code is the requirement for hearth extensions. These extensions are designed to prevent burning embers or hot debris from falling onto combustible flooring. The required size of the hearth extension is typically dictated by the fireplace opening size and the manufacturer's specifications. Generally, a minimum depth is required in front of the fireplace opening, and a minimum width is necessary on either side.
For example, if the fireplace opening is less than six square feet, the hearth extension might need to extend at least 16 inches in front of the fireplace and 8 inches beyond each side of the opening. If the fireplace opening is larger, the required extension dimensions will typically increase. These dimensions are usually specified in the fireplace's installation manual and should be carefully followed.
The materials used for the hearth extension must also meet specific requirements. They must be non-combustible, meaning they will not ignite and burn when exposed to high temperatures. Common materials used for hearth extensions include brick, stone, concrete, tile, and other approved non-combustible materials. Wood, carpet, and other combustible materials are strictly prohibited within the hearth extension area.
The thickness of the non-combustible material is also subject to code requirements. Often, a minimum thickness is specified to provide adequate insulation and prevent heat transfer to the subfloor. The specific thickness requirement will depend on the fireplace model and local building codes. It is crucial to consult the manufacturer's specifications and local building codes to determine the appropriate thickness for the hearth extension material.
Clearances to Combustible Materials
In addition to the hearth extension, gas fireplace codes also address clearances to combustible materials surrounding the fireplace. These clearances are designed to prevent the radiant heat from the fireplace from igniting nearby walls, mantels, or other combustible surfaces. The required clearances depend on the fireplace model, BTU output, and the type of combustible materials involved.
The manufacturer's installation manual will typically specify the minimum clearances to combustible materials. These clearances may vary depending on the specific fireplace model and its design. It is crucial to adhere to these clearances to prevent the risk of fire.
Walls surrounding the fireplace must maintain a certain distance from the firebox. This distance will often increase the closer the wall is to the fireplace opening. Mantels, shelves, and other decorative elements placed above the fireplace also require specific clearances. The higher the mantel is above the fireplace opening, the less stringent the clearance requirements might be. However, all clearances must be carefully considered and followed to ensure safety.
In some cases, heat shields might be required to reduce the clearance to combustible materials. These shields are designed to deflect heat away from combustible surfaces, allowing for a closer installation. The use of heat shields must be approved by the fireplace manufacturer and must be installed according to their instructions. It is essential to ensure that the heat shields are properly installed and maintained to ensure their effectiveness.
Ventilation and Gas Supply Considerations
While the hearth area is a critical focus of gas fireplace codes, it is also essential to consider ventilation and gas supply requirements. Proper ventilation is crucial for removing combustion byproducts, such as carbon monoxide, from the fireplace. Gas fireplaces must be vented to the outside, either through a chimney or a direct vent system. The venting system must be installed according to the manufacturer's instructions and must comply with local building codes. Incorrect venting can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning, a serious health hazard.
The gas supply to the fireplace must also be properly sized and installed. The gas line must be sized appropriately to provide adequate gas pressure to the fireplace. The installation must comply with local gas piping codes and must be performed by a qualified gas fitter. Leaks in the gas line can create a fire hazard or lead to gas poisoning. Regular inspections of the gas line and connections are essential to ensure safety.
Furthermore, carbon monoxide detectors should be installed in the vicinity of the gas fireplace. These detectors will provide an early warning of carbon monoxide buildup, allowing occupants to evacuate the building and seek medical attention. Carbon monoxide detectors are a vital safety measure for any home with a gas fireplace.
In conclusion, understanding and adhering to gas fireplace hearth codes and related regulations is paramount for ensuring safety and compliance. Careful attention to hearth extension requirements, clearances to combustible materials, and ventilation and gas supply considerations is essential for a safe and properly functioning gas fireplace installation. Consulting with qualified professionals, such as fireplace installers and building inspectors, is highly recommended to ensure compliance with all applicable codes and regulations.

Fireplace Hearth Extension Rules Structure Tech Home Inspections

Fireplace Surround Code Requirements Outdoor Designs Hearth

Fireplace Safety And Codes

Gas Fireplace Surround Code Requirements Myfire Place

What Is A Fireplace Hearth And How Far Should It Extend Building Code Trainer
Is It Necessary To Have A Hearth By Natural Gas Fireplace That 6 Inches From The Floor Quora

Chapter 10 Chimneys And Fireplaces Michigan Residential Code 2024 Upcodes

Gas Fireplace Hearth Requirements With Real Examples

Gas Fireplace Surround Code Requirements Myfire Place
Mantle And Fireplace Surround Minimum Clearances
Related Posts