Energy-Saving Fireplace Heaters: A Comprehensive Overview
Fireplace heaters offer a potential solution for supplemental heating, particularly during colder months. The efficiency of these heaters, and their overall energy consumption, has become a central concern for homeowners seeking to lower utility bills and reduce their environmental impact. Understanding the various types of fireplace heaters, their energy-saving potential, and factors influencing their performance is crucial for making informed decisions about home heating systems.
The term "fireplace heater" encompasses a range of devices, from traditional wood-burning stoves to electric fireplace inserts. Each type possesses distinct characteristics affecting its energy efficiency and suitability for different homes and heating needs. The operational costs and environmental impact also vary significantly across these technologies.
Types of Energy-Saving Fireplace Heaters
Several types of fireplace heaters claim energy-saving benefits. These utilize diverse heating mechanisms, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the best option for a specific application.
Electric Fireplace Inserts: These units are designed to fit into existing fireplace openings, converting a traditional fireplace into an electric heater. They operate by passing electricity through a heating element, which then radiates heat into the room. Many models utilize LED technology to simulate realistic flames, providing an aesthetic appeal similar to a traditional fireplace without the need for wood or gas.
Electric fireplace inserts are generally considered to be highly efficient in terms of energy conversion. Most models boast near 100% efficiency, meaning virtually all the electricity consumed is converted into heat. However, the overall cost-effectiveness depends on the local price of electricity. In areas with high electricity rates, even a highly efficient electric fireplace can be more expensive to operate than other heating options.
Furthermore, electric fireplace inserts are zone heating solutions. They are most effective at heating a single room or area, rather than an entire house. This makes them suitable for supplementing a central heating system or providing targeted warmth in specific living spaces.
Gas Fireplace Inserts: Similar to electric inserts, gas fireplace inserts are designed to fit into existing fireplace openings, but they burn natural gas or propane to generate heat. They are typically more powerful than electric inserts, capable of heating larger areas more quickly.
The energy efficiency of gas fireplace inserts varies depending on the model and its features. Direct-vent models are generally more efficient than vent-free models. Direct-vent inserts draw combustion air from outside the house and vent exhaust gases directly outdoors, preventing the loss of heated indoor air. Vent-free models, on the other hand, draw combustion air from within the room and release exhaust gases into the room, which can potentially impact indoor air quality.
Gas fireplace inserts offer a good balance of heating power and energy efficiency, but they require a gas line connection and professional installation. The cost of natural gas or propane is a significant factor in their overall operating cost.
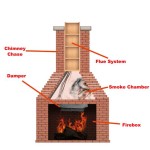
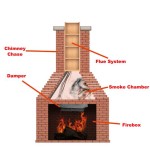
Wood-Burning Stoves: While traditionally associated with lower energy efficiency, modern wood-burning stoves have undergone significant improvements in design and technology. Certified EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) stoves are designed to burn wood more cleanly and efficiently, reducing emissions and improving heat output.
Newer wood-burning stoves often incorporate features like catalytic combustors or secondary combustion chambers, which burn off smoke and other pollutants, resulting in a more complete combustion process. This not only reduces emissions but also extracts more heat from the wood, increasing the stove's overall efficiency.
The energy efficiency of a wood-burning stove depends heavily on the quality of the wood used. Seasoned hardwood burns more efficiently and produces more heat than green or soft wood. Regular maintenance, including cleaning the chimney and ensuring proper airflow, is also crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
While wood-burning stoves can be a cost-effective heating option in areas with readily available and affordable wood, they require significant manual effort and attention. Stoking the fire, managing the wood supply, and regularly cleaning the stove are all necessary tasks.
Factors Influencing Energy Efficiency
The energy efficiency of any fireplace heater is not solely determined by the type of heater itself. Several external factors can significantly influence its performance and overall energy consumption. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing the efficiency of a fireplace heating system.
Insulation: Proper insulation of the home is paramount for maximizing the benefit of any heating system, including fireplace heaters. Adequate insulation in walls, ceilings, and floors reduces heat loss, allowing the heater to maintain a comfortable temperature with less energy consumption. Inadequately insulated homes will experience significant heat loss, negating much of the energy-saving potential of a fireplace heater.
Drafts and Air Leaks: Similar to insulation, eliminating drafts and air leaks is essential for reducing heat loss. Sealing gaps around windows, doors, and other openings prevents cold air from entering the home and warm air from escaping. This simple step can significantly improve the efficiency of any heating system.
Room Size and Layout: The size and layout of the room being heated also play a crucial role. A fireplace heater that is too small for the room will struggle to maintain a comfortable temperature, leading to increased energy consumption. Conversely, a heater that is too large may overheat the room, resulting in wasted energy. The layout of the room, including the placement of furniture and the presence of obstructions, can also affect the distribution of heat.
Thermostat Control: A thermostat is essential for regulating the temperature and preventing overheating. Programmable thermostats offer even greater control, allowing users to set different temperature schedules for different times of the day and days of the week. This can significantly reduce energy consumption by lowering the temperature when the room is not in use.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance of any fireplace heater. For electric and gas inserts, this may involve cleaning the unit and inspecting the wiring or gas lines. For wood-burning stoves, it includes cleaning the chimney, removing ash, and inspecting the stove for damage. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced efficiency, increased emissions, and potential safety hazards.
Optimizing Energy Savings from Fireplace Heaters
Maximizing energy savings from a fireplace heater requires a comprehensive approach that considers the type of heater, the characteristics of the home, and the user's heating habits. Several strategies can be employed to optimize energy efficiency and reduce heating costs.
Zone Heating: Utilizing the fireplace heater for zone heating is a highly effective strategy. By focusing on heating only the rooms that are being used, homeowners can avoid wasting energy heating unoccupied spaces. This is particularly effective with electric and gas fireplace inserts, which are well-suited for targeted heating.
Supplementing Central Heating: Fireplace heaters can be used to supplement a central heating system, allowing homeowners to lower the thermostat setting on their central heating system while still maintaining a comfortable temperature in the occupied rooms. This can result in significant energy savings, especially during peak heating hours.
Proper Wood Selection and Storage (for Wood Stoves): For those using wood-burning stoves, selecting seasoned hardwood is crucial for maximizing efficiency and minimizing emissions. Wood should be stored in a dry, well-ventilated area to prevent rot and ensure proper drying. Burning green or damp wood results in lower heat output and increased emissions.
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance: As mentioned previously, regular cleaning and maintenance are essential for maintaining optimal performance. This includes cleaning the chimney, removing ash, and inspecting the heater for any signs of damage. Proper maintenance ensures that the heater operates efficiently and safely.
Use of Fans: Circulating the warm air produced by the fireplace heater can improve its effectiveness and reduce energy consumption. Using a ceiling fan or a portable fan to distribute the heat throughout the room can prevent hot spots and ensure that the heat is evenly distributed.
Sealing the Fireplace Damper (when not in use): When a traditional fireplace is not in use, it's crucial to ensure the damper is tightly sealed. An open damper allows warm air to escape from the house and cold air to enter, significantly increasing heating costs. Consider installing a fireplace plug or inflatable damper to create a tighter seal.
The choice of fireplace heater and the strategies employed to optimize its performance will depend on individual circumstances and preferences. Evaluating the various options, considering the factors influencing energy efficiency, and implementing appropriate strategies can lead to significant energy savings and reduced heating costs.
Ultimately, the goal is to find a balance between comfort, cost-effectiveness, and environmental responsibility. By making informed decisions and adopting energy-conscious practices, homeowners can enjoy the warmth and ambiance of a fireplace heater while minimizing its impact on their wallets and the environment.

Are Electric Fireplaces Energy Efficient We Love Fire

Ce Rohs Approved Energy Saving Electric Wall Fireplace S Home Appliance Room Heaters China Made In Com

White Electric Fireplaces Heater Wall Fireplace Insert Energy Saving Remote Control China Heaters Made In Com

Lifeplus Electric Fireplace Stove Heater Infrared 3d Flame Effect Thermostat Freestanding For Indoor Room 1500w 27 Com

3d Simulation Flame Heater Fireplace Design Home Temu

14 6 Mini Portable Electric Fireplace 750w 1500w Tabletop Stove Heater Home

14 Electric Fireplace 1400w Led Energy Saving Freestanding Heater With Over Heating Protection Com

Electric Fireplace Stove 23 Inches Freestanding Infrared He Grillpartsreplacement Bbq Parts Retailer

Mythbusters Electric Fires Dimplex

Auseo 60 Inch Embedded Wall Mounted Indoor Fireplace Ultra Thin Low N
Related Posts