Standard Depth of Fireplace Hearths: A Comprehensive Guide
Fireplace hearths serve a crucial functional and aesthetic purpose in a home. They provide a non-combustible surface in front of the fireplace opening, protecting the surrounding floor and furnishings from sparks, embers, and radiant heat. Understanding the standard depth requirements for a fireplace hearth is essential for ensuring safety, compliance with building codes, and maintaining the overall integrity of the fireplace system. This article aims to provide a detailed overview of hearth depth standards, factors influencing these standards, and best practices for hearth construction.
The depth of a fireplace hearth isn't a one-size-fits-all measurement. Building codes and safety regulations dictate the minimum depth based on several factors, primarily the size of the fireplace opening. These regulations are put in place to minimize the risk of fire hazards and protect the occupants of the dwelling. Failure to adhere to these standards can result in failed inspections, insurance complications, and, most importantly, an increased risk of fire.
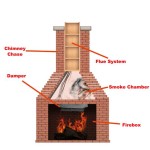
Generally, the hearth depth is measured from the front of the fireplace opening to the front edge of the hearth itself. This measurement essentially represents the distance the non-combustible material extends beyond the firebox. This distance is designed to catch any stray embers or sparks that might escape the fireplace before they can ignite surrounding combustible materials like carpets or wood flooring.
Key Point 1: Understanding Building Codes and Standards
Building codes, often based on the International Residential Code (IRC) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards, specify the minimum hearth depth requirements. These codes are adopted and adapted by local jurisdictions, so it is imperative to consult local building officials or a qualified fireplace installer to determine the specific requirements for a particular location. These requirements can vary depending on the fuel type (wood, gas, or electric) and the size of the fireplace opening.
For example, the IRC typically dictates different hearth depth requirements based on the firebox opening size. For fireplaces with an opening of less than 6 square feet, the hearth must extend at least 16 inches from the front of the fireplace opening and at least 8 inches beyond each side of the fireplace opening. For fireplaces with an opening of 6 square feet or greater, the hearth must extend at least 20 inches from the front of the fireplace opening and at least 12 inches beyond each side of the fireplace opening.
It's crucial to note that these are minimum requirements. Exceeding these minimums can provide an extra measure of safety and aesthetic appeal. However, exceeding the minimum requirements does not negate the need to comply with other aspects of the fireplace construction, such as proper clearances to combustible materials and proper venting.
Furthermore, manufactured fireplaces often have specific hearth requirements outlined in the manufacturer's installation instructions. These instructions supersede general building codes in some cases, as they are tailored to the specific design and performance characteristics of the appliance. Always consult the manufacturer's documentation before installing or modifying a fireplace hearth.
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) also plays a role in developing standards for fireplace safety and performance. While ANSI standards are not legally binding in themselves, they are often referenced in building codes and regulations. These standards can provide valuable guidance on hearth construction and other aspects of fireplace design and installation.
Key Point 2: Factors Influencing Hearth Depth Requirements
Several factors beyond the firebox opening size can influence the required depth of a fireplace hearth. These factors include the type of fuel burned, the presence of a fireplace insert, and the design of the firebox itself.
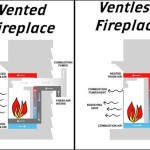
For wood-burning fireplaces, a deeper hearth is generally recommended due to the potential for sparks and embers to escape the firebox. Wood-burning fireplaces tend to generate more particulate matter and require more frequent cleaning, increasing the chance of embers exiting the fireplace. Alternatively, gas fireplaces produce less particulate matter and may have slightly less stringent hearth depth requirements in some jurisdictions. However, local codes and manufacturer's instructions always take precedence.
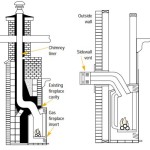
The installation of a fireplace insert can also affect hearth depth requirements. Fireplace inserts are designed to improve the efficiency and safety of existing fireplaces. However, installing an insert may change the way heat is distributed and the potential for sparks or embers to escape. In such cases, the insert manufacturer's instructions should be consulted to determine the appropriate hearth depth requirements. These instructions often specify minimum hearth dimensions that are specific to the insert model.
The design of the firebox itself can also play a role. Fireboxes with deeper setbacks or those equipped with spark screens may require a slightly shallower hearth than fireboxes with a more open design. However, it is essential to ensure that the hearth still provides adequate protection against sparks and embers, regardless of the firebox design. A professional inspection can help determine the appropriate hearth depth for a specific fireplace design.
Beyond the functional requirements, aesthetic considerations can also influence the perceived depth of the hearth. Design elements like raised hearths or decorative surrounds can create the illusion of a deeper hearth, even if the actual depth meets the minimum code requirements. However, it's crucial to ensure that any aesthetic modifications do not compromise the safety or functionality of the hearth.
Key Point 3: Hearth Construction Best Practices
Constructing a fireplace hearth that meets safety standards and provides long-lasting performance requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to use non-combustible materials and follow proper construction techniques to ensure the hearth effectively protects the surrounding floor and furnishings from fire hazards.
Common materials used for hearth construction include brick, stone, concrete, and tile. These materials offer excellent fire resistance and durability. The specific material choice often depends on the overall design aesthetic of the fireplace and the surrounding room. However, it is essential to verify that the selected material meets the requirements for non-combustibility as defined by local building codes.
The hearth should be constructed on a solid, level foundation. This foundation may consist of a concrete slab or a reinforced frame. The foundation should be designed to support the weight of the hearth materials and any additional loads, such as people sitting on the hearth. Proper leveling is critical to ensure the hearth is stable and the surface is even.
When installing brick or stone, a layer of mortar is used to bond the individual units together. The mortar should be specifically designed for fireplace applications and should be resistant to high temperatures. The joints between the bricks or stones should be filled completely with mortar to prevent gaps that could allow embers or sparks to escape.
Tile hearths require a solid substrate, such as cement board or concrete backer board. The tile is then applied to the substrate using thin-set mortar. The grout between the tiles should also be heat-resistant and properly sealed to prevent water or moisture damage. Choosing the right tile is just as crucial as the substrate. Porcelain or stone tiles are good choices. Avoid using tiles that are not rated for high heat environments.
Clearances to combustible materials are another vital consideration during hearth construction. Building codes specify minimum clearances between the fireplace opening and any combustible materials, such as wood framing or drywall. These clearances are designed to prevent the combustible materials from overheating and igniting. Ensure all framing elements and combustible finishes meet the minimum safe distance to the firebox.
Finally, it is highly recommended to consult with a qualified fireplace installer or contractor before undertaking any hearth construction project. A professional can assess the specific requirements of the fireplace and ensure that the hearth is built in accordance with all applicable codes and safety standards. They can also provide valuable advice on material selection, construction techniques, and other critical aspects of the project.
The presence of cracks in the hearth can pose a safety risk, potentially allowing heat and embers to reach combustible materials underneath. Regular inspections of the hearth are recommended to identify and address any cracks or damage promptly. Small cracks can often be repaired with patching compounds, while larger cracks may necessitate more extensive repairs or even replacement of the affected area.
Proper maintenance of the fireplace and hearth is essential for ensuring their long-term safety and performance. This includes regular cleaning of the fireplace and chimney to remove soot and creosote buildup. Maintaining the proper function and build-up protects homeowners and their homes. The hearth should also be cleaned regularly to remove ash and debris, along with inspecting flue.

Fireplace Hearth Extension Rules Structure Tech Home Inspections

The Proper Way To Measure Dimensions Of A Fireplace

Average Fireplace Dimensions Small Design

Fireplace Dimensions Standard Sizes Explained

Fireplace Mantel Worksheet

Fireplace Dimensions Gas Electric Outdoor

Average Fireplace Dimensions Diy Building Plans House

Buy Standard 16 Rectangular Bullnose Hearth San Francisco Bay Area Ca The Fireplace Element

Soliftec Bs1251 Fireplaces

What Is A Fireplace Hearth And How Far Should It Extend Building Code Trainer
Related Posts