Understanding Vented Gas Fireplaces
Vented gas fireplaces represent a significant segment of the home heating and decorative appliance market. These fireplaces are characterized by their reliance on a chimney or vent system to expel combustion byproducts outside the home. The design and operation of vented gas fireplaces offer a specific set of advantages and disadvantages compared to ventless alternatives, impacting installation requirements, efficiency, and overall aesthetic.
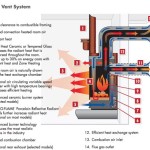
The term "vented" refers to the necessity of a direct pathway for the removal of exhaust gases. These gases, produced during the burning of natural gas or propane, include carbon dioxide, water vapor, and potentially, small amounts of carbon monoxide. A properly functioning vent system is critical for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a vented gas fireplace.
The installation process for a vented gas fireplace is typically more complex and costly than that of a ventless model. This is primarily due to the requirement of a suitable chimney or vent system. Existing chimneys can often be adapted for use with a gas fireplace, but this adaptation needs to be performed by a qualified professional to ensure compliance with local building codes and safety standards. In situations where an existing chimney is not available, a new venting system must be installed, adding considerably to the overall project cost.
The design of vented gas fireplaces often prioritizes realistic flame appearance. Because the combustion process is not optimized for complete burning, the flames tend to be larger and more yellow, mimicking the look of a traditional wood-burning fire. This visual appeal is a major factor in the popularity of vented gas fireplaces among homeowners seeking a classic fireplace aesthetic.
The efficiency of vented gas fireplaces is generally lower than that of ventless models. The process of venting exhaust gases inevitably carries away a significant portion of the heat generated by the fireplace. This heat loss can result in higher energy bills, especially if the fireplace is used frequently as a primary heating source. However, advancements in fireplace technology have led to improvements in the efficiency of some vented models, making them a more viable option for supplemental heating.
The selection of a vented gas fireplace involves considering various factors, including the size of the room, the desired heat output, the available venting options, and the homeowner's aesthetic preferences. Consulting with a qualified fireplace installer is highly recommended to ensure that the chosen fireplace is appropriate for the specific application and that it is installed safely and correctly.
Key Point 1: Installation Requirements and Venting Systems
The defining characteristic of a vented gas fireplace is its dependence on a venting system. This system serves the essential function of removing combustion byproducts from the living space, ensuring the air inside the home remains safe and breathable. The proper design and installation of the venting system are paramount to the safe and efficient operation of the fireplace.
There are several types of venting systems commonly used with vented gas fireplaces. The most common is a traditional chimney, which relies on natural draft to draw exhaust gases upwards and out of the house. This type of venting typically requires a masonry chimney or a listed prefabricated metal chimney system. The chimney must be properly sized and maintained to ensure adequate draft and prevent the buildup of dangerous gases.
Another type of venting system is a direct vent system. Direct vent fireplaces are sealed units that draw combustion air from outside the home and vent exhaust gases directly to the exterior through a dedicated vent pipe. This system offers several advantages, including improved efficiency and greater flexibility in terms of installation location. Direct vent fireplaces can be vented horizontally through an exterior wall or vertically through the roof, allowing for installation in rooms that do not have an existing chimney.
A third type of venting system is a B-vent system. B-vent systems are designed for use with gas appliances that produce relatively low levels of carbon monoxide. These systems typically consist of double-walled metal pipes that are suitable for venting gas fireplaces, water heaters, and other gas-fired appliances. B-vent systems are generally less expensive than direct vent systems, but they are also less versatile in terms of installation options.
Regardless of the type of venting system used, it is crucial to ensure that it is properly installed and maintained. This includes regular inspections to check for leaks, blockages, and other potential problems. A qualified professional should be consulted to perform these inspections and to make any necessary repairs or adjustments. Improperly installed or maintained venting systems can pose a serious safety hazard, potentially leading to carbon monoxide poisoning or other health problems.
Key Point 2: Efficiency and Heat Output
The efficiency of a vented gas fireplace is a key consideration for homeowners who plan to use the fireplace as a supplemental heating source. Efficiency is typically measured as the percentage of fuel energy that is converted into usable heat. Vented gas fireplaces generally have lower efficiency ratings than ventless models due to the heat loss associated with venting exhaust gases.
The efficiency of a vented gas fireplace can vary depending on several factors, including the design of the fireplace, the type of venting system used, and the quality of the installation. Some vented gas fireplaces are designed with features that improve efficiency, such as insulated fireboxes and variable-speed blowers that circulate heat more effectively.
The heat output of a vented gas fireplace is measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs). The appropriate BTU rating for a particular fireplace will depend on the size of the room and the desired level of heating. A general rule of thumb is that 20 BTU per square foot of living space is required to provide adequate supplemental heating. However, this number can vary depending on factors such as the insulation level of the home and the climate.
It is important to note that vented gas fireplaces are typically not designed to be primary heating sources. They are best suited for providing supplemental heat to a specific room or area. Using a vented gas fireplace as a primary heating source can result in high energy bills and may not provide sufficient heat to keep the entire home comfortable.
Homeowners seeking to maximize the efficiency of their vented gas fireplace should consider several strategies. These include ensuring that the fireplace is properly installed and maintained, using a programmable thermostat to control the fireplace's operation, and sealing any air leaks around the fireplace and venting system. Regular maintenance, including cleaning the burner and inspecting the venting system, can also help to improve efficiency and ensure safe operation.
Key Point 3: Aesthetics and Design Options
Beyond their functionality as heating appliances, vented gas fireplaces offer a significant aesthetic contribution to a home's interior design. The wide range of available styles, finishes, and features allows homeowners to select a fireplace that complements their individual tastes and the overall décor of their living space.
One of the primary aesthetic considerations for vented gas fireplaces is the flame appearance. Vented models are often designed to produce larger, more realistic flames that mimic the look of a traditional wood-burning fire. This is achieved through a combination of burner design, gas pressure, and the use of artificial logs or other decorative elements.
The choice of firebox materials and finishes is another important aesthetic factor. Vented gas fireplaces are available with fireboxes made of various materials, including steel, cast iron, and ceramic. These materials can be finished in a variety of colors and textures to match the surrounding décor. Common finishes include black, brass, and antique bronze.
The type of logs or decorative elements used in the fireplace also contributes to its overall aesthetic appeal. Artificial logs are available in a wide range of styles, from traditional split logs to more contemporary designs. Some fireplaces also feature decorative glass beads, stones, or other materials that add visual interest to the flame presentation.
The surround or mantel that surrounds the fireplace is another opportunity to enhance its aesthetic appeal. Surrounds and mantels are available in a variety of materials, including wood, stone, and metal. They can be designed to complement the style of the fireplace and the overall décor of the room. The surround can be a simple, minimalist design or a more elaborate, ornate style, depending on the homeowner's preferences.
The control features of a vented gas fireplace can also contribute to its aesthetic appeal. Some models feature remote controls that allow homeowners to adjust the flame height, heat output, and other settings from a distance. These remote controls can be integrated into the fireplace's design, providing a seamless and convenient user experience.
The selection of a vented gas fireplace requires a careful consideration of both functional and aesthetic factors. By taking the time to assess their individual needs and preferences, homeowners can choose a fireplace that provides both warmth and visual appeal, enhancing the comfort and beauty of their homes.

How To Find The Most Efficient Direct Vent Gas Fireplace For Your Next Project
Gas Fireplace Venting Explained Heat Glo

12 Types Of Gas Fireplaces You Need To Know

What Are The Best Ways To Vent A Gas Fireplace Zoroast

Guide To Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces

Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces Fireplace

Vented Vs B Vent Direct Free Dixie S

Freestanding High Efficiency Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces Inserts Stoves Godby Hearth And Home

Napoleon Ascent Dx42 Direct Vent Gas Burning Fireplace

Pros And Cons Of Direct Vent Gas Fireplaces Tarantin Industries
Related Posts